Politics of China is the politics of the People's Republic of China, a single-party socialist state.
Politics of China may also refer to
Democrat, Democrats, or Democratic may refer to:

The Democratic Progressive Party (DPP) is a Taiwanese nationalist and centre-left political party in the Republic of China (Taiwan). Currently controlling both the Republic of China presidency and the unicameral Legislative Yuan, it is the majority ruling party and the dominant party in the Pan-Green Coalition as of 2023.

The Kuomintang (KMT), also referred to as the Guomindang (GMD), the Nationalist Party of China (NPC) or the Chinese Nationalist Party (CNP), is a major political party in the Republic of China, initially based on the Chinese mainland and then in Taiwan since 1949. It was the sole ruling party in China during the Republican Era from 1928 to 1949, when most of the Chinese mainland was under its control. The party retreated from the mainland to Taiwan on 7 December 1949, following its defeat in the Chinese Civil War. Chiang Kai-shek declared martial law and retained his authoritarian rule over Taiwan under the Dang Guo system until democratic reforms were enacted in the 1980s and full democratization in the 1990s. In Taiwanese politics today, the KMT is a centre-right to right-wing party and is the largest party in the Pan-Blue Coalition. The KMT's primary rival in elections is the Democratic Progressive Party (DPP) and its allies in the Pan-Green Coalition. As of 2023, the KMT is the largest opposition party in the Legislative Yuan. The current chairman is Eric Chu.
The politics of the People's Republic of China takes place in a framework of a unitary Marxist–Leninist one-party socialist state under the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). The Chinese political system is authoritarian. There are no freely elected national leaders, political opposition is suppressed, all religious activity is controlled by the CCP, dissent is not permitted, and civil rights are curtailed. Direct elections occur only at the local level, not the national level, with all candidate nominations controlled by the CCP.
The Republic of China (ROC), commonly known as Taiwan, is governed in a framework of a representative democratic republic under a five-power system first envisioned by Sun Yat-sen in 1906, whereby under the constitutional amendments, the President is head of state and the Premier is head of government, and of a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in primarily with the parliament and limited by government. The judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature. In addition, the civil service's powers is being in charge of validating the qualification of civil servants and the supervision auditory power inspects, reviews, and audits the policies and operations of the government. The party system is dominated by two parties, the Kuomintang, which broadly favors closer links to mainland China and the status quo, and the Democratic Progressive Party (DPP), which broadly favors Taiwanese nationalism and independence.
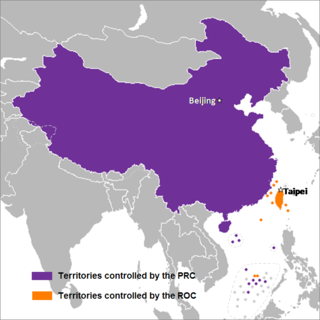
Chinese unification, also known as Cross-Strait unification or Chinese reunification, is the potential unification of territories currently controlled, or claimed, by the People's Republic of China and the Republic of China ("Taiwan") under one political entity, possibly the formation of a political union between the two republics. Together with full Taiwan independence, unification is one of the main proposals to address questions on the political status of Taiwan, which is a central focus of Cross-Strait relations.

Zhao Ziyang was a Chinese politician. He was the third premier of the People's Republic of China from 1980 to 1987, vice chairman of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) from 1981 to 1982, and CCP general secretary from 1987 to 1989. He was in charge of the political reforms in China from 1986, but lost power in connection with the reformative neoauthoritarianism current and his support of the 1989 Tiananmen Square protests.

The Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference, also known as the People's PCC or simply the PCC (政协), is a political advisory body in the People's Republic of China and a central part of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP)'s united front system. Its members advise and put proposals for political and social issues to government bodies. However, the CPPCC is a body without real legislative power. While consultation does take place, it is supervised and directed by the CCP.

Paramount leader is an informal term for the most important political figure in the People's Republic of China (PRC). The paramount leader typically controls the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) and the People's Liberation Army (PLA), often holding the titles of CCP General Secretary and Chairman of the Central Military Commission (CMC). The head of state (president) or head of government (premier) are not necessarily paramount leader—under China's party-state system, CCP roles are politically more important than state titles.
New Republic may refer to:
Republican Party is a name used by many political parties around the world, though the term most commonly refers to the United States' Republican Party.

The debate over democracy in China has been a major ideological battleground in Chinese politics since the 19th century. China is not a liberal democracy. The Chinese government and the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) state that China is democratic nonetheless. Many foreign and some domestic observers categorize China as an authoritarian one-party state, with some saying it has shifted to neoauthoritarianism. Some characterize it as a dictatorship.

The government of the People's Republic of China is based on a system of people's congress within the parameters of a Marxism–Leninist state, in which the ruling Chinese Communist Party (CCP) enacts its policies through people's congresses. This system is based on the principle of unitary power, also termed unified state power, in which the legislature, the National People's Congress (NPC), is constitutionally enshrined as "the highest state organ of power." As China's political system has no separation of powers, there is only one branch of government which is represented by the legislature. The CCP through the NPC enacts unified leadership, which requires that all state organs, from the Supreme People's Court to the President of the People's Republic of China, are elected by, answerable to, and have no separate powers than those granted to them by the NPC. The CCP controls appointments in all state bodies through a two-thirds majority in the NPC. The remaining seats are held by nominally independent delegates and eight minor political parties, which are non-oppositional and support the CCP. All government bodies and state-owned enterprises have internal CCP committees that lead the decision-making in these institutions.
Constitution Party, Constitutional Party, or Constitutionalist Party may refer to one of several political parties.
Third Force may refer to:

The Founding of a Republic is a Chinese historical drama produced in 2009 to mark the 60th anniversary of the People's Republic of China and was made to portray the final years of the Chinese Communist Revolution that followed the end of the Second Sino-Japanese War (1937-1945). This film was co-directed by Huang Jianxin and Han Sanping, and includes many famous actors such as Andy Lau, Ge You, as well as other directors such as Jiang Wen, and Chen Kaige. The main protagonists Mao Zedong and Chiang Kai-shek were played by highly renowned actors, Tang Guoqiang and Zhang Guoli. One of the purposes of this movie aside from reenacting the events of the Chinese Communist Revolution was to also attract a younger audience to view films that revolved around government propaganda, which they aim to accomplish by including famous actors that would draw the attention of the youth. According to the executive at one of China's top multiplex chains, this film is also unique because the film unusually marries "the core of an 'ethically inspiring' film with commercial packaging.". Additionally, this is the first zhuxuanlu film to work solely with cinematic audio-visual methods to achieve its political and ideological goals. It is a milestone in that since its production in 2009, the distinction between zhuxuanlu and commercial film has become blurred; they have become primarily indistinguishable from each other. This film was released on September 16, 2009, in mainland China and during its release, it had a tremendous amount of support from the Communist Party.

The National People's Congress (NPC) is the national legislature of the People's Republic of China. With 2,980 members in 2023, it is the largest legislative body in the world. The NPC is elected for a term of five years. It holds annual sessions every spring, usually lasting from 10 to 14 days, in the Great Hall of the People on the west side of Tiananmen Square in Beijing.

The president of the People's Republic of China, commonly called the president of China, is the head of state of the People's Republic of China. The presidency on its own is a ceremonial office and has no real power in China's political system. However, since 1993, the post has been held by the general secretary of the Chinese Communist Party and chairman of the Central Military Commission, who is China's de facto leader.