
A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, properties, and applications of these heterocycles.

A metallocene is a compound typically consisting of two cyclopentadienyl anions (C
5H−
5, abbreviated Cp) bound to a metal center (M) in the oxidation state II, with the resulting general formula (C5H5)2M. Closely related to the metallocenes are the metallocene derivatives, e.g. titanocene dichloride, vanadocene dichloride. Certain metallocenes and their derivatives exhibit catalytic properties, although metallocenes are rarely used industrially. Cationic group 4 metallocene derivatives related to [Cp2ZrCH3]+ catalyze olefin polymerization.
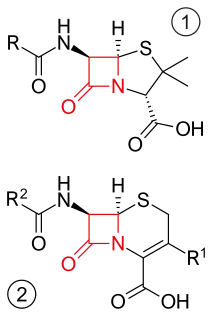
β-lactam antibiotics are a class of antibiotic consisting of all antibiotic agents that contain a beta-lactam ring in their molecular structures. This includes penicillin derivatives (penams), cephalosporins (cephems), monobactams, and carbapenems. Most β-lactam antibiotics work by inhibiting cell wall biosynthesis in the bacterial organism and are the most widely used group of antibiotics. Until 2003, when measured by sales, more than half of all commercially available antibiotics in use were β-lactam compounds.
Pyrrole is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound, a five-membered ring with the formula C4H4NH. It is a colorless volatile liquid that darkens readily upon exposure to air. Substituted derivatives are also called pyrroles, e.g., N-methylpyrrole, C4H4NCH3. Porphobilinogen, a trisubstituted pyrrole, is the biosynthetic precursor to many natural products such as heme.
Thiazole, or 1,3-thiazole, is a heterocyclic compound that contains both sulfur and nitrogen; the term 'thiazole' also refers to a large family of derivatives. Thiazole itself is a pale yellow liquid with a pyridine-like odor and the molecular formula C3H3NS. The thiazole ring is notable as a component of the vitamin thiamine (B1).
Dodecahedrane is a chemical compound, a hydrocarbon with formula C
20H
20, whose carbon atoms are arranged as the vertices (corners) of a regular dodecahedron. Each carbon is bound to three neighbouring carbon atoms and to a hydrogen atom. This compound is one of the three possible Platonic hydrocarbons, the other two being cubane and tetrahedrane.

In organic chemistry, helicenes are ortho-condensed polycyclic aromatic compounds in which benzene rings or other aromatics are angularly annulated to give helically-shaped chiral molecules. The chemistry of helicenes has attracted continuing attention because of their unique structural, spectral, and optical features.

The Martinet dioxindole synthesis was first reported in 1913 by J. Marinet. It is a chemical reaction in which a primary or secondary aniline or substituted aromatic amine is condensed with ethyl or methyl ester of mesoxalic acid to make a dioxindole in the absence of oxygen.

Prismane or 'Ladenburg benzene' is a polycyclic hydrocarbon with the formula C6H6. It is an isomer of benzene, specifically a valence isomer. Prismane is far less stable than benzene. The carbon (and hydrogen) atoms of the prismane molecule are arranged in the shape of a six-atom triangular prism—this compound is the parent and simplest member of the prismanes class of molecules. Albert Ladenburg proposed this structure for the compound now known as benzene. The compound was not synthesized until 1973.

Pentacene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon consisting of five linearly-fused benzene rings. This highly conjugated compound is an organic semiconductor. The compound generates excitons upon absorption of ultra-violet (UV) or visible light; this makes it very sensitive to oxidation. For this reason, this compound, which is a purple powder, slowly degrades upon exposure to air and light.

Hexacene is an aromatic molecule consisting of six linearly-fused benzene rings. Hexacene and its derivatives are investigated for potential applications as organic semiconductor.
A circulene is a macrocyclic arene in which a central polygon is completely surrounded and fused by benzenoids. Nomenclature within this class of molecules is based on the number of benzene rings surrounding the core, which is equivalent to the size of the central polygon. Examples which have been synthesized include [5]circulene (corannulene), [6]circulene (coronene), [7]circulene, and [12]circulene (kekulene) These compounds belong to a larger class of geodesic polyarenes. Whereas [5]circulene is bowl-shaped and [6]circulene is planar, [7]circulene has a unique saddle-shaped structure. The helicenes are a conceptually related class of structures in which the array of benzene rings form an open helix rather than a closed ring.

Heptacene is an organic compound and a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and the seventh member of the acene or polyacene family of linear fused benzene rings. This compound has long been pursued by chemists because of its potential interest in electronic applications and was first synthesized but not cleanly isolated until 2006. Heptacene was finally fully characterized in bulk by researchers in Germany and the United States in 2017.

A fenestrane in organic chemistry is a type of chemical compound with a central quaternary carbon atom which serves as a common vertex for four fused carbocycles. They can be regarded as spiro compounds twice over. Because of their inherent strain and instability, fenestranes are of theoretical interest to chemists. The name—proposed in 1972 by Vlasios Georgian and Martin Saltzman—is derived from the Latin word for window, fenestra. Georgian had intended that "fenestrane" solely referred to [4.4.4.4]fenestrane, whose skeletal structure looks like windows, and Kenneth B. Wiberg called that specific structure "windowpane". The term fenestrane has since become generalized to refer to the whole class of molecules that have various other ring-sizes. Georgian recommended rosettane for the class, based on the structural appearance as a rosette of flowers.
The total synthesis of quinine, a naturally-occurring antimalarial drug, was developed over a 150-year period. The development of synthetic quinine is considered a milestone in organic chemistry although it has never been produced industrially as a substitute for natural occurring quinine. The subject has also been attended with some controversy: Gilbert Stork published the first stereoselective total synthesis of quinine in 2001, meanwhile shedding doubt on the earlier claim by Robert Burns Woodward and William Doering in 1944, claiming that the final steps required to convert their last synthetic intermediate, quinotoxine, into quinine would not have worked had Woodward and Doering attempted to perform the experiment. A 2001 editorial published in Chemical & Engineering News sided with Stork, but the controversy was eventually laid to rest once and for all when Williams and coworkers successfully repeated Woodward's proposed conversion of quinotoxine to quinine in 2007.

In chemistry, a ladderane is an organic molecule containing two or more fused cyclobutane rings. The name arises from the resemblance of a series of fused cyclobutane rings to a ladder. Numerous synthetic approaches have been developed for the synthesis of ladderane compounds of various lengths. The mechanisms often involve [2 + 2] photocycloadditions, a useful reaction for creating strained 4-membered rings. Naturally occurring ladderanes have been identified as major components of the anammoxosome membrane of the anammox bacteria Planctomycetes.

Pagodane is an organic compound with formula C
20H
20 whose carbon skeleton was said to resemble a pagoda, hence the name. It is a polycyclic hydrocarbon whose molecule has the D2h point symmetry group. The compound is a highly crystalline solid that melts at 243 °C, is barely soluble in most organic solvents and moderately soluble in benzene and chloroform. It sublimes at low pressure.
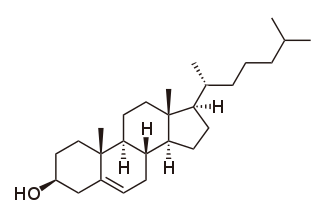
Cholesterol total synthesis in chemistry describes the total synthesis of the complex biomolecule cholesterol and is considered a great scientific achievement. The research group of Robert Robinson with John Cornforth published their synthesis in 1951 and that of Robert Burns Woodward with Franz Sondheimer in 1952. Both groups competed for the first publication since 1950 with Robinson having started in 1932 and Woodward in 1949. According to historian Greg Mulheirn the Robinson effort was hampered by his micromanagement style of leadership and the Woodward effort was greatly facilitated by his good relationships with chemical industry. Around 1949 steroids like cortisone were produced from natural resources but expensive. Chemical companies Merck & Co. and Monsanto saw commercial opportunities for steroid synthesis and not only funded Woodward but also provided him with large quantities of certain chemical intermediates from pilot plants. Hard work also helped the Woodward effort: one of the intermediate compounds was named Christmasterone as it was synthesized on Christmas Day 1950 by Sondheimer.
![Bicyclo[3.3.0]octane Bicyclo(3.3.0)octane.png](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/3d/Bicyclo%283.3.0%29octane.png/440px-Bicyclo%283.3.0%29octane.png)


















