
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates and facilitates international trade. With effective cooperation in the United Nations System, governments use the organization to establish, revise, and enforce the rules that govern international trade. It officially commenced operations on 1 January 1995, pursuant to the 1994 Marrakesh Agreement, thus replacing the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) that had been established in 1948. The WTO is the world's largest international economic organization, with 164 member states representing over 98% of global trade and global GDP.

Cosmetics are constituted mixtures of chemical compounds derived from either natural sources, or synthetically created ones. Cosmetics have various purposes. Those designed for personal care and skin care can be used to cleanse or protect the body or skin. Cosmetics designed to enhance or alter one's appearance (makeup) can be used to conceal blemishes, enhance one's natural features, add color to a person's face, or change the appearance of the face entirely to resemble a different person, creature or object. Cosmetics can also be designed to add fragrance to the body.

Agricultural policy describes a set of laws relating to domestic agriculture and imports of foreign agricultural products. Governments usually implement agricultural policies with the goal of achieving a specific outcome in the domestic agricultural product markets.
Dumping, in economics, is a kind of injuring pricing, especially in the context of international trade. It occurs when manufacturers export a product to another country at a price below the normal price with an injuring effect. The objective of dumping is to increase market share in a foreign market by driving out competition and thereby create a monopoly situation where the exporter will be able to unilaterally dictate price and quality of the product. Trade treaties might include mechanisms to alleviate problems related to dumping, such as countervailing duty penalties and anti-dumping statutes.

Non-tariff barriers to trade are trade barriers that restrict imports or exports of goods or services through mechanisms other than the simple imposition of tariffs.
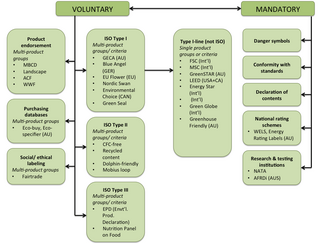
Ecolabels and Green Stickers are labeling systems for food and consumer products. The use of ecolabels is voluntary, whereas green stickers are mandated by law; for example, in North America major appliances and automobiles use Energy Star. They are a form of sustainability measurement directed at consumers, intended to make it easy to take environmental concerns into account when shopping. Some labels quantify pollution or energy consumption by way of index scores or units of measurement, while others assert compliance with a set of practices or minimum requirements for sustainability or reduction of harm to the environment. Many ecolabels are focused on minimising the negative ecological impacts of primary production or resource extraction in a given sector or commodity through a set of good practices that are captured in a sustainability standard. Through a verification process, usually referred to as "certification", a farm, forest, fishery, or mine can show that it complies with a standard and earn the right to sell its products as certified through the supply chain, often resulting in a consumer-facing ecolabel.
A free-trade agreement (FTA) or treaty is an agreement according to international law to form a free-trade area between the cooperating states. There are two types of trade agreements: bilateral and multilateral. Bilateral trade agreements occur when two countries agree to loosen trade restrictions between the two of them, generally to expand business opportunities. Multilateral trade agreements are agreements among three or more countries, and are the most difficult to negotiate and agree.
The Agreement on Agriculture (AoA) is an international treaty of the World Trade Organization. It was negotiated during the Uruguay Round of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade, and entered into force with the establishment of the WTO on January 1, 1995.
The Agreement on the Application of Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures, also known as the SPS Agreement or just SPS, is an international treaty of the World Trade Organization (WTO). It was negotiated during the Uruguay Round of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), and entered into force with the establishment of the WTO at the beginning of 1995. Broadly, the sanitary and phytosanitary ("SPS") measures covered by the agreement are those aimed at the protection of human, animal or plant life or health from certain risks.
The Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade, commonly referred to as the TBT Agreement, is an international treaty administered by the World Trade Organization. It was last renegotiated during the Uruguay Round of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade, with its present form entering into force with the establishment of the WTO at the beginning of 1995, binding on all WTO members.
The Beef Hormone Dispute is one of the most intractable agricultural controversies since the establishment of the World Trade Organization (WTO).

Cosmetic testing on animals is a type of animal testing used to test the safety and hypoallergenic properties of cosmetic products for use by humans.
In 1994, the WTO intervened to address member concerns regarding the import of shrimp and its impact on turtles. This became known as the Shrimp and Turtle case. The ruling was adopted on November 6, 1998. However, Malaysia persisted in their complaint and initiated DSU Article 21.5 proceedings against the U.S. in 2001, but the U.S. prevailed in those hearings.
Since 1970s, there has been on going trade disputes between Mexico against the United States. The complaints were taken to General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) committee and its 1995 successor; the World Trade Organization (WTO). The case became known as Tuna-Dolphin I, Tuna-Dolphin II and US-Tuna II (Mexico). Complaints concerned the USA embargo on yellowfin tuna and yellowfin tuna product imports that used purse-seine fishing methods and the labeling there of. Purse-seine fishing has resulted in a high number of dolphin kills.

EU Ecolabel or EU Flower is a voluntary ecolabel scheme established in 1992 by the European Union.

The cosmetic industry describes the industry that manufactures and distributes cosmetic products. These include colour cosmetics, like foundation and mascara, skincare such as moisturisers and cleansers, haircare such as shampoos, conditioners and hair colours, and toiletries such as bubble bath and soap. The manufacturing industry is dominated by a small number of multinational corporations that originated in the early 20th century, but the distribution and sale of cosmetics is spread among a wide range of different businesses.

The European Union banned seal products in 2009 for reasons of animal welfare. The ban was a continuation of a sealskin ban by the European Economic Community imposed in 1983.
European Union and its Member States — Certain Measures Relating to the Energy Sector, DS476, is the formal name of a case brought by the Russian Federation against the European Union and its member states in the World Trade Organization's Dispute Settlement Body.
In the 1990s, a trade dispute over fresh salmon arose between the Commonwealth nations of Canada and Australia. In 1995, Canada made a complaint to the World Trade Organization, of which both countries are members, about Australia's restriction on imports of fresh salmon, which were part of a quarantine measure for health purposes.
The trade policy of Switzerland refers to Switzerland's approach to importing and exporting with other countries.








