Related Research Articles

An assembly line is a manufacturing process in which parts are added as the semi-finished assembly moves from workstation to workstation where the parts are added in sequence until the final assembly is produced. By mechanically moving the parts to the assembly work and moving the semi-finished assembly from work station to work station, a finished product can be assembled faster and with less labor than by having workers carry parts to a stationary piece for assembly.

Mass production, also known as flow production or continuous production, is the production of substantial amounts of standardized products in a constant flow, including and especially on assembly lines. Together with job production and batch production, it is one of the three main production methods.

A factory, manufacturing plant or a production plant is an industrial facility, often a complex consisting of several buildings filled with machinery, where workers manufacture items or operate machines which process each item into another. They are a critical part of modern economic production, with the majority of the world's goods being created or processed within factories.

An aisle is, in general, a space for walking with rows of non-walking spaces on both sides. Aisles with seating on both sides can be seen in airplanes, certain types of buildings, such as churches, cathedrals, synagogues, meeting halls, parliaments and legislatures, courtrooms, theatres, and in certain types of passenger vehicles. Their floors may be flat or, as in theatres, stepped upwards from a stage.

A substation is a part of an electrical generation, transmission, and distribution system. Substations transform voltage from high to low, or the reverse, or perform any of several other important functions. Between the generating station and consumer, electric power may flow through several substations at different voltage levels. A substation may include transformers to change voltage levels between high transmission voltages and lower distribution voltages, or at the interconnection of two different transmission voltages. They are a common component of the infrastructure. There are 55,000 substations in the United States.
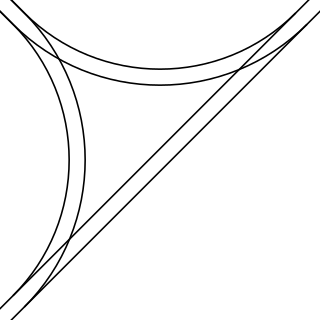
In railroad structures, and rail terminology, a wye or triangular junction is a triangular joining arrangement of three rail lines with a railroad switch at each corner connecting to the incoming lines. A turning wye is a specific case.
Batch production is a method of manufacturing where the products are made as specified groups or amounts, within a time frame. A batch can go through a series of steps in a large manufacturing process to make the final desired product. Batch production is used for many types of manufacturing that may need smaller amounts of production at a time to ensure specific quality standards or changes in the process. This is opposed to large mass production or continuous production methods where the product or process does not need to be checked or changed as frequently or periodically.
Methods engineering is a subspecialty of industrial engineering and manufacturing engineering concerned with human integration in industrial production processes.

Operations management is concerned with designing and controlling the production of goods or services, ensuring that businesses are efficient in using resources to meet customer requirements.
Computer-aided production engineering (CAPE) is a relatively new and significant branch of engineering. Global manufacturing has changed the environment in which goods are produced. Meanwhile, the rapid development of electronics and communication technologies has required design and manufacturing to keep pace.

Integrated circuit design, or IC design, is a sub-field of electronics engineering, encompassing the particular logic and circuit design techniques required to design integrated circuits, or ICs. ICs consist of miniaturized electronic components built into an electrical network on a monolithic semiconductor substrate by photolithography.
Manufacturing process management (MPM) is a collection of technologies and methods used to define how products are to be manufactured. MPM differs from ERP/MRP which is used to plan the ordering of materials and other resources, set manufacturing schedules, and compile cost data.

A pilot plant is a pre-commercial production system that employs new production technology and/or produces small volumes of new technology-based products, mainly for the purpose of learning about the new technology. The knowledge obtained is then used for design of full-scale production systems and commercial products, as well as for identification of further research objectives and support of investment decisions. Other (non-technical) purposes include gaining public support for new technologies and questioning government regulations. Pilot plant is a relative term in the sense that pilot plants are typically smaller than full-scale production plants, but are built in a range of sizes. Also, as pilot plants are intended for learning, they typically are more flexible, possibly at the expense of economy. Some pilot plants are built in laboratories using stock lab equipment, while others require substantial engineering efforts, cost millions of dollars, and are custom-assembled and fabricated from process equipment, instrumentation and piping. They can also be used to train personnel for a full-scale plant. Pilot plants tend to be smaller compared to demonstration plants.
Twin-turbo refers to an engine in which two turbochargers work in tandem to compress the intake fuel/air mixture. The most common layout features two identical or mirrored turbochargers in parallel, each processing half of a V engine's produced exhaust through independent piping. The two turbochargers can either be matching or different sizes.
Takt time, or simply takt, is a manufacturing term to describe the required product assembly duration that is needed to match the demand. Often confused with cycle time, takt time is a tool used to design work and it measures the average time interval between the start of production of one unit and the start of production of the next unit when items are produced sequentially. For calculations, it is the time to produce parts divided by the number of parts demanded in that time interval. The takt time is based on customer demand; if a process or a production line are unable to produce at takt time, either demand leveling, additional resources, or process re-engineering is needed to ensure on-time delivery.

Tool and die makers are highly skilled crafters working in the manufacturing industries. Variations on the name include tool maker,toolmaker, die maker,diemaker, mold maker,moldmaker or tool jig and die-maker depending on which area of concentration or industry an individual works in.
Cellular manufacturing is a process of manufacturing which is a subsection of just-in-time manufacturing and lean manufacturing encompassing group technology. The goal of cellular manufacturing is to move as quickly as possible, make a wide variety of similar products, while making as little waste as possible. Cellular manufacturing involves the use of multiple "cells" in an assembly line fashion. Each of these cells is composed of one or multiple different machines which accomplish a certain task. The product moves from one cell to the next, each station completing part of the manufacturing process. Often the cells are arranged in a "U-shape" design because this allows for the overseer to move less and have the ability to more readily watch over the entire process. One of the biggest advantages of cellular manufacturing is the amount of flexibility that it has. Since most of the machines are automatic, simple changes can be made very rapidly. This allows for a variety of scaling for a product, minor changes to the overall design, and in extreme cases, entirely changing the overall design. These changes, although tedious, can be accomplished extremely quickly and precisely.

Material handling involves short-distance movement within the confines of a building or between a building and a transportation vehicle. It uses a wide range of manual, semi-automated, and automated equipment and includes consideration of the protection, storage, and control of materials throughout their manufacturing, warehousing, distribution, consumption, and disposal. Material handling can be used to create time and place utility through the handling, storage, and control of waste, as distinct from manufacturing, which creates form utility by changing the shape, form, and makeup of material.
Order processing is the process or work-flow associated with the picking, packing, and delivery of the packed items to a shipping carrier and is a key element of order fulfillment. Order processing operations or facilities are commonly called “distribution centers” or “DC 's”. There are wide variances in the level of automation associating to the “pick-pack-and-ship” process, ranging from completely manual and paper-driven to highly automated and completely mechanized; computer systems overseeing this process are generally referred to as Warehouse Management Systems or “WMS”.

In manufacturing engineering, process layout is a design for the floor plan of a plant which aims to improve efficiency by arranging equipment according to its function. The production line should ideally be designed to eliminate waste in material flows, inventory handling and management. In process layout, the work stations and machinery are not arranged according to a particular production sequence. Instead, there is an assembly of similar operations or similar machinery in each department
References
- Mikell P. Groover (2007). Work Systems: The Methods, Measurement & Management of Work. Prentice Hall. ISBN 978-0-13-140650-6