
The International Astronomical Union is a non-governmental organisation with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreach, education, and development through global cooperation. It was founded in 1919 and is based in Paris, France.
The Astrophysical Journal (ApJ) is a peer-reviewed scientific journal of astrophysics and astronomy, established in 1895 by American astronomers George Ellery Hale and James Edward Keeler. The journal discontinued its print edition and became an electronic-only journal in 2015.

The American Astronomical Society is an American society of professional astronomers and other interested individuals, headquartered in Washington, DC. The primary objective of the AAS is to promote the advancement of astronomy and closely related branches of science, while the secondary purpose includes enhancing astronomy education and providing a political voice for its members through lobbying and grassroots activities. Its current mission is to enhance and share humanity's scientific understanding of the universe as a diverse and inclusive astronomical community.
The SAO/NASA Astrophysics Data System (ADS) is an online database of over 16 million astronomy and physics papers that are both from peer reviewed and non-peer reviewed sources. Abstracts are available online for free for almost all articles, and fully scanned articles are available in Graphics Interchange Format (GIF), and Portable Document Format (PDF) for older articles. It was developed by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and it is managed by the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory.

The Astronomical Society of the Pacific (ASP) is an American scientific and educational organization, founded in San Francisco on February 7, 1889, immediately following the solar eclipse of January 1, 1889. Its name derives from its origins on the Pacific Coast, but today it has members all over the country and the world. It has the legal status of a nonprofit organization.

Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (MNRAS) is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research in astronomy and astrophysics. It has been in continuous existence since 1827 and publishes letters and papers reporting original research in relevant fields. Despite the name, the journal is no longer monthly, nor does it carry the notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.

Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal managed by the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. It publishes research and review papers, instrumentation papers and dissertation summaries in the fields of astronomy and astrophysics. Between 1999 and 2016 it was published by the University of Chicago Press and since 2016, it has been published by IOP Publishing. The current editor-in-chief is Jeff Mangum of the National Radio Astronomy Observatory.
12 Andromedae is a single star in the northern constellation of Andromeda. The designation is from the star catalogue of English astronomer John Flamsteed, first published in 1712. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 5.87, which indicates it is just visible to the naked eye under good seeing conditions. An annual parallax shift of 23.7806 mas provides a distance estimate of 137 light years. The star is moving closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −10.5 km/s.
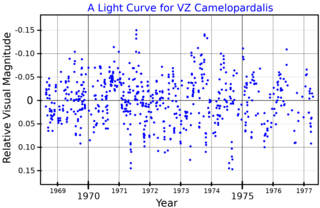
VZ Camelopardalis is a single, variable star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Camelopardalis. It has a reddish hue and is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude that fluctuates around 4.92. The star is located at a distance of approximately 500 light years from the Sun based on parallax, and is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +12 km/s. It was considered a member of the Hyades Supercluster, but in 1990 this was brought into question.
The Astronomical Society of Australia (ASA) is the professional body representing astronomers in Australia. Established in 1966, it is incorporated in the Australian Capital Territory. Membership of the ASA is open to people "capable of contributing to the advancement of astronomy or a closely related field". This means that the members are mainly active professional astronomers and postgraduate students. Some retired astronomers and distinguished amateur astronomers are also members, and several organisations are corporate members of the society. The ASA currently has around 600 members. It publishes a peer-reviewed journal, Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia.

Astronomy & Geophysics (A&G) is a scientific journal and trade magazine published on behalf of the Royal Astronomical Society (RAS) by Oxford University Press. It is distributed bimonthly to members of the RAS.
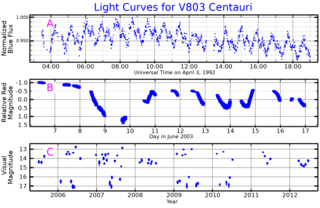
V803 Centauri is a cataclysmic binary consisting of a dwarf helium star losing mass to a white dwarf. It is an example of the AM Canum Venaticorum type of cataclysmic variable stars.

HR 4072 is a binary star system in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Major. It has the variable star designation ET Ursae Majoris, abbreviated ET Uma, while HR 4072 is the system's designation from the Bright Star Catalogue. It has a white hue and is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude that fluctuates around 4.94. The system is located at a distance of approximately 339 light years from the Sun based on parallax measurements. The radial velocity measurement is poorly constrained, but it appears to be drifting closer to the Sun at the rate of around −3 km/s.
17 Cygni is the Flamsteed designation for a multiple star system in the northern constellation of Cygnus. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 5.00, so, according to the Bortle scale, it is visible from suburban skies at night. Measurements of the annual parallax find a shift of 0.0477″, which is equivalent to a distance of around 68.5 ly (21.0 pc) from the Sun. It has a relatively high proper motion, traversing the celestial sphere at the rate of 0.451″/year.
KS Persei is a binary system in the equatorial constellation of Perseus. It is sometimes known as Bidelman's Star, named after William P. Bidelman. The star is invisible to the naked eye with a mean apparent visual magnitude of 7.70. As of 2018, the structure and evolutionary history of this system remain uncertain, although some form of mass transfer is likely to have occurred to explain the observed properties.

BH Virginis is a binary star system in the equatorial constellation of Virgo. With a typical apparent visual magnitude of 9.6, it is too faint to be visible to the naked eye. Based on parallax measurements, it is located at a distance of approximately 488 light years from the Sun. The system is drifting closer with a net radial velocity of −23 km/s.

PU Vulpeculae is a very slowly evolving symbiotic nova in the northern constellation of Vulpecula, abbreviated PU Vul. It is too faint to be visible to the naked eye, reaching a maximum apparent visual magnitude of 8.7 following a minimum of 16.6. The system is located at a distance of approximately 17,000 light years from the Sun based on parallax measurements.

AH Virginis is a contact binary star system in the equatorial constellation of Virgo, abbreviated AH Vir. It is a variable star with a brightness that peaks at an apparent visual magnitude of 9.18, making it too faint to be viewed with the naked eye. The distance to this system is approximately 338 light years based on parallax measurements, and it is drifting further away with a mean radial velocity of 7 km/s. O. J. Eggen in 1969 included this system as a probable member of the Wolf 630 group of co-moving stars.

ER Ursae Majoris is a variable star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Major, abbreviated ER UMa. It is a prototype system for a subclass of SU Ursae Majoris dwarf novae. The system ranges in brightness from a peak apparent visual magnitude of 12.4 down to 15.2, which is too faint to be visible to the naked eye. The distance to this system, based on parallax measurements, is approximately 1,163 light years.













