Related Research Articles

RatuSir Josefa Lalabalavu Vanayaliyali Sukuna was a Fijian chief, scholar, soldier, and statesman. He is regarded as the forerunner of the post-independence leadership of Fiji. He did more than anybody to lay the groundwork for self-government by fostering the development of modern institutions in Fiji, and although he died a dozen years before independence from the United Kingdom was achieved in 1970, his vision set the course that Fiji was to follow in the years to come.
Ratu is an Austronesian title used by male Fijians of chiefly rank. An equivalent title, adi, is used by females of chiefly rank. In the Malay language, the title ratu is also the traditional honorific title to refer to the ruling king or queen in Javanese culture. Thus in Java, a royal palace is called "keraton", constructed from the circumfix ke- -an and Ratu, to describe the residence of the ratu.
The House of Chiefs in Fiji consists of the Fijian nobility, composed of about seventy chiefs of various ranks, majority of which are related. It is not a formal political body and is not the same as the former Great Council of Chiefs, which was a political body with a prescribed constitutional role, although the membership of the two bodies did overlap to a great extent.

Kubuna is one of the three confederacies that make up Fiji's House of Chiefs, to which all of Fiji's chiefs belong.
Ratu Inoke Takiveikata is a Fijian high chief and former politician. Since 1997 he has held the title of Qaranivalu, a senior chiefly title in Naitasiri Province. He served in the interim Cabinet of Prime Minister Laisenia Qarase as Minister for Regional Development and Multi-ethnic Affairs, in 2000 and 2001, when he was appointed to the Senate and sworn in on 14 September.

Turaga na Vunivalu na Tui Kaba, shortened as Vunivalu, is the Paramount Chief of the Kubuna Confederacy of the island of Bau in Fiji. Loosely translated the title means Warlord of Bau or "Root of War". The succession to the title does not follow primogeniture, but the candidate must be a high-ranking member of the Tui Kaba clan.
The Roko Tui Namata is the title of the Paramount Chief of the Namata district in Fiji's Tailevu Province.
There are three confederacies in the Fijian Traditional Government, Kubuna, Tovata and Burebasaga. One of the two Paramount chiefly tribes in the Kubuna Confederacy is the "ToraniBau" the other

Bau is a small island in Fiji, off the east coast of the main island of Viti Levu. Bau rose to prominence in the mid-1800s and became Fiji's dominant power; until its cession to Britain, it has maintained its influence in politics and leadership right through to modern Fiji. Due to its sacred nature, foreigners have to apply for a permit to visit.
Naitasiri is one of the 14 provinces of Fiji and one of eight located on Viti Levu, Fiji's largest island.
Nakorotubu is one of nineteen districts in Fiji's Ra Province. It consists of seven sub-districts or sub-regions: the five villages of Namarai, Nacobau, Nadavacia, Saioko and Verevere.

Lomaloma is a village at the south of the island of Vanua Balavu in the Lau archipelago of Fiji. The settlement is part of the tribal district of Tikina, Lomaloma and consists of 9 villages, 13 Yavusa (tribes), 42 Mataqali (clans), and 54 family units known as Tokatoka. The nine villages of Lomaloma Tikina are Lomaloma, Sawana, Susui, Narocivo, Namalata, Uruone, Levukana, Dakuilomaloma, and Tuvuca.
Elenoa Serukeirewa (1875–1930) was a Fijian Adi (chief), the daughter of Ro Waisea. L. Qioniwailevu and Adi Veniana Draukibei. Ro Waisea was the "Vunivalu na Vosaibaleni" of the Yavusa Nawainovo from the tokatoka Nauluvatu. Adi Elenoa was the last member of this lineage. Before she died in 1930, she held the title "Vunivalu na Vosaibaleni", inheriting it from her father. She was also the last person to have been installed to this position. Her village was Kasavu, now located in the province and district of Naitasiri. Formerly, this village consisted of three tribes, including the Yavusa Nawainovo, where the "Marama na Vunivalu" is from, and which comprises the Mataqali Vunivesi. The other two tribes were the Yavusa Sawa, consisting of the Mataqali Rokoraite, and the Yavusa Burenitu, consisting of the Mataqali Aisokula, Rokotuinakoro, Vunileba, Tabuicovi and Naisogo. However, after the sitting of the Native Lands Commission the three tribes were combined into one known as the Burenitu tribe.

RatuTanoa Visawaqa was a Fijian Chieftain who held the title 5th Vunivalu of Bau. With Adi Savusavu, one of his nine wives, he was the father of Ratu Seru Epenisa Cakobau, who succeeded in unifying Fiji with the help from British missionaries and the crown into forming the contemporary Fiji today.
Turaga na Rasau is a traditional Fijian chiefly title of the Lau Islands. Prior to Fiji's colonial days, Fiji had many different Vanua with their own Paramount Chieftain which exercised no authority over the other; a saying from the island of Kadavu aptly summarises it "Nomu Turaga o sega na noqu Turaga" or "Your Chief is not my Chief" also the people of Beqa Island were of a similar opinion saying "Qali Cuva Ki Lagi" or "Subject only to heaven" and would bow to no outside Chieftain, but at the turn of the 20th century aspects of the traditional social structure remained, but for administrative purposes three main Matanitu were solidified and formed as they were the dominant consolidated powers at the time being that of Kubuna, Burebasaga and Tovata. With regard to the Rasau while its traditional origins were in Kubuna on Bau the titles traditional authority in modern Fiji is now in Tovata, Lau in particular Lomaloma Tikina on the Island of Vanua Balavu.
Taukei ni Waluvu is a Fijian phrase for "Owner of the Flood." It is the traditional chiefly title of the warrior hill clan Siko-Natabutale of Nairukuruku village. The history of the clan from the mid- nineteenth century, represent the social structures of the chiefly system, religion and western culture that supported colonialism in Fiji. Tradition, Christianity and British indirect rule were combined to legitimize what was accepted as the right way to govern. Condemned by some modern day critics as exploitative, the Fijian chiefly system was the medium of native social interdependence and a traditional contract shared by the indigenous clans of pre-colonial Fiji, that was utilized for colonial rule. Since Independence the chiefly system has had to adapt to the demands of modernity. Anthropologist Arthur Capell in his study of early tribal migration within Fiji made the point that, "the history of Fiji is the history of chiefly families." The phrase in fact emphasized the hierarchical nature of Fijian traditional society where chiefly power was held sacred. The relationship between Chiefs and Westerners in especially Missionaries thus became a focal point for gathering insight into Fijian culture and tradition in the nineteenth century. James Turner a latter anthropologist found, "The chiefly families of Nairukuruku were the first in the eastern highlands of Viti Levu to declare their allegiance to the central government and as a result of this support their influence expanded throughout the area".
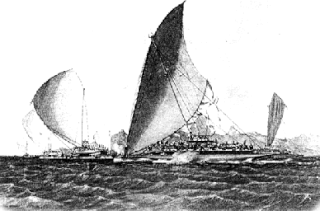
The Lasakau Sea Warriors were a 19th-century warrior sub-culture in the pre-colonial state of Bau, in Fiji. The sea warriors were instrumental in spreading Bau's political power throughout the South Pacific archipelagic islands. The rise of the eminent islet of Bau amongst other embryonic states was due mainly to the projection of sea power through its naval forces. Bauan chief Ratu Loaloadravu Tubuanakoro was praised by French Captain Dumont D'Urville in May 1827 for his geographic knowledge of the Fijian archipelago signifying Bau's naval influence. More far-ranging than Bau's land warriors led by the Vusaradave clan, the Lasakau clan became the leading proponents of war and tribute for the emerging island kingdom. They became known as the Bai kei Bau or 'War fence of Bau'. Sahlins made the crucial observation that," The kings of Bau based their rule not on native cultivators but on native sailors and fishers-which is to say in Fijian categories, as in political strategies, not on the land but on the sea". This was the great political transformation that catapulted Bau to power over other pre-colonial kingdoms.

Verata is a tikina in Fiji's Tailevu Province. It is made up of several sub-districts or Tikina makawa, namely: Verata, Namalata, Tai, Vugalei, and Taivugalei.
In Fiji, Turaga na Roko Tui Bau is a vassal chief of the Vunivalu of Bau. From his seat at the residence of Naicobocobo, the Roko Tui Bau rules the Vusaratu chiefs and has relationships with the Roko Tui Dreketi, Ratu Mai Verata, Roko Tui Namata, Roko Tui Veikau, Tui Vuya and other members of Fiji's House of Chiefs.

Navatu is a sub district in Cakaudrove; one of 3 provinces situated in Vanua Levu, the second largest island in Fiji. The sub-district, or "tikina" as it is known in the iTaukei language, comprises nine villages mainly occupying the eastern peninsular of the Natewa Bay. While Copra has been the main source of income for villages in the Navatu tikina, kava or yaqona is also becoming a fast growing commodity for villages within the Navatu sub-district.
References
- Viceroy of the Pacific: Life of Sir John Bates Thurston, By Deryck Scarr (Page 92)Published 1980, Australian University Press, ISBN 0-909150-88-5, Original from the University of Michigan, the University of California, Digitized Nov 21, 2006, Reference to the title of the Qaranivalu
- The Majesty of Colour, By Scarr, Deryck, (Page 78, Published 1980, Australian University Press, ISBN 0-7081-0704-4. reference to the title and its ties to Bau.
- King of the cannibal isles - Page 120, Published 1937, Original from the University of California, Digitized Nov 21, 2006.