
Falcons are birds of prey in the genus Falco, which includes about 40 species. Falcons are widely distributed on all continents of the world except Antarctica, though closely related raptors did occur there in the Eocene.

The peregrine falcon, also known simply as the peregrine, and historically as the duck hawk in North America, is a cosmopolitan bird of prey (raptor) in the family Falconidae. A large, crow-sized falcon, it has a blue-grey back, barred white underparts, and a black head. The peregrine is renowned for its speed. It can reach over 320 km/h (200 mph) during its characteristic hunting stoop, making it the fastest member of the animal kingdom. According to a National Geographic TV program, the highest measured speed of a peregrine falcon is 389 km/h (242 mph). As is typical for bird-eating (avivore) raptors, peregrine falcons are sexually dimorphic, with females being considerably larger than males.

Falconry is the hunting of wild animals in their natural state and habitat by means of a trained bird of prey. Small animals are hunted; squirrels and rabbits often fall prey to these birds. Two traditional terms are used to describe a person involved in falconry: a "falconer" flies a falcon; an "austringer" flies a hawk or an eagle. In modern falconry, the red-tailed hawk, Harris's hawk, and the peregrine falcon are some of the more commonly used birds of prey. The practice of hunting with a conditioned falconry bird is also called "hawking" or "gamehawking", although the words hawking and hawker have become used so much to refer to petty traveling traders, that the terms "falconer" and "falconry" now apply to most use of trained birds of prey to catch game. Many contemporary practitioners still use these words in their original meaning, however.
Peregrine, Latin Peregrinus, is a name originally meaning "one from abroad", that is, a foreigner, traveller, or pilgrim. It may refer to:

The American kestrel, also called the sparrow hawk, is the smallest and most common falcon in North America. It has a roughly two-to-one range in size over subspecies and sex, varying in size from about the weight of a blue jay to a mourning dove. It also ranges to South America and is a well-established species that has evolved into 17 subspecies adapted to different environments and habitats throughout the Americas. It exhibits sexual dimorphism in size and plumage, although both sexes have a rufous back with noticeable barring. Its plumage is colorful and attractive, and juveniles are similar in plumage to adults.

The lanner falcon is a medium-sized bird of prey that breeds in Africa, southeast Europe and just into Asia. It prefers open habitat and is mainly resident, but some birds disperse more widely after the breeding season. A large falcon, it preys on birds and bats. Most likely either the lanner or peregrine falcon was the sacred species of falcon to the ancient Egyptians, and some ancient Egyptian deities, like Ra and Horus, were often represented as a man with the head of a lanner falcon.

The Barbary falcon is a medium-sized falcon about the size of a crow. This bird of prey is mainly resident. It ranges from the Canary Islands eastwards across some parts of North Africa, the Middle East and Central Asia.

The saker falcon is a large species of falcon. This species breeds from central Europe eastwards across the Palearctic to Manchuria. It is mainly migratory except in the southernmost parts of its range, wintering in Ethiopia, the Arabian peninsula, northern Pakistan and western China. The saker falcon is the second fastest bird in level flight after the white-throated needletail swift, capable of reaching 150 km/h (93 mph). It is also the 3rd fastest animal in the world overall after the peregrine falcon and the golden eagle, with all three species capable of executing high speed dives known as “swooping”, in excess of 320 km/h. The saker falcon is the national bird of Hungary, the United Arab Emirates, and Mongolia.

The prairie falcon is a medium-large sized falcon of western North America. It is about the size of a peregrine falcon or a crow, with an average length of 40 cm (16 in), wingspan of approximately 1 meter (40 in), and average weight of 720 g (1.6 lb). As in all falcons, females are noticeably bigger than males. Though a separate species from the peregrine, the prairie falcon is basically an arid environment divergence of the early peregrine falcon lineage, able to subsist on less food than the peregrine, and generally lighter in weight than a peregrine of similar wing span. Having evolved in a harsh desert environment with low prey density, the prairie falcon has developed into an aggressive and opportunistic hunter of a wide range of both mammal and bird prey. It will regularly take prey from the size of sparrows to approximately its own weight, and occasionally much larger. It is the only larger falcon native only to North America. It is resident from southern Canada, through western United States, and into northern Mexico. The prairie falcon is popular as a falconry bird, where with proper training it is regarded as being as effective as the more well known peregrine falcon.

The aplomado falcon is a medium-sized falcon of the Americas. The species' largest continuous range is in South America, but not in the deep interior Amazon Basin. It was long known as Falco fusco-coerulescens or Falco fuscocaerulescens, but these names are now believed to refer to the bat falcon. Its resemblance in shape to the hobbies accounts for its old name orange-chested hobby. Aplomado is an unusual Spanish word for "lead-colored", referring to the blue-grey areas of the plumage – an approximate English translation would be "plumbeous falcon". Spanish names for the species include halcón aplomado and halcón fajado ; in Brazil it is known as falcão-de-coleira.
The World Center for Birds of Prey in Boise, Idaho, is the headquarters for The Peregrine Fund, an international non-profit organization founded in 1970 that conserves endangered raptors around the world.
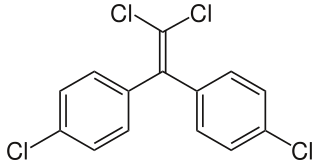
Dichlorodiphenyldichloroethylene (DDE) is a chemical compound formed by the loss of hydrogen chloride (dehydrohalogenation) from DDT, of which it is one of the more common breakdown products. Due to DDT's massive prevalence in society and agriculture during the mid 20th century, DDT and DDE are still widely seen in animal tissue samples. DDE is particularly dangerous because it is fat-soluble like other organochlorines; thus, it is rarely excreted from the body, and concentrations tend to increase throughout life. The major exception is the excretion of DDE in breast milk, which transfers a substantial portion of the mother's DDE burden to the young animal or child. Along with accumulation over an organism's lifetime, this stability leads to bioaccumulation in the environment, which amplifies DDE's negative effects.

The Australian hobby, also known as the little falcon, is one of six Australian members of the family Falconidae. This predominantly diurnal bird of prey derives its name ‘longipennis’ from its long primary wing feathers. It occurs throughout Australia and other neighbouring countries with migrating individuals found on the islands of Indonesia and New Guinea.

Bird control or bird abatement involves the methods to eliminate or deter pest birds from landing, roosting and nesting.

The barred forest falcon is a species of bird of prey in subfamily Herpetotherinae of family Falconidae, the falcons and caracaras. It occurs from southern Mexico south through most of Central America and in every mainland South American country except Chile and Uruguay.
The Peregrine Fund is a non-profit organization founded in 1970 that conserves threatened and endangered birds of prey worldwide. The successful recovery of the peregrine falcon in the United States, which was removed from the U.S. Endangered Species List in 1999, enabled the organization to expand its mission to include other endangered raptors around the world. The Peregrine Fund is headquartered at its World Center for Birds of Prey in Boise, Idaho, on a 580-acre (2.3 km2) campus with breeding and research facilities, an administrative office, interpretive center, research library, and archives.
Buckaringa Sanctuary is a 20 km2 nature reserve in the southern Flinders Ranges of South Australia. It is 30 km north of the town of Quorn. It is owned and managed by the Australian Wildlife Conservancy (AWC).

The gyrfalcon, the largest of the falcon species, is a bird of prey. The abbreviation gyr is also used. It breeds on Arctic coasts and tundra, and the islands of northern North America and the Eurosiberian region. It is mainly a resident there also, but some gyrfalcons disperse more widely after the breeding season, or in winter. Individual vagrancy can take birds for long distances. Its plumage varies with location, with birds being coloured from all-white to dark brown. These colour variations are called morphs. Like other falcons, it shows sexual dimorphism, with the female much larger than the male. For centuries, the gyrfalcon has been valued as a hunting bird. Typical prey includes the ptarmigan and waterfowl, which it may take in flight; it also takes fish and mammals.

The shaheen falcon is a non-migratory subspecies of the peregrine falcon found mainly in the Indian subcontinent. It has also been described as a migratory subspecies. Other common names for the subspecies include the black shaheen and Indian peregrine falcon. The word shaheen in these names may also be spelled as shahin. This species was termed as the black shaheen by falconers to separate it from the true shaheen of Persian literature. Scholars of Persian and the Russian ornithologist Georgi Petrovich Dementiev have noted that the name shaheen in Persian literature actually referred to Falco peregrinus babylonicus.















