
Vojvodina, officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia, located in Central Europe. It lies within the Pannonian Basin, bordered to the south by the national capital Belgrade and the Sava and Danube Rivers. The administrative centre, Novi Sad, is the second-largest city in Serbia.

Banat is a geographical and historical region located in the Pannonian Basin that straddles Central and Eastern Europe. It is currently divided among three countries: the eastern part lies in western Romania ; the western part of Banat is in northeastern Serbia ; and a small northern part lies within southeastern Hungary.
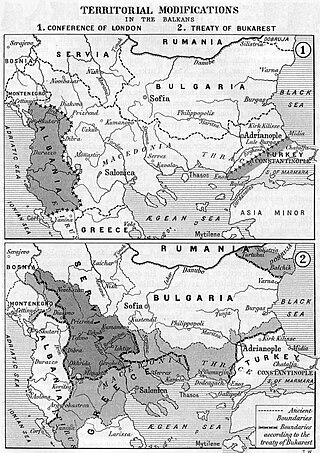
The Treaty of Bucharest was concluded on 10 August 1913, by the delegates of Bulgaria, Romania, Serbia, Montenegro and Greece. The Treaty was concluded in the aftermath of the Second Balkan War and amended the previous Treaty of London, which ended the First Balkan War. About one month later, the Bulgarians signed a separate border treaty with the Ottomans, who had regained some territory west of the Enos-Midia Line during the second war.

Central Serbia, also referred to as Serbia proper, is the region of Serbia lying outside the autonomous province of Vojvodina to the north and the autonomous province of Kosovo and Metohija to the south. Central Serbia is a term of convenience, not an administrative division of Serbia as such, and does not have any form of separate administration.
Podunavlje is the name of the Danube river basin parts located in Croatia and Serbia. Podunavlje is located on the southern edge of Pannonian Basin. In its wider meaning, the Croatian term refers to the area around the entire flow of the river Danube.

Romanians in Serbia are a recognized national minority in Serbia. The total number of self-declared Romanians according to the 2022 census was 23,044, while 21,013 people declared themselves Vlachs; there are differing views among some of the Vlachs over whether they should be regarded as Romanians or as members of a distinctive nationality. Declared Romanians are mostly concentrated in Banat, in Vojvodina, while declared Vlachs are mostly concentrated in the Timok Valley, in eastern Serbia.

Russia–Serbia relations are the bilateral foreign relations between the Russian Federation and the Republic of Serbia. The countries established official diplomatic relations as the Russian Empire and Principality of Serbia in 1816. Russia has an honorary consulate and embassy in Belgrade, and a liaison office to UNMIK, the capital of the disputed territory of Kosovo. Serbia has an embassy in Moscow, an honorary consulate in St. Petersburg and has announced to open a consulate-general in Yekaterinburg.

The Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of Serbia is the ministry in the government of Serbia which is in the charge of maintaining the consular affairs and foreign relations of Serbia. The current minister is Marko Đurić, in office since 26 October 2022.

Foreign relations between Croatia and Serbia are bound together by shared history, cultural ties and geography. The two states established diplomatic relations in 1996, following the dissolution of Yugoslavia, the Croatian War of Independence and the independence of Croatia. Modern diplomatic relations are functional but cool, stemming from historic nation-building conflict and divergent political ideologies. Their relationship holds geopolitical importance in Southeast Europe given their economic influence in the region.

Relations between Hungary and Serbia, or Serbo-Hungarian relations form a part of the wider politics of Central and Southeast Europe. The two countries have a long relationship stretching back to the Middle Ages. History of official diplomatic relations of Hungary and Serbia dates back to 21 November 1882, when they were established between the Kingdom of Serbia and Austria-Hungary. Today, Hungary has an embassy in Belgrade and a general consulate in Subotica, while Serbia has an embassy in Budapest and an honorary consulate in Szeged.

Polish-Serbian relations are foreign relations between Poland and Serbia. Diplomatic relations have been maintained since Poland and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes established them in 1919. Poland is a European Union member state and Serbia is a European Union candidate.

Italy–Serbia relations are diplomatic relations between Italy and Serbia. Kingdom of Italy established formal bilateral relations with the Principality of Serbia on 18 January 1879. The strategic partnership between the Republic of Serbia and the Republic of Italy was established in Rome on 13 November 2009. Italy is one of the member states of the European Union which strongly support Accession of Serbia to the European Union. Both countries are members of the Central European Initiative, OSCE, Council of Europe and the World Trade Organization.

Portuguese-Serbian relations date back to 1882. Portugal has an embassy in Belgrade, and Serbia has an embassy in Lisbon. Despite support by Portugal for the independence of Kosovo, Serbian Prime Minister Mirko Cvetković was keen to improve bilateral cooperation. Also, Portugal is backing Serbia's accession to the European Union (EU).
Serbian-Spanish relations are foreign relations between Serbia and Spain. Both countries established diplomatic relations on October 14, 1916. Serbia has an embassy in Madrid. Spain has an embassy in Belgrade. Both countries are member states of the United Nations, Interpol, Council of Europe and Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe. Spain is member state of the European Union since 1986 and Serbia is a candidate country since 2012 negotiating its future membership which Spain is strongly supporting. Spain is member state of NATO alliance while Serbia is a militarily neutral country with strong historical relations with the Non-Aligned Movement. In relation to third parties, both countries supported position of Argentina in its Falkland Islands sovereignty dispute with the United Kingdom in the past.

Relations between Albania and Serbia have been complex and largely unfriendly due to a number of historical and political events.

Finland–Yugoslavia relations were historical foreign relations between Finland and now split-up Kingdom of Yugoslavia or Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. Both countries gained their independence during or in the immediate aftermath of the World War I and the collapse of Austria-Hungary (Yugoslavia) or Russian Empire (Finland). Two parties established formal bilateral relations in 1928. Two countries developed their relations after the end of the World War II and 1948 Tito–Stalin split. At the time neither one of them was a part of either Eastern or Western Bloc in the Cold War divided Europe. Both countries perceived development of relations among non-bloc neutral European states as a way to avoid isolation and preserve certain level of independence without alienating major powers. Belgrade however perceived that in deeply divided Europe there was shrinking maneuvering space for neutral countries and followed the development of what will be called process of Finlandization with great concern. It therefore turned its focus on new allies among former colonies and mandate territories outside of Europe where it developed its policy of equidistant active neutrality via its activities in the newly founded Non-Aligned Movement.

Turkey–Yugoslavia relations were historical foreign relations between Turkey and now broken up Yugoslavia.

Romania–Yugoslavia relations were historical foreign relations between Romania and now broken up Yugoslavia. Relations between Romania and independent South Slavic states developed before creation of Yugoslavia and union of Transylvania with Romania and those relations played prominent role during the Second Balkan War. Relations between the two states were generally friendly and were only occasionally affected by wider alliance policies.
France–Yugoslavia relations were the historical foreign relations between France and Yugoslavia. These spanned from just after the First World War, to the eventual break-up of Yugoslavia in the aftermath of the Cold War. Over this period, there were several successive governments in both countries. France was variously: the Third Republic, Free France, the wartime Provisional Government, the post-war Fourth Republic, and the modern Fifth Republic. Coterminously, the states governing what is today the former Yugoslavia were: the Kingdom of Yugoslavia, the wartime government in exile, the wartime provisional Democratic Federal Yugoslavia, and the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia.

China–Yugoslavia relations were historical foreign relations between China and now split-up Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. For a long period during the Cold War China was critical towards perceived excessive liberalism, too close cooperation with Western Bloc or market socialism of Yugoslavia, therefore the Chinese communists accused the Yugoslav communists of being revisionists, while the Yugoslav communists accused the Chinese communists of being dogmatics. But, the good relations between both socialist states were restored at the end of the 1960s, and improved even more since the Sino-Albanian rupture occurred, with the trend of improved relations continuing in relations with successor states, particularly Serbia. In the 1980s Deng Xiaoping's foreign policy resembled Yugoslavia's stance of being non-aligned and non-confrontational and with Hu Yaobang’s 1983 appraisal of ‘Josip Tito's principles of independence and equality among all communist parties, and of opposing imperialism, colonialism, and hegemonism’. All six former Yugoslav republics have memoranda of understanding with China on Belt and Road Initiative.






















