
Mindanao is the second-largest island in the Philippines, after Luzon, and seventh-most populous island in the world. Located in the southern region of the archipelago, the island is part of an island group of the same name that also includes its adjacent islands, notably the Sulu Archipelago. According to the 2020 census, Mindanao had a population of 26,252,442, while the entire island group had an estimated population of 27,021,036.

The Philippines is an archipelago that comprises 7,641 islands, and with a total land area of 300,000 square kilometers (115,831 sq mi), it is the world's fifth largest island country. The eleven largest islands contain 95% of the total land area. The largest of these islands is Luzon at about 105,000 square kilometers (40,541 sq mi). The next largest island is Mindanao at about 95,000 square kilometers (36,680 sq mi). The archipelago is around 800 kilometers (500 mi) from the Asian mainland and is located between Taiwan and Borneo.

Bukidnon, officially the Province of Bukidnon, is a landlocked province in the Philippines located in the Northern Mindanao region. Its capital is the city of Malaybalay while Valencia is the largest city. The province borders, clockwise from the north, Misamis Oriental, Agusan del Sur, Davao del Norte, Cotabato, Lanao del Sur, and Lanao del Norte. According to the 2020 census, the province is inhabited by 1,541,308 residents. The province is composed of 2 component cities and 20 municipalities. It is the third largest province in the country in terms of total area of jurisdiction behind Palawan and Isabela respectively.

Davao del Sur, officially the Province of Davao del Sur, is a province in the Philippines located in the Davao Region in Mindanao. Its capital is Digos. Davao City is the largest city in terms of area and population within the province's jurisdiction, yet it is administratively independent from the province; as such, Davao City is only grouped for geographical and statistical purposes and serves as the regional center of Davao Region.

Cotabato, formerly and still commonly referred to as North Cotabato and officially the Province of Cotabato, is a landlocked province in the Philippines located in the Soccsksargen region in Mindanao. Its capital is the city of Kidapawan, the most populous in the province. Some of its municipalities are under the jurisdiction of the nearby Bangsamoro Autonomous Region.

Kitaotao, officially the Municipality of Kitaotao, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Bukidnon, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 53,796 people.

Quezon, officially the Municipality of Quezon, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Bukidnon, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 109,624 people.

San Fernando, officially the Municipality of San Fernando, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Bukidnon, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 63,045 people.
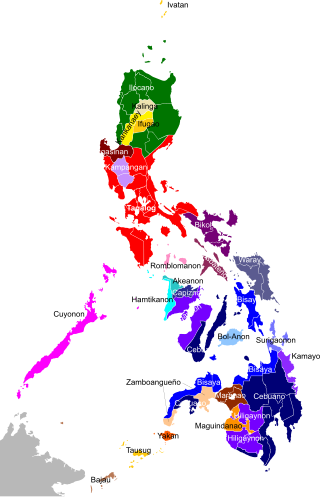
The Philippines is inhabited by more than 182 ethnolinguistic groups, many of which are classified as "Indigenous Peoples" under the country's Indigenous Peoples' Rights Act of 1997. Traditionally-Muslim peoples from the southernmost island group of Mindanao are usually categorized together as Moro peoples, whether they are classified as Indigenous peoples or not. About 142 are classified as non-Muslim Indigenous people groups, and about 19 ethnolinguistic groups are classified as neither Indigenous nor Moro. Various migrant groups have also had a significant presence throughout the country's history.

The Lumad are a group of Austronesian indigenous peoples in the southern Philippines. It is a Cebuano term meaning "native" or "indigenous". The term is short for Katawhang Lumad, the autonym officially adopted by the delegates of the Lumad Mindanao Peoples Federation (LMPF) founding assembly on 26 June 1986 at the Guadalupe Formation Center, Balindog, Kidapawan, Cotabato. Usage of the term was accepted in Philippine jurisprudence when President Corazon Aquino signed into law Republic Act 6734, where the word was used in Art. XIII sec. 8(2) to distinguish Lumad ethnic communities from the islands of Mindanao.

Musuan Peak or Mount Musuan, also known as Mount Calayo is an active volcano in Maramag, Bukidnon, on the island of Mindanao in the Philippines. It is 4.5 kilometres (2.8 mi) south of the city of Valencia, province of Bukidnon, and 81 kilometres (50 mi) southeast of Cagayan de Oro.

The Matigsalug are an Indigenous group who live in the Tigwa-Salug Valley in San Fernando in Bukidnon province, Philippines. "Matigsalug" means "people along the Salug River". Although often classified under the Manobo ethnolinguistic group, the Matigsalug are a distinct subgroup from the Manobos.

The Kalaság or Kalasak is a large rectangular wooden shield used by precolonial Filipinos. The shield is made of hardwood and is decorated with intricate carvings and an elaborate rattan binding on the front. The wood comes from native trees such as the dapdap, polay and sablang. The shield usually measured about 1.5 m (4.9 ft) in length and 0.5 m (1.6 ft) in width. Its base is composed of rattan wood which is strengthened by the application of resin coating that turned rock-hard upon drying.

The Roman Catholic Diocese of Malaybalay is a diocese of the Latin Church of the Roman Catholic Church in the Philippines.

Butuan, also called the Rajahnate of Butuan and the Kingdom of Butuan, was a precolonial Bisaya polity (lungsod) centered around northeastern Mindanao island in present-day Butuan, Philippines. It was known for its gold mining, gold jewelry and other wares, and its extensive trade network across maritime Southeast Asia and elsewhere. Over its long history the lungsod had direct trading relationships with the ancient civilizations of China, Champa, Đại Việt, Pon-i (Brunei), Srivijaya, Majapahit, Kambuja, and even Persia as well as areas now comprised in Thailand.
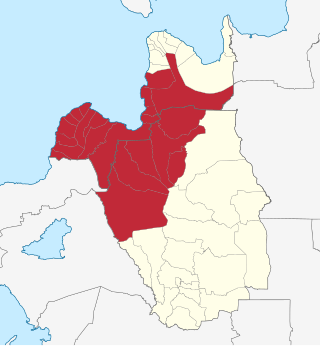
Metropolitan Cagayan de Oro, also known as Metro Cagayan de Oro, is the fourth largest metropolitan area in the Philippines. It is located on the northern coast of Mindanao, and comprises the two chartered cities of Cagayan de Oro and El Salvador and the fourteen municipalities of Misamis Oriental which are Alubijid, Balingasag, Claveria, Gitagum, Initao, Jasaan, Laguindingan, Libertad, Lugait, Manticao, Naawan, Opol, Tagoloan, and Villanueva and the six municipalities of Bukidnon which are Manolo Fortich, Baungon, Libona, Malitbog, Sumilao and Talakag. According to the 2015 Philippine census, Metro Cagayan de Oro has a population of 1,687,159 people.
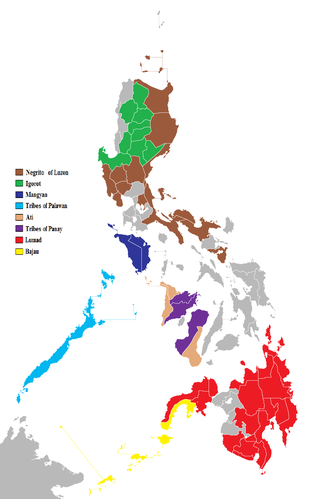
The indigenous peoples of the Philippines are ethnolinguistic groups or subgroups that maintain partial isolation or independence throughout the colonial era, and have retained much of their traditional pre-colonial culture and practices.
The Manobo are an indigenous peoples from Mindanao in the Philippines, whose core lands cover most of the Mindanao island group, from Sarangani island into the Mindanao mainland in the regions of Agusan, Davao, Bukidnon, Surigao, Misamis, and Cotabato. The Manobo are considered the most diverse among the many indigenous peoples of the Philippines, with the largest number of subgroups within its family of languages. The Philippine Statistics Authority listed 644,904 persons as Manobo in its 2020 Census of Population and Housing.
Matigsalug is a Manobo language of Mindanao in the Philippines. It belongs to the Austronesian language family.

The Pantaron Mountain Range, also called the Central Cordillera of Mindanao, Philippines straddles across the provinces of Misamis Oriental, Bukidnon, Agusan del Norte, Agusan del Sur, Davao del Norte and Davao del Sur. The range contains one of the last remaining old growth or primary forest blocks in Mindanao. Major rivers on the island also have their headwaters on the mountain range, including Mindanao River, Pulangi River, Davao River, Tagoloan River and major tributaries of Agusan River.



















