Non-cognitivism is the meta-ethical view that ethical sentences do not express propositions and thus cannot be true or false. A noncognitivist denies the cognitivist claim that "moral judgments are capable of being objectively true, because they describe some feature of the world". If moral statements cannot be true, and if one cannot know something that is not true, noncognitivism implies that moral knowledge is impossible.

The problem of universals is an ancient question from metaphysics that has inspired a range of philosophical topics and disputes: "Should the properties an object has in common with other objects, such as color and shape, be considered to exist beyond those objects? And if a property exists separately from objects, what is the nature of that existence?"
Substance theory, or substance–attribute theory, is an ontological theory positing that objects are constituted each by a substance and properties borne by the substance but distinct from it. In this role, a substance can be referred to as a substratum or a thing-in-itself. Substances are particulars that are ontologically independent: they are able to exist all by themselves. Another defining feature often attributed to substances is their ability to undergo changes. Changes involve something existing before, during and after the change. They can be described in terms of a persisting substance gaining or losing properties. Attributes or properties, on the other hand, are entities that can be exemplified by substances. Properties characterize their bearers; they express what their bearer is like.

A sign is an object, quality, event, or entity whose presence or occurrence indicates the probable presence or occurrence of something else. A natural sign bears a causal relation to its object—for instance, thunder is a sign of storm, or medical symptoms a sign of disease. A conventional sign signifies by agreement, as a full stop signifies the end of a sentence; similarly the words and expressions of a language, as well as bodily gestures, can be regarded as signs, expressing particular meanings. The physical objects most commonly referred to as signs generally inform or instruct using written text, symbols, pictures or a combination of these.
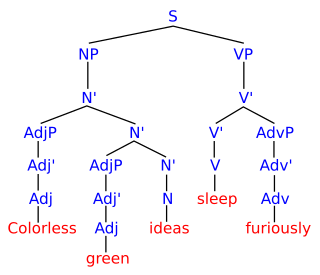
Colorless green ideas sleep furiously was composed by Noam Chomsky in his 1957 book Syntactic Structures as an example of a sentence that is grammatically well-formed, but semantically nonsensical. The sentence was originally used in his 1955 thesis The Logical Structure of Linguistic Theory and in his 1956 paper "Three Models for the Description of Language". There is no obvious understandable meaning that can be derived from it, which demonstrates the distinction between syntax and semantics, and the idea that a syntactically well-formed sentence is not guaranteed to be semantically well-formed as well. As an example of a category mistake, it was intended to show the inadequacy of certain probabilistic models of grammar, and the need for more structured models.
In grammar, a conjunction is a part of speech that connects words, phrases, or clauses that are called the conjuncts of the conjunctions. That definition may overlap with that of other parts of speech, and so what constitutes a "conjunction" must be defined for each language. In English, a given word may have several senses, and be either a preposition or a conjunction depending on the syntax of the sentence. For example, after is a preposition in "he left after the fight" but is a conjunction in "he left after they fought". In general, a conjunction is an invariable (non-inflected) grammatical particle that may or may not stand between the items conjoined.

A double negative is a construction occurring when two forms of grammatical negation are used in the same sentence. This is typically used to convey a different shade of meaning from a strictly positive sentence. Multiple negation is the more general term referring to the occurrence of more than one negative in a clause. In some languages, double negatives cancel one another and produce an affirmative; in other languages, doubled negatives intensify the negation. Languages where multiple negatives affirm each other are said to have negative concord or emphatic negation. Portuguese, Persian, French, Russian, Polish, Bulgarian, Greek, Spanish, Old English, Italian, Afrikaans, and Hebrew are examples of negative-concord languages. This is also true of many vernacular dialects of modern English. Chinese, Latin, German, Dutch, Japanese, Swedish and modern Standard English are examples of languages that do not have negative concord. Typologically, negative concord occurs in a minority of languages.
Cognitivism is the meta-ethical view that ethical sentences express propositions and can therefore be true or false, which noncognitivists deny. Cognitivism is so broad a thesis that it encompasses moral realism, ethical subjectivism, and error theory.
In semiotics, a sign is anything that communicates a meaning that is not the sign itself to the interpreter of the sign. The meaning can be intentional, as when a word is uttered with a specific meaning, or unintentional, as when a symptom is taken as a sign of a particular medical condition. Signs can communicate through any of the senses, visual, auditory, tactile, olfactory, or taste.

An Essay Concerning Human Understanding is a work by John Locke concerning the foundation of human knowledge and understanding. It first appeared in 1689 with the printed title An Essay Concerning Humane Understanding. He describes the mind at birth as a blank slate filled later through experience. The essay was one of the principal sources of empiricism in modern philosophy, and influenced many enlightenment philosophers, such as David Hume and George Berkeley.

A Treatise Concerning the Principles of Human Knowledge is a 1710 work, in English, by Irish Empiricist philosopher George Berkeley. This book largely seeks to refute the claims made by Berkeley's contemporary John Locke about the nature of human perception. Whilst, like all the Empiricist philosophers, both Locke and Berkeley agreed that we are having experiences, regardless of whether material objects exist, Berkeley sought to prove that the outside world is also composed solely of ideas. Berkeley did this by suggesting that "Ideas can only resemble Ideas" – the mental ideas that we possess can only resemble other ideas and thus the external world consists not of physical form, but rather of ideas. This world is given logic and regularity by some other force, which Berkeley concludes is God.
"Critique of the Kantian philosophy" is a criticism Arthur Schopenhauer appended to the first volume of his The World as Will and Representation (1818). He wanted to show Immanuel Kant's errors so that Kant's merits would be appreciated and his achievements furthered.

Relevance theory is a framework for understanding the interpretation of utterances. It was first proposed by Dan Sperber and Deirdre Wilson, and is used within cognitive linguistics and pragmatics. The theory was originally inspired by the work of Paul Grice and developed out of his ideas, but has since become a pragmatic framework in its own right. The seminal book, Relevance, was first published in 1986 and revised in 1995.
"On Denoting" is an essay by Bertrand Russell. It was published in the philosophy journal Mind in 1905. In it, Russell introduces and advocates his theory of denoting phrases, according to which definite descriptions and other "denoting phrases ... never have any meaning in themselves, but every proposition in whose verbal expression they occur has a meaning." This theory later became the basis for Russell's descriptivism with regard to proper names, and his view that proper names are "disguised" or "abbreviated" definite descriptions.
A truth-bearer is an entity that is said to be either true or false and nothing else. The thesis that some things are true while others are false has led to different theories about the nature of these entities. Since there is divergence of opinion on the matter, the term truth-bearer is used to be neutral among the various theories. Truth-bearer candidates include propositions, sentences, sentence-tokens, statements, beliefs, thoughts, intuitions, utterances, and judgements but different authors exclude one or more of these, deny their existence, argue that they are true only in a derivative sense, assert or assume that the terms are synonymous, or seek to avoid addressing their distinction or do not clarify it.

The primary–secondary quality distinction is a conceptual distinction in epistemology and metaphysics, concerning the nature of reality. It is most explicitly articulated by John Locke in his Essay concerning Human Understanding, but earlier thinkers such as Galileo and Descartes made similar distinctions.
Cebuano grammar encompasses the rules that define the Cebuano language, the most widely spoken of all the languages in the Visayan Group of languages, spoken in Cebu, Bohol, Siquijor, part of Leyte island, part of Samar island, Negros Oriental, especially in Dumaguete, and the majority of cities and provinces of Mindanao.
Music semantics refers to the ability of music to convey semantic meaning. Semantics are a key feature of language, and whether music shares some of the same ability to prime and convey meaning has been the subject of recent study.
In linguistics and grammar, affirmation and negation are ways in which grammar encodes positive and negative polarity into verb phrases, clauses, or other utterances. An affirmative (positive) form is used to express the validity or truth of a basic assertion, while a negative form expresses its falsity. For example, the affirmative sentence "Joe is here" asserts that it is true that Joe is currently located near the speaker. Conversely, the negative sentence "Joe is not here" asserts that it is not true that Joe is currently located near the speaker.
Sam Glucksberg was a Canadian professor in the Psychology Department at Princeton University in New Jersey, known for his works on figurative language: metaphors, irony, sarcasm, and idioms. He is particularly known for manipulating the Candle Problem experiment which had participants figure out the best way to erect a candle on a wall. Along with performing experiments, Glucksberg has also written Understanding Figurative Language: From Metaphors to Idioms, published by Oxford University Press in 2001.