
A letter is a written message conveyed from one person to another through a medium. The term usually excludes written material intended to be read in its original form by large numbers of people, such as newspapers and placards, although even these may include material in the form of an "open letter". The typical form of a letter for many centuries, and the archetypal concept even today, is a sheet of paper that is sent to a correspondent through a postal system. A letter can be formal or informal, depending on its audience and purpose. Besides being a means of communication and a store of information, letter writing has played a role in the reproduction of writing as an art throughout history. Letters have been sent since antiquity and are mentioned in the Iliad. Historians Herodotus and Thucydides mention and use letters in their writings.
The Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is an internet standard communication protocol for electronic mail transmission. Mail servers and other message transfer agents use SMTP to send and receive mail messages. User-level email clients typically use SMTP only for sending messages to a mail server for relaying, and typically submit outgoing email to the mail server on port 587 or 465 per RFC 8314. For retrieving messages, IMAP is standard, but proprietary servers also often implement proprietary protocols, e.g., Exchange ActiveSync.

The United States Postal Service (USPS), also known as the Post Office, U.S. Mail, or Postal Service, is an independent agency of the executive branch of the United States federal government responsible for providing postal service in the United States, including its insular areas and associated states. It is one of the few government agencies explicitly authorized by the United States Constitution. The USPS, as of 2021, has 516,636 career employees and 136,531 non-career employees.

The mail or post is a system for physically transporting postcards, letters, and parcels. A postal service can be private or public, though many governments place restrictions on private systems. Since the mid-19th century, national postal systems have generally been established as a government monopoly, with a fee on the article prepaid. Proof of payment is usually in the form of an adhesive postage stamp, but a postage meter is also used for bulk mailing. With the advent of email, the retronym "snail mail" was coined.

A postal code is a series of letters or digits or both, sometimes including spaces or punctuation, included in a postal address for the purpose of sorting mail.

A ZIP Code is a postal code used by the United States Postal Service (USPS). Introduced on July 1, 1963, the basic format consisted of five digits. In 1983, an extended ZIP+4 code was introduced; it included the five digits of the ZIP Code, followed by a hyphen and four digits that designated a more specific location.
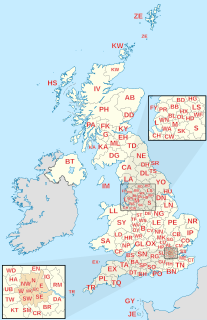
Postal codes used in the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies are known as postcodes. They are alphanumeric and were adopted nationally between 11 October 1959 and 1974, having been devised by the General Post Office. A full postcode is known as a "postcode unit" and designates an area with several addresses or a single major delivery point.

An aerogram, aerogramme, aérogramme, air letter or airletter is a thin lightweight piece of foldable and gummed paper for writing a letter for transit via airmail, in which the letter and envelope are one and the same. Most postal administrations forbid enclosures in these light letters, which are usually sent abroad at a preferential rate. Printed warnings existed to say that an enclosure would cause the mail to go at the higher letter rate.

Registered mail is a mail service offered by postal services in many countries, which allows the sender proof of mailing via a mailing receipt and, upon request, electronic verification that an article was delivered or that a delivery attempt was made. Depending on the country, additional services may also be available, such as:
In the context of information security, and especially network security, a spoofing attack is a situation in which a person or program successfully identifies as another by falsifying data, to gain an illegitimate advantage.
Poste restante, also known as general delivery in North American English, is a service where the post office holds the mail until the recipient calls for it. It is a common destination for mail for people who are visiting a particular location and have no need, or no way, of having mail delivered directly to their place of residence at that time.

The British Forces Post Office (BFPO) provides a postal service to HM Forces, separate from that provided by Royal Mail in the United Kingdom. BFPO addresses are used for the delivery of mail in the UK and around the world. BFPO moved from its original base at Inglis Barracks, Mill Hill to its current base at RAF Northolt in northwest London in 2007.

In postal mail, a return address is an explicit inclusion of the address of the person sending the message. It provides the recipient with a means to determine how to respond to the sender of the message if needed.
An address is a collection of information, presented in a mostly fixed format, used to give the location of a building, apartment, or other structure or a plot of land, generally using political boundaries and street names as references, along with other identifiers such as house or apartment numbers and organization name. Some addresses also contain special codes, such as a postal code, to make identification easier and aid in the routing of mail.
In computer science, message passing is a technique for invoking behavior on a computer. The invoking program sends a message to a process and relies on that process and its supporting infrastructure to then select and run some appropriate code. Message passing differs from conventional programming where a process, subroutine, or function is directly invoked by name. Message passing is key to some models of concurrency and object-oriented programming.
Variable data printing (VDP) is a form of digital printing, including on-demand printing, in which elements such as text, graphics and images may be changed from one printed piece to the next, without stopping or slowing down the printing process and using information from a database or external file. For example, a set of personalized letters, each with the same basic layout, can be printed with a different name and address on each letter. Variable data printing is mainly used for direct marketing, customer relationship management, advertising, invoicing and applying addressing on selfmailers, brochures or postcard campaigns.

Freepost is a postal service provided by various postal administrations, whereby a person sends mail without affixing postage, and the recipient pays the postage when collecting the mail. Freepost differs from self-addressed stamped envelopes, courtesy reply mail, and metered reply mail in that the recipient of the freepost pays only for those items that are actually received, rather than for all that are distributed. Freepost of preprinted cards issued by businesses is also different from postal stationery sold by postal administrations.
A multiline optical-character reader, or MLOCR, is a type of mail sorting machine that uses optical character recognition (OCR) technology to determine how to route mail through the postal system.
Remote Bar Coding System (RBCS), also called Remote Video Encoding (RVE) is a method used by the United States Postal Service to encode the address of letter-sized mailpieces that are not decipherable by a Multiline Optical Character Reader (MLOCR). When an MLOCR does not recognize a valid address on a letter, it sends an image of the mailpiece to a central RBCS (RVE) site where more sophisticated optical character recognition software is able to interpret many hand-written addresses using neural net and fuzzy logic algorithms. If this does not succeed, human operators visually examine the image and enter the address. In both cases, the data is sent back to the originating mail facility where mailpieces are then automatically matched back up with data through the use of a unique fluorescent barcode printed on the back during initial MLOCR attempt, and receive a POSTNET barcode representing the full address.
A communication protocol is a system of rules that allows two or more entities of a communications system to transmit information via any kind of variation of a physical quantity. The protocol defines the rules, syntax, semantics and synchronization of communication and possible error recovery methods. Protocols may be implemented by hardware, software, or a combination of both.










