
Alaska is a U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S., it borders British Columbia and Yukon in Canada to the east, and it shares a western maritime border in the Bering Strait with the Russian Federation's Chukotka Autonomous Okrug. To the north are the Chukchi and Beaufort Seas of the Arctic Ocean, and the Pacific Ocean lies to the south and southwest.

The Trans-Alaska Pipeline System (TAPS) is an oil transportation system spanning Alaska, including the trans-Alaska crude-oil pipeline, 11 pump stations, several hundred miles of feeder pipelines, and the Valdez Marine Terminal. TAPS is one of the world's largest pipeline systems. The core pipeline itself, which is commonly called the Alaska pipeline, trans-Alaska pipeline, or Alyeska pipeline,, is an 800-mile (1,287 km) long, 48-inch (1.22 m) diameter pipeline that conveys oil from Prudhoe Bay, on Alaska's North Slope, south to Valdez, on the shores of Prince William Sound in southcentral Alaska. The crude oil pipeline is privately owned by the Alyeska Pipeline Service Company.

The 1964 Alaskan earthquake, also known as the Great Alaskan earthquake and Good Friday earthquake, occurred at 5:36 PM AKST on Good Friday, March 27. Across south-central Alaska, ground fissures, collapsing structures, and tsunamis resulting from the earthquake caused about 131 deaths.

Cook Inlet stretches 180 miles (290 km) from the Gulf of Alaska to Anchorage in south-central Alaska. Cook Inlet branches into the Knik Arm and Turnagain Arm at its northern end, almost surrounding Anchorage. On its southern end, it merges with Shelikof Strait, Stevenson Entrance, Kennedy Entrance and Chugach Passage.

The James W. Dalton Highway, usually referred to as the Dalton Highway, is a 414-mile (666 km) road in Alaska. It begins at the Elliott Highway, north of Fairbanks, and ends at Deadhorse near the Arctic Ocean and the Prudhoe Bay Oil Fields. Once called the North Slope Haul Road, it was built as a supply road to support the Trans-Alaska Pipeline System in 1974. It is named after James Dalton, a lifelong Alaskan and an engineer who supervised construction of the Distant Early Warning Line in Alaska and, as an expert in Arctic engineering, served as a consultant in early oil exploration in northern Alaska. It is also the subject of the second episode of America's Toughest Jobs and the first episode of the BBC's World's Most Dangerous Roads.

Keith Harvey Miller was an American Republican politician from Alaska. Miller was the second secretary of state of Alaska under Walter Hickel. He became the third governor of Alaska after Hickel’s resignation to become U.S. Secretary of the Interior. Under his tenure, Alaska came into sudden wealth after an oil lease sale on the North Slope created a revenue of $900 million.

The Alaska Railroad is a Class II railroad that operates freight and passenger trains in the state of Alaska. The railroad's mainline is over 470 miles (760 km) long and runs between Seward on the southern coast and Fairbanks, near the center of the state and the Arctic Circle, passing through Anchorage and Denali National Park where 17% of visitors arrive by train. The railroad has about 656 miles (1,056 km) of track, including sidings, rail yards and branch lines, including the branch to Whittier, where the railroad interchanges freight railcars with the contiguous United States via rail barges that sail between the Port of Whittier and Harbor Island in Seattle.
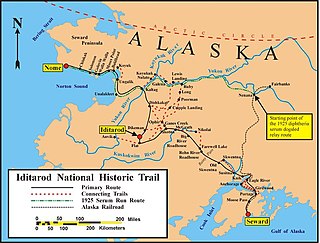
The Iditarod Trail, also known historically as the Seward-to-Nome Trail, is a thousand-plus mile (1,600 km) historic and contemporary trail system in the US state of Alaska. The trail began as a composite of trails established by Alaskan native peoples. Its route crossed several mountain ranges and valleys and passed through numerous historical settlements en route from Seward to Nome. The discovery of gold around Nome brought thousands of people over this route beginning in 1908. Roadhouses for people and dog barns sprang up every 20 or so miles. By 1918 World War I and the lack of 'gold fever' resulted in far less travel. The trail might have been forgotten except for the 1925 diphtheria outbreak in Nome. In one of the final great feats of dog sleds, twenty drivers and teams carried the life-saving serum 674 miles (1,085 km) in 127 hours. Today, the Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race serves to commemorate the part the trail and its dog sleds played in the development of Alaska, and the route and a series of connecting trails have been designated Iditarod National Historic Trail.

A domed city is a hypothetical structure that encloses a large urban area under a single roof. In most descriptions, the dome is airtight and pressurized, creating a habitat that can be controlled for air temperature, composition and quality, typically due to an external atmosphere that is inimical to habitation for one or more reasons. Domed cities have been a fixture of science fiction and futurology since the early 20th century, offer inspirations for potential utopias and may be situated on Earth, a moon or other planet.

The history of Alaska dates back to the Upper Paleolithic period, when foraging groups crossed the Bering land bridge into what is now western Alaska. At the time of European contact by the Russian explorers, the area was populated by Alaska Native groups. The name "Alaska" derives from the Aleut word Alaxsxaq, meaning "mainland".

After congress approved the completion of the Alaska Railroad from Seward to Fairbanks in 1914, it was decided that a new town should be built as a port and rail hub along the route. The decision was made to develop a site near Ship Creek on Cook Inlet. Survey parties visited the area in 1914 and researched possible routes for the rails and options for siting the new town. Anchorage was originally settled as a tent city near the mouth of Ship Creek in 1915, and a planned townsite was platted alongside the bluff to the south. Anchorage was mostly a company town for the Alaska Railroad for its first several decades of existence.

Robert Christian Hansen, known in the media as the Butcher Baker, was an American serial killer. Between 1971 and 1983, Hansen abducted, raped, and murdered at least seventeen women in and around Anchorage, Alaska; he hunted many of them down in the wilderness with a Ruger Mini-14 and a knife. He was arrested and convicted in 1983, and was sentenced to 461 years without the possibility of parole. He died in 2014 of natural causes due to lingering health conditions at age 75.
The Alaska gas pipeline is a joint project of TransCanada Corp. and ExxonMobil Corp. to develop a natural gas pipeline under the AGIA, a.k.a. the Alaska Gas Inducement Act, adopted by Alaska Legislature in 2007. The project originally proposed two options during its open season offering over a three-month period from April 30 to July 30, 2010. An 'open season' in layman's terms is when a company conducts a non-binding show of interest or poll in the marketplace, they ask potential customers "if we build it, will you come?".

The Municipality of Anchorage is the largest city in the U.S. state of Alaska by population. With a population of 291,247 at the 2020 census, it contains nearly 40% of the state's population. The Anchorage metropolitan area, which includes Anchorage and the neighboring Matanuska-Susitna Borough, had a population of 398,328 in 2020, accounting for more than half the state's population. At 1,706 sq mi (4,420 km2) of land area, the city is the fourth-largest by area in the United States and larger than the smallest state, Rhode Island, which has 1,212 sq mi (3,140 km2).

Knik Arm ferry or Cook Inlet ferry, was a proposed year-round passenger and auto ferry across Knik Arm between Anchorage and Point MacKenzie in Alaska. The project was to use the MV Susitna SWATH / barge convertible expedition craft, which was built for US$80,000,000, to connect Alaska's financial center with the fastest growing community in Alaska, just two miles across water. No ferry landings were ever built, and the ship was never put into commission. Eventually, the Borough offered to either transfer the ferry for free to government entities in the U.S. in January 2013 or to sell the ship to a commercial interest. Sealed bids were taken through March 29, 2013. but the ship was not actually sold until 2016, for substantially below the cost of building it, just US$1.75 million

The Prudhoe Bay oil spill was an oil spill that was discovered on March 2, 2006 at a pipeline owned by BP Exploration, Alaska (BPXA) in western Prudhoe Bay, Alaska. Initial estimates of the five-day leak said that up to 267,000 US gallons (6,400 bbl) were spilled over 1.9 acres (7,700 m2), making it the largest oil spill on Alaska's north slope to date. Alaska's unified command ratified the volume of crude oil spilled as 212,252 US gallons (5,053.6 bbl) in March 2008. The spill originated from a 0.25-inch (0.64 cm) hole in a 34-inch (86 cm) diameter pipeline. The pipeline was decommissioned and later replaced with a 20-inch (51 cm) diameter pipeline with its own pipeline inspection gauge (pig) launch and recovery sites for easier inspection.

In 2006, Sarah Palin was elected governor of Alaska. Running on a clean-government platform, Palin defeated incumbent Governor Frank Murkowski in the Republican gubernatorial primary election in August. She then went on to win the general election in November, defeating former Governor Tony Knowles 48.3% to 40.9%. Her running mate was State Senator Sean Parnell.

The State of Alaska is both a producer and consumer of natural gas. In 2006, Alaska consumed 180.4 Bcf of natural gas.

In a report compiled by the Alaskan Government, the real GDP of Alaska was $51.1 billion in 2011, $52.9 billion in 2012 and $51.5 billion in 2013. The drop-off that occurred between 2012 and 2013 has been attributed to the decline in the mining sector, specifically the oil and gas sectors, a consequence of declined production. The state's economy has been described by University of Alaska Anchorage economist Scott Goldsmith as a "three-legged stool" - with one leg being the petroleum and gas industry, the second leg being the federal government and the third leg being all other industries and services. Between 2004 and 2006, the federal government was responsible for 135,000 Alaska jobs, the petroleum sector provided 110,000 jobs and all other industries and services combined for 122,000 jobs.



















