U.S. Route 340 is a part of the U.S. Highway System that runs from Greenville, Virginia to Frederick, Maryland. In Virginia, it runs north–south, parallel and east of U.S. Route 11, from US 11 north of Greenville via Waynesboro, Grottoes, Elkton, Luray, Front Royal, and Berryville to the West Virginia state line. A short separate piece crosses northern Loudoun County on its way from West Virginia to Maryland.

The Dan River flows 214 miles (344 km) in the U.S. states of North Carolina and Virginia. It rises in Patrick County, Virginia, and crosses the state border into Stokes County, North Carolina. It then flows into Rockingham County. From there it goes back into Virginia. It reenters North Carolina near the border between Caswell County and Rockingham County. It flows into northern Caswell County and then back into southern Virginia and finally into Kerr Reservoir on the Roanoke River.
Catoctin Creek is a 14.1-mile-long (22.7 km) tributary of the Potomac River in Loudoun County, Virginia, with a watershed of 59,000 acres (240 km2). Agricultural lands make up 67 percent and forests 30 percent of Catoctin Creek's watershed. It is the main drainage system for the northern Loudoun Valley, including all of the Catoctin Valley.
Lunice Creek is a 7.3-mile-long (11.7 km) tributary of the South Branch Potomac River, belonging to the Potomac River and Chesapeake Bay watersheds. The creek is located in Grant County, West Virginia. Lunice Creek is created by its North and South Forks and empties into the South Branch at Petersburg.
Green Spring Run is an 8.9-mile-long (14.3 km) tributary stream of the North Branch Potomac River in Hampshire County in the U.S. state of West Virginia. Green Spring Run rises in Greenwood Hollow north of Springfield and meanders northeast through Green Spring Valley. The South Branch Valley Railroad and Green Spring Road run parallel to the stream. It runs through the community of Green Spring, from which the stream takes its name. From Green Spring, Green Spring Run flows east where it reaches its confluence with the North Branch Potomac shortly before the North Branch joins with the South Branch Potomac River to form the Potomac River.
Trout Run is an 18.5-mile-long (29.8 km) tributary of the Cacapon River, belonging to the Potomac River and Chesapeake Bay watersheds. The stream is located in Hardy County in West Virginia's Eastern Panhandle. Trout Run rises between Devils Hole Mountain and Great North Mountain near the Virginia state line in the George Washington National Forest. The stream empties into the Cacapon River at Wardensville.
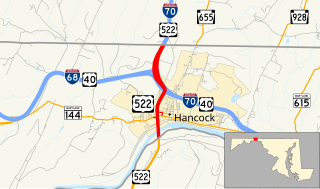
U.S. Route 522 is a part of the U.S. Highway System that runs from Powhatan, Virginia to Selinsgrove, Pennsylvania. In Maryland, it runs 2.35 miles (3.78 km) from the West Virginia state line at the Potomac River north to the Pennsylvania state line within Hancock in western Washington County. US 522 crosses Maryland at its narrowest north–south point, meeting Maryland Route 144, Interstate 70 (I-70), US 40, and I-68 before entering Pennsylvania concurrent with I-70. Warfordsburg Road from US 40 north to Pennsylvania was paved around 1920 and designated US 522 in the late 1920s. US 522 was extended south into West Virginia shortly after a new bridge was completed over the Potomac River in the late 1930s. It was moved onto I-70 north of Hancock when the Interstate highway was completed in the area in the mid 1960s.

The Buffalo River is a 31.5-mile-long (50.7 km) tributary of the Tye River in the U.S. state of Virginia. It is part of the James River watershed.
The Dry River is a 22.6-mile-long (36.4 km) tributary of the North River in the U.S. state of Virginia. It flows entirely within Rockingham County, rising within the George Washington National Forest east of the West Virginia border and flowing south to the North River at Bridgewater. Via the North River, it is part of the Shenandoah River system, flowing to the Potomac River.
The Little River is a 44.7-mile-long (71.9 km) river in Louisa and Hanover counties in the U.S. state of Virginia. It is a tributary of the North Anna River, and via the North Anna, Pamunkey, and York rivers is part of the Chesapeake Bay watershed.
Two streams named Little River flow to the North River, a tributary of the South Fork Shenandoah River in the U.S. state of Virginia. Both rivers flow within the George Washington National Forest.
The Middle River is a 70.6-mile-long (113.6 km) river in the U.S. state of Virginia. Flowing entirely within Augusta County, the Middle River joins the North River, which in turn meets the South River at Port Republic to form the South Fork Shenandoah River.
North Buffalo Creek is a 7.5-mile-long (12.1 km) tributary of Buffalo Creek in Rockbridge County in the U.S. state of Virginia. Via Buffalo Creek and the Maury River, it is part of the James River watershed.
The North River is a 7.6-mile-long (12.2 km) tidal river in the U.S. state of Virginia. It is an arm of Mobjack Bay, itself part of Chesapeake Bay. The North River forms the boundary between Mathews and Gloucester counties.
The North River is a 9.3-mile-long (15.0 km) tributary of the Slate River in Buckingham County in the U.S. state of Virginia. It is part of the James River watershed.
The Roach River is an 11.0-mile-long (17.7 km) tributary of the North Fork Rivanna River in the U.S. state of Virginia. It is part of the James River watershed.
The Southern Branch Elizabeth River is a 14.5-mile-long (23.3 km), primarily tidal river in the U.S. state of Virginia. It flows from south to north through the city of Chesapeake and forms the boundary between the cities of Portsmouth and Chesapeake for its northernmost 3 miles (5 km). It is a tributary of the Elizabeth River, connecting to the harbor of Hampton Roads to the north. It is part of the Intracoastal Waterway of the Atlantic coast of the United States, connecting by it to the North Landing River, which flows into North Carolina.

The Lost River is a 31.1-mile-long (50.1 km) river in the Appalachian Mountains of Hardy County in West Virginia's Eastern Panhandle region. The Lost River is geologically the same river as the Cacapon River: It flows into an underground channel northeast of McCauley along West Virginia Route 259 at "the Sinks" and reappears near Wardensville as the Cacapon. The source of the Lost River lies south of Mathias near the West Virginia/Virginia border. Along with the Cacapon and North rivers, the Lost River serves as one of the three main segments of the Cacapon River and its watershed.

The Laurel Fork is a 15.7-mile-long (25.3 km) stream in Virginia and West Virginia, United States. The stream flows north from Highland County, Virginia, where its source and the majority of its length is located, to its mouth in Pendleton County, West Virginia. Laurel Fork is a tributary to the North Fork South Branch Potomac River, making it a part of the Potomac River watershed. The area surrounding Laurel Fork is home to several plant and animal species found nowhere else in Virginia, and is a prime example of a northern boreal forest in the state.









