The Sangre de Cristo Mountains are the southernmost subrange of the Rocky Mountains. They are located in southern Colorado and northern New Mexico in the United States. The mountains run from Poncha Pass in South-Central Colorado, trending southeast and south, ending at Glorieta Pass, southeast of Santa Fe, New Mexico. The mountains contain a number of fourteen thousand foot peaks in the Colorado portion, as well as all the peaks in New Mexico which are over thirteen thousand feet.

The Sierra Madre Oriental is a mountain range in northeastern Mexico. The Sierra Madre Oriental is part of the American Cordillera, a chain of mountain ranges (cordillera) that consists of an almost continuous sequence of mountain ranges that form the western "backbone" of North America, Central America, South America and Antarctica.

The Cerro de la Silla is a mountain and natural monument located within the metropolitan area of the city of Monterrey, Nuevo León, in northeastern Mexico. Named for its distinctive saddle-shaped profile when viewed from the west, it is a well-known symbol of the city of Monterrey, despite being located in the adjacent municipality of Guadalupe.

Pico da Neblina is the highest peak in Brazil, 2,995.3 metres (9,827 ft) above sea level, in the Serra da Neblina, part of the Serra do Imeri, a section of the Guiana Highlands on the Brazil–Venezuela border. As determined by a border survey expedition in 1962, its summit lies just within Brazilian territory, at a horizontal distance of only 687 m (2,254 ft) from the Venezuelan border at Pico 31 de Março.

The Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta is an isolated mountain range separated from the Andes chain that runs through Colombia. Reaching an altitude of 5,700 m (18,700 ft) just 42 km (26 mi) from the Caribbean coast, the Sierra Nevada is one of the world's highest coastal ranges, being 250m shorter than the Saint Elias Mountains in Canada. The Sierra Nevada encompasses about 17,000 km2 (6,600 sq mi) and serves as the source of 36 rivers. The range is in the Departments of Magdalena, Cesar and La Guajira.

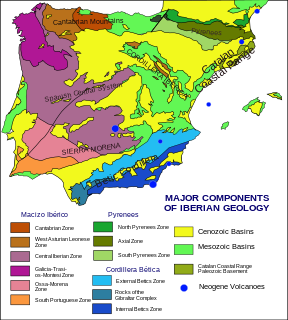
The Cantabrian Mountains or Cantabrian Range are one of the main systems of mountain ranges in Spain. They stretch for over 300 km (180 miles) across northern Spain, from the western limit of the Pyrenees to the Galician Massif in Galicia, along the coast of the Cantabrian Sea. Their easternmost end meets the Sistema Ibérico.

Sierra Negra is an extinct volcano located in the Mexican state of Puebla, close to the border with Veracruz. At officially 4,580 metres (15,030 ft) above sea level, it is the fifth-highest peak in Mexico. However, because it is overshadowed by nearby Pico de Orizaba, it is not too well known and often left out of lists of Mexico's mountains.

The Central System, Spanish and Portuguese: Sistema Central, is one of the main systems of mountain ranges in the Iberian Peninsula. 2,592 m high Pico Almanzor is its highest summit.

Aracena is a town and municipality located in the province of Huelva, south-western Spain. As of 2012, the city has a population of 7,814 inhabitants. The town derived its name from the Sierra de Aracena, which is part of the Sierra Morena system.

The Sierra de Guadarrama is a mountain range forming the main eastern section of the Sistema Central, the system of mountain ranges along the centre of the Iberian Peninsula. It is located between the systems Sierra de Gredos in the province of Ávila, and Sierra de Ayllón in the province of Guadalajara.

The Autovía A-47 is a proposed highway in Spain, it is planned as an upgrade of the N-433.

The Sierra de Francia is a mountain range located in Sierra de Francia Comarca at the southern end of Salamanca Province, Castile and León, Spain. It is located about 70 km from Salamanca city. The region is sparsely inhabited and its few towns have great cultural value.
The Sierra Sur de Jaén is a mountain range that is part of the central belt of the Baetic System, Andalusia, Spain. Its name derives from its location in the southwestern part of Jaén Province. The highest summit in the range is 1,872 m high Pico Pandera; 1,722 m high Cerro de la Cruz is another notable peak.

Sierra Norte de Sevilla or Sierra Norte is one of the western mountain ranges of the Sierra Morena, Andalusia, Spain. Its name derives from its location at the northern part of Sevilla Province. The highest point of the range is the 960 m high Cerro de La Capitana.

The Sierra de Huétor is a mountain range of the Baetic System in Granada Province, Andalusia, Spain.

Sierra Blanca is a mountain range of the Penibaetic System in Málaga Province, Andalusia, Spain. Its highest point is the 1,275 m high Pico del Lastonar.

Sierra de Alhama is a mountain range of the Penibaetic System in Málaga and Granada provinces, Andalusia, Spain. Its highest point is the 1,500 m high Pico de la Torca. Other notable summits are Hoyo del Toro, 1,353 m, Cerro de Marchamonas, 1,272 m and Morrón de la Cuna 1,222 m.

Pico Mágina is a 2,165-metre-high (7,103 ft) mountain in Spain.