
The Chiasmodontidae, snaketooth fishes or swallowers, are a family of deep-sea predatory ray-finned fishes, part of the order Scombriformes, that are found in all oceans.

The smalleye squaretail, Tetragonurus cuvieri, is a squaretail of the genus Tetragonurus found in all tropical and temperate oceans of the world, at depths up to 800 m. Its length is 20 to 70 cm.

Tetrapturus is a genus of marlins commonly called spearfish, found in tropical and subtropical oceans throughout the world. Some are popular sport fish in big-game fishing.

Cubiceps is a genus of driftfishes found circumglobally.

The spiny turbots are a family, Psettodidae, of relatively large, primitive flatfish found in the tropical waters of the east Atlantic and Indo-Pacific. The family contains just three species, all in the same genus, Psettodes. The common name comes from the presence of spines in the dorsal and anal fins, which may indicate an evolutionary relationship with the Perciformes. They are less asymmetrical than other flatfish, although the region around the eyes is twisted. They reach lengths of 55–80 cm (22–31 in).
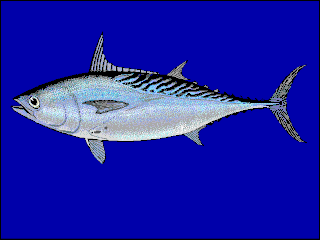
Euthynnus is a genus of ray-finned bony fish in the family Scombridae, or mackerel family, and in the tribe Thunnini, more commonly known as the tunas.

Sarda is a genus of medium-sized, predatory ray-finned fish in the family Scombridae, and belonging to the tribe Sardini, more commonly called the bonito tribe. There are four species which comprise the genus Sarda. One of those species, the Pacific bonito, is further divided into two subspecies.

Rastrelliger is a mackerel genus in the family Scombridae. The three species of Rastrelliger together with the four species of Scomber comprise the tribe Scombrini, known as the "true mackerels".
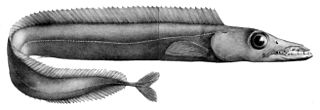
Aphanopus, the black scabbardfishes, is a genus of Cutlassfish which contains the following species:

Lepidorhombus is a genus of turbots native to the northeastern Atlantic Ocean.

Microchirus is a genus of soles native to the Eastern Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea.

Monochirus is a genus of small soles. It contains two species; one from the northeast Atlantic and Mediterranean, and the second from the South China Sea.

Pardachirus is a genus of soles mainly native to coastal water in the Indo-Pacific. A single species, P. poropterus is restricted to estuaries and lower sections of freshwater streams. At least some species in the genus are toxic.

Pegusa is a genus of soles native to the Eastern Atlantic Ocean, Mediterranean Sea, and Black Sea.

Pteraclis is a genus of ray-finned fish in the family Bramidae, the pomfrets. They are known commonly as fanfishes. The three species are distributed throughout the oceans of the world.
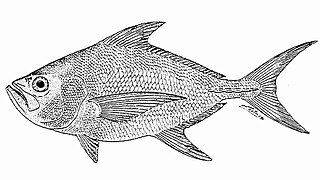
Taractes is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes from the family Bramidae, the pomfrets. Taractes can be distinguished from other bramid genera but having a flat, or slightly curved profile, between the eyes and by having scales on both the dorsal and anal fins.

Taractichthys is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes from the family Bramidae, the pomfrets.
Neocaristius heemstrai is a species of fish in the family Caristiidae, the manefishes. It is native to the oceans of the southern hemisphere where it is known to occur at depths of from 420 to 1,360 metres. This species grows to a length of 11.8 centimetres (4.6 in) SL.

Dysalotus is a genus of ray-finned fish in the family Chiasmodontidae found in the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Ocean.

Stromateus is a genus of ray-finned fish from the butterfish family Stromateidae, of which it is the type genus.



















