
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital digestive organ. In the digestive system the stomach is involved in the second phase of digestion, following chewing. It performs a chemical breakdown by means of enzymes and hydrochloric acid.

Galangal is a common name for several tropical rhizomatous spices.
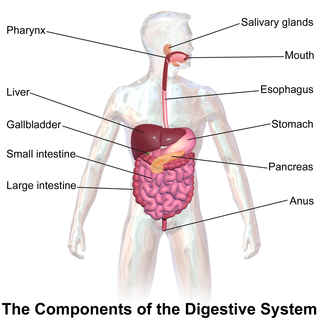
Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food molecules into small water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the watery blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed through the small intestine into the blood stream. Digestion is a form of catabolism that is often divided into two processes based on how food is broken down: mechanical and chemical digestion. The term mechanical digestion refers to the physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces which can subsequently be accessed by digestive enzymes. In chemical digestion, enzymes break down food into the small molecules the body can use.

The esophagus, or oesophagus, informally known as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to the stomach. The esophagus is a fibromuscular tube, about 25 cm (10 in) long in adults, which travels behind the trachea and heart, passes through the diaphragm and empties into the uppermost region of the stomach. During swallowing, the epiglottis tilts backwards to prevent food from going down the larynx and lungs. The word oesophagus is from Ancient Greek οἰσοφάγος (oisophágos), from οἴσω (oísō), future form of φέρω + ἔφαγον.

Tripe is a type of edible lining from the stomachs of various farm animals. Most tripe is from cattle and sheep.

Sadaharu Oh, also known as Wang Chen-chih, is a retired Chinese baseball player and manager in Japan. Oh holds the world lifetime home run record, having hit 868 home runs during his professional career. He established many NPB batting records, including runs batted in (RBIs) (2,170), slugging percentage (.634), bases on balls (2,390), and on-base plus slugging percentage (OPS) (1.080). In 1977, Oh became the first recipient of the People's Honour Award. He was inducted into the Japanese Baseball Hall of Fame in 1994.

Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a cancer that develops from the lining of the stomach. Most cases of stomach cancers are gastric carcinomas, which can be divided into a number of subtypes including gastric adenocarcinomas. Lymphomas and mesenchymal tumors may also develop in the stomach. Early symptoms may include heartburn, upper abdominal pain, nausea and loss of appetite. Later signs and symptoms may include weight loss, yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes, vomiting, difficulty swallowing and blood in the stool among others. The cancer may spread from the stomach to other parts of the body, particularly the liver, lungs, bones, lining of the abdomen and lymph nodes.

Offal, also called variety meats, pluck or organ meats, is the viscera and entrails of a butchered animal. As an English mass noun, the term "offal" has no plural form. The word does not refer to a particular list of edible organs, which varies by culture and region, but includes most internal organs and excludes muscle and bone. Offal may also refer to the by-products of milled grains, such as corn or wheat.

The gizzard, also referred to as the ventriculus, gastric mill, and gigerium, is an organ found in the digestive tract of some animals, including archosaurs, earthworms, some gastropods, some fish, and some crustaceans. This specialized stomach constructed of thick muscular walls is used for grinding up food, often aided by particles of stone or grit. In certain insects and molluscs, the gizzard features chitinous plates or teeth.
San Jiao is a concept in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) and acupuncture. It is the sixth organ of Fu, which has no equivalent in western medicine. In TCM, there are five solid organs and each solid organ has its counterpart in a hollow organ. For instance, the heart is considered a solid organ, and the small intestine its hollow counterpart, or Fu organ. San Jiao is believed to be a body cavity of some kind which has the ability to influence other organs, and overall health, mainly through the free movement of Qi, the fundamental energy or life force.

Gastritis is inflammation of the lining of the stomach. It may occur as a short episode or may be of a long duration. There may be no symptoms but, when symptoms are present, the most common is upper abdominal pain. Other possible symptoms include nausea and vomiting, bloating, loss of appetite and heartburn. Complications may include stomach bleeding, stomach ulcers, and stomach tumors. When due to autoimmune problems, low red blood cells due to not enough vitamin B12 may occur, a condition known as pernicious anemia.
Digestive enzymes are a group of enzymes that break down polymeric macromolecules into their smaller building blocks, in order to facilitate their absorption by the body. Digestive enzymes are found in the digestive tracts of animals and in the tracts of carnivorous plants, where they aid in the digestion of food, as well as inside cells, especially in their lysosomes, where they function to maintain cellular survival. Digestive enzymes of diverse specificities are found in the saliva secreted by the salivary glands, in the secretions of cells lining the stomach, in the pancreatic juice secreted by pancreatic exocrine cells, and in the secretions of cells lining the small and large intestines.

Atrophic gastritis is a process of chronic inflammation of the gastric mucosa of the stomach, leading to a loss of gastric glandular cells and their eventual replacement by intestinal and fibrous tissues. As a result, the stomach's secretion of essential substances such as hydrochloric acid, pepsin, and intrinsic factor is impaired, leading to digestive problems. The most common are vitamin B12 deficiency which results in a megaloblastic anemia and malabsorption of iron, leading to iron deficiency anaemia. It can be caused by persistent infection with Helicobacter pylori, or can be autoimmune in origin. Those with the autoimmune version of atrophic gastritis are statistically more likely to develop gastric carcinoma, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, and achlorhydria.

The Black Tortoise or Black Turtle is one of the Four Symbols of the Chinese constellations. Despite its English name, it is usually depicted as a turtle entwined together with a snake. Furthermore, in East Asian mythology it is not called after either animal, but is instead known as the "Black Warrior" under various local pronunciations. It is known as Xuanwu in Chinese, Genbu in Japanese, Huyền Vũ in Vietnamese and Hyeonmu or Hyunmoo in Korean. It represents the north and the winter season, thus it is sometimes called Black Tortoise of the North.
Traditional Mongolian medicine developed over many years among the Mongolian people. Mongolian medical practice spread across their empire and became an ingrained part of many other people's medical systems.

Pig's organ soup or chheng-thng (清湯) is a Malaysian and Singaporean soup originating in Teochew/Chaozhou, China. The dish is a clear soup, served with other optional side dishes as well as rice. The broth is boiled from a mix of pig offal including liver, heart, intestines, stomach, tongue, blood cubes, as well as pork meat slices, strips of salted vegetables, celtuce and a sprinkle of chopped onion leaves and pepper. Side dishes include braised tofu puffs, and eggs and salted vegetables sometime are served. The meal is usually served with a special chili sauce or soy sauce with chopped hot chili.

Yanornis is an extinct genus of fish-eating Early Cretaceous birds. Two species have been described, both from Liaoning province, China: Yanornis martini, based on several fossils found in the 120-million-year-old Jiufotang Formation at Chaoyang, and Yanornis guozhangi, from the 124-million-year-old Yixian Formation.

Radical 102 is number 102 out of 214 Kangxi radicals. It is one of 23 radicals composed of five strokes. With 192 signs derived from this character in the Kangxi dictionary, it has a frequency somewhat below average.
Stomach, a concept from traditional Chinese medicine as distinct from the Western medical concept of stomach, is more a way of describing a set of interrelated parts than an anatomical organ.

A dudou is a traditional Chinese form of the bodice, originally worn as an undershirt with medicinal properties. With the opening of China, it is sometimes encountered in Western and modern Chinese fashion as a sleeveless shirt and backless halter-top blouse.















