Related Research Articles

Divine Liturgy or Holy Liturgy is the usual name used in most Eastern Christian rites for the Eucharistic service.

The Didache, also known as The Lord's Teaching Through the Twelve Apostles to the Nations, is a brief anonymous early Christian treatise written in Koine Greek, dated by modern scholars to the first or second century AD.
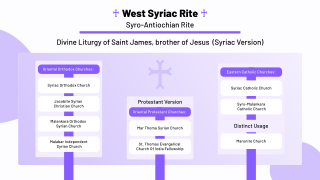
The Liturgy of Saint James is a form of Christian liturgy used by some Eastern Christians of the Byzantine rite and West Syriac Rite. It is influenced by the traditions of the rite of the Church of Jerusalem, as the Mystagogic Catecheses of Cyril of Jerusalem imply. It became widespread in Church of Antioch from the fourth or fifth century onwards, replacing the older Basilean Liturgy of Antioch. It is still the principal liturgy of the Syriac Orthodox Church, the Malankara Orthodox Syrian Church, the Maronite Church, the Syriac Catholic Church, Syro-Malankara Catholic Church and other churches employing the West Syriac Rite. It is also occasionally used in the Eastern Orthodox Church and Melkite Catholic Church. The Malankara Mar Thoma Syrian Church uses a reformed variant of this liturgy, omitting intercession of saints and prayer for the dead.
The Sacramentary of Serapion of Thmuis is a work of Saint Serapion, bishop of Thmuis in the Nile Delta and a prominent supporter of Athanasius in the struggle against Arianism. He is sometimes called Serapion the Scholastic for his learning. He is best known in connection with this prayer-book or sacramentary (euchologion) intended for the use of bishops.

The Words of Institution are words echoing those of Jesus himself at his Last Supper that, when consecrating bread and wine, Christian Eucharistic liturgies include in a narrative of that event. Eucharistic scholars sometimes refer to them simply as the verba.

The Liturgy of the Presanctified Gifts is a Byzantine Rite liturgical service which is performed on the weekdays of Great Lent wherein communion is received from Gifts that are sanctified (consecrated) in advance, hence its name; this Divine Liturgy has no anaphora.

The Anaphora, Eucharistic Prayer, or Great Thanksgiving is a portion of the Christian liturgy of the Eucharist in which, through a prayer of thanksgiving, the elements of bread and wine are consecrated. The prevalent historical Roman Rite form is called the "Canon of the Mass."
The Apostolic Constitutions or Constitutions of the Holy Apostles is a Christian collection divided into eight books which is classified among the Church Orders, a genre of early Christian literature, that offered authoritative pseudo-apostolic prescriptions on moral conduct, liturgy and Church organization. The work can be dated from 375 to 380 AD. The provenance is usually regarded as Syria, probably Antioch. The author is unknown, although since James Ussher it has often considered to be the author of the letters of Pseudo-Ignatius, perhaps the 4th-century Eunomian bishop Julian of Cilicia.

The Canon of the Mass, also known as the Canon of the Roman Mass and in the Mass of Paul VI as the Roman Canon or Eucharistic Prayer I, is the oldest anaphora used in the Roman Rite of Mass. The name Canon Missæ was used in the Tridentine Missal from the first typical edition of Pope Pius V in 1570 to that of Pope John XXIII in 1962 to describe the part of the Mass of the Roman Rite that began after the Sanctus with the words Te igitur. All editions preceding that of 1962 place the indication "Canon Missae" at the head of each page from that point until the end of the Mass; that of 1962 does so only until the page preceding the Pater Noster and places the heading "Ordo Missae" on the following pages.
The Roman Canon is the oldest eucharistic prayer used in the Mass of the Roman Rite, and dates its arrangement to at least the 7th century; its core, however, is much older. Through the centuries, the Roman Canon has undergone minor alterations and modifications, but retains the same essential form it took in the seventh century under Pope Gregory I. Before 1970, it was the only eucharistic prayer used in the Roman Missal, but since then three other eucharistic prayers were newly composed for the Mass of Paul VI.

The Alexandrian rites are a collection of ritual families and uses of Christian liturgy employed by three Oriental Orthodox churches, and by three Eastern Catholic Churches.
The Liturgy of Saint Basil or, more formally, the Divine Liturgy of Saint Basil the Great, is a term for several Eastern Christian celebrations of the Divine Liturgy (Eucharist), or at least several anaphoras, which are named after Basil of Caesarea. Two of these liturgies are in common use today: the one used in the Byzantine Rite ten times a year, and the one ordinarily used by the Coptic Church.
The Anaphora of the Apostolic Tradition, also known as the Anaphora of Hippolytus, is an ancient Christian Anaphora which is found in chapter four of the Apostolic Tradition. It should not be confused with the Syriac Orthodox Anaphora of the Twelve Apostles, which is similar, and may be one of several liturgies derived from this Anaphora, yet is considerably longer and more ornate.

Some Christian denominations place the origin of the Eucharist in the Last Supper of Jesus with his disciples, at which he is believed to have taken bread and given it to his disciples, telling them to eat of it, because it was his body, and to have taken a cup and given it to his disciples, telling them to drink of it because it was the cup of the covenant in his blood.

The Liturgy of Addai and Mari is the Eucharistic liturgy belonging to the East Syriac Rite and was historically used in the Church of the East of the Sasanian (Persian) Empire. This liturgy is traditionally attributed to Saint Addai and Saint Mari. It is currently in regular use in the Assyrian Church of the East, the Ancient Church of the East, the Syro-Malabar Catholic Church of India, and the Chaldean Catholic Church. The latter two are Eastern Catholic churches in full communion with the Holy See of Rome.
The Barcelona Papyrus is a 4th-century papyrus codex, coming from Egypt and cataloged as P.Monts.Roca inv.128-178. It is the oldest liturgical manuscript containing a complete anaphora.
The Deir Balyzeh Papyrus is a 6th-century papyrus, coming from Egypt. It contains early fragmentary Christian texts: three prayers, a short creed and a portion of Anaphora.

The Liturgy of Saint Cyril is one of the three Anaphoras used at present by the Coptic Catholic Church and the Coptic Orthodox Church and it retains the liturgical peculiarities which have originated in the early Christian Egypt, thus forming the core of the historical Alexandrian Rite. When reference is made to its Greek Byzantine Rite version, this text is usually known as Liturgy of Saint Mark.

The Liturgy of Saint Gregory the Theologian is one of the three Anaphoras retained by the Coptic Church. The text is named after Saint Gregory of Nazianzus, one of the Cappadocian Fathers.

The Holy Qurobo or Holy Qurbono refers to the Eucharist as celebrated in Syro-Antiochene Rite and the liturgical books containing rubrics for its celebration. West Syriac Rite includes various descendants of the Oriental Orthodox and Eastern Catholic churches. It consists of two distinct liturgical traditions: the Maronite Rite, and the Jacobite Rite. The major Anaphora of both the traditions is the Divine Liturgy of Saint James in Syriac language. The Churches are primarily based in the Middle East, Africa, and India.
References
- ↑ Michel Andrieu and Paul Collomp Fragments sur papyrus de l'anaphore de Saint Marc, in Revue des sciences religieuses, pag 500-501, 1928
- ↑ Walter D. Ray The Strasbourg Papyrus in ed. Paul F. Bradshaw Essays on Early Eastern Eucharistic Prayers, ISBN 0-8146-6153-X (1997)
- ↑ Enrico Mazza The Origins of the Eucharistic Prayer, ISBN 0-8146-6119-X (1995)
- ↑ R.C.D Jasper, G.J. Cuming Prayers of the Eucharist: Early and reformed, ISBN 0-8146-6085-1 (1987), pag 52
- ↑ Zheltov, Michael (2008). "The Anaphora and the thanksgiving Prayer from the Barcelona Papyrus: An Underestimated Testimony to the Anaphoral History in the Fourth Century" (PDF). Vigiliae Christianae. 62 (5): 467–504. doi:10.1163/157007208x306551. ISSN 0042-6032.[ permanent dead link ]