
A tumor suppressor gene (TSG), or anti-oncogene, is a gene that regulates a cell during cell division and replication. If the cell grows uncontrollably, it will result in cancer. When a tumor suppressor gene is mutated, it results in a loss or reduction in its function. In combination with other genetic mutations, this could allow the cell to grow abnormally. The loss of function for these genes may be even more significant in the development of human cancers, compared to the activation of oncogenes.

Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BRCA1 gene. Orthologs are common in other vertebrate species, whereas invertebrate genomes may encode a more distantly related gene. BRCA1 is a human tumor suppressor gene and is responsible for repairing DNA.
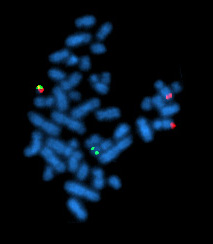
The Philadelphia chromosome or Philadelphia translocation (Ph) is a specific genetic abnormality in chromosome 22 of leukemia cancer cells. This chromosome is defective and unusually short because of reciprocal translocation, t(9;22)(q34;q11), of genetic material between chromosome 9 and chromosome 22, and contains a fusion gene called BCR-ABL1. This gene is the ABL1 gene of chromosome 9 juxtaposed onto the breakpoint cluster region BCR gene of chromosome 22, coding for a hybrid protein: a tyrosine kinase signaling protein that is "always on", causing the cell to divide uncontrollably by interrupting the stability of the genome and impairing various signaling pathways governing the cell cycle.

A fusion gene is a hybrid gene formed from two previously independent genes. It can occur as a result of translocation, interstitial deletion, or chromosomal inversion. Fusion genes have been found to be prevalent in all main types of human neoplasia. The identification of these fusion genes play a prominent role in being a diagnostic and prognostic marker.
Double minutes are small fragments of extrachromosomal DNA, which have been observed in a large number of human tumors including breast, lung, ovary, colon, and most notably, neuroblastoma. They are a manifestation of gene amplification as a result of chromothripsis, during the development of tumors, which give the cells selective advantages for growth and survival. This selective advantage is as a result of double minutes frequently harboring amplified oncogenes and genes involved in drug resistance. DMs, like actual chromosomes, are composed of chromatin and replicate in the nucleus of the cell during cell division. Unlike typical chromosomes, they are composed of circular fragments of DNA, up to only a few million base pairs in size, and contain no centromere or telomere. Further to this, they often lack key regulatory elements, allowing genes to be constitutively expressed. The term ecDNA may be used to refer to DMs in a more general manner.

Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ERBB2 gene. ERBB is abbreviated from erythroblastic oncogene B, a gene originally isolated from the avian genome. The human protein is also frequently referred to as HER2 or CD340.

Bert Vogelstein is director of the Ludwig Center, Clayton Professor of Oncology and Pathology and a Howard Hughes Medical Institute investigator at The Johns Hopkins Medical School and Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center. A pioneer in the field of cancer genomics, his studies on colorectal cancers revealed that they result from the sequential accumulation of mutations in oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. These studies now form the paradigm for modern cancer research and provided the basis for the notion of the somatic evolution of cancer.

Oncogenomics is a sub-field of genomics that characterizes cancer-associated genes. It focuses on genomic, epigenomic and transcript alterations in cancer.
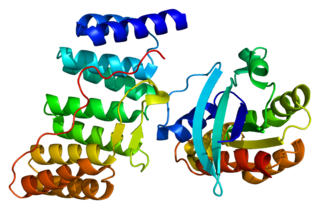
Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 3 (Rac3) is a G protein that in humans is encoded by the RAC3 gene. It is an important component of intracellular signalling pathways. Rac3 is a member of the Rac subfamily of the Rho family of small G proteins. Members of this superfamily appear to regulate a diverse array of cellular events, including the control of cell growth, cytoskeletal reorganization, and the activation of protein kinases.

Cell adhesion molecule 1 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the CADM1 gene.

Suppressor of tumorigenicity 14 protein, also known as matriptase, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ST14 gene. ST14 orthologs have been identified in most mammals for which complete genome data are available.

DNA mismatch repair protein, MutS Homolog 3 (MSH3) is a human homologue of the bacterial mismatch repair protein MutS that participates in the mismatch repair (MMR) system. MSH3 typically forms the heterodimer MutSβ with MSH2 in order to correct long insertion/deletion loops and base-base mispairs in microsatellites during DNA synthesis. Deficient capacity for MMR is found in approximately 15% of colorectal cancers, and somatic mutations in the MSH3 gene can be found in nearly 50% of MMR-deficient colorectal cancers.

H19 is a gene for a long noncoding RNA, found in humans and elsewhere. H19 has a role in the negative regulation of body weight and cell proliferation. This gene also has a role in the formation of some cancers and in the regulation of gene expression. .

Suppressor of tumorigenicity protein 7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ST7 gene. ST7 orthologs have been identified in all mammals for which complete genome data are available.

Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 6 (USB6), also termed TRE17 and Tre-2, is a deubiquitinating enzyme that in humans is encoded by the homanid USP6 gene located at band 13.2 on the short arm of chromosome 17. Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) are enzymes that act within cells to remove ubiquitins from various functionally important proteins. Ubiquitin enzymes add ubiquitin to these proteins and thereby regulate their cellular location, alter their activity, and/or promote their degradation. By deubiquitinating these proteins, DUBs counter the effects of the ubiquinating enzymes and contribute to regulating the actions of the targeted proteins. In normal adult tissues, USP6 is highly expressed in testicle tissue, modestly expressed in ovarian tissue, and absent or minimally expressed in other tissues. It is also highly expressed in fetal brain tissue. The specific functions of USP6 are poorly defined primarily because its presence is restricted to primates: there are no available animal models to determine the effects of its deletion, although some studies suggest that UPSP6 contributes to normal brain development. In all events, USP6 has gained wide interest because of its abnormally increased expression by the neoplastic cells in various tumors derived from mesenchymal tissue.

Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase ROS is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ROS1 gene.
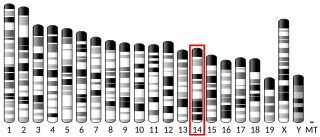
PIN2/TERF1-interacting telomerase inhibitor 1, also known as PINX1, is a human gene. PINX1 is also known as PIN2 interacting protein 1. PINX1 is a telomerase inhibitor and a possible tumor suppressor.

Ribonuclease T2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RNASET2 gene. It is a type of endoribonuclease.

Tumor suppressor candidate 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TUSC2 gene.
Synthetic lethality is defined as a type of genetic interaction where the combination of two genetic events results in cell death or death of an organism. Although the foregoing explanation is wider than this, it is common when referring to synthetic lethality to mean the situation arising by virtue of a combination of deficiencies of two or more genes leading to cell death, whereas a deficiency of only one of these genes does not. In a synthetic lethal genetic screen, it is necessary to begin with a mutation that does not result in cell death, although the effect of that mutation could result in a differing phenotype, and then systematically test other mutations at additional loci to determine which, in combination with the first mutation, causes cell death arising by way of deficiency or abolition of expression.














