
Sydnone imine is a mesoionic heterocyclic aromatic chemical compound. Sydnone imine is the imine of sydnone where the keto functional group of sydnone (=O) has been replaced with an imine (=NH) group.

Sydnone imine is a mesoionic heterocyclic aromatic chemical compound. Sydnone imine is the imine of sydnone where the keto functional group of sydnone (=O) has been replaced with an imine (=NH) group.
A variety of pharmaceutical drugs include sydnone imines in their chemical structure including feprosidnine, linsidomine, mesocarb, and molsidomine, among others.
In sydnone imines, both the negative and the positive charges are delocalized within the ring and the imine group.


In organic chemistry, a ketene is an organic compound of the form RR'C=C=O, where R and R' are two arbitrary monovalent chemical groups. The name may also refer to the specific compound ethenone H2C=C=O, the simplest ketene.

In organic chemistry, an imine is a functional group or organic compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond. The nitrogen atom can be attached to a hydrogen or an organic group (R). The carbon atom has two additional single bonds. Imines are common in synthetic and naturally occurring compounds and they participate in many reactions.

In organic chemistry, a Schiff base is a compound with the general structure R1R2C=NR3. They can be considered a sub-class of imines, being either secondary ketimines or secondary aldimines depending on their structure. Anil refers to a common subset of Schiff bases: imines derived from anilines. The term can be synonymous with azomethine which refers specifically to secondary aldimines.

In organic chemistry, an allyl group is a substituent with the structural formula −CH2−HC=CH2. It consists of a methylene bridge attached to a vinyl group. The name is derived from the scientific name for garlic, Allium sativum. In 1844, Theodor Wertheim isolated an allyl derivative from garlic oil and named it "Schwefelallyl". The term allyl applies to many compounds related to H2C=CH−CH2, some of which are of practical or of everyday importance, for example, allyl chloride.

Tautomers are structural isomers of chemical compounds that readily interconvert. The chemical reaction interconverting the two is called tautomerization. This conversion commonly results from the relocation of a hydrogen atom within the compound. The phenomenon of tautomerization is called tautomerism, also called desmotropism. Tautomerism is for example relevant to the behavior of amino acids and nucleic acids, two of the fundamental building blocks of life.
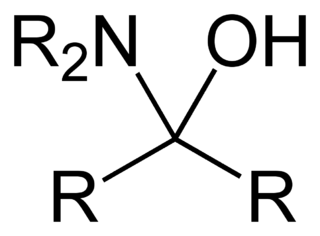
In organic chemistry, a hemiaminal is a functional group or type of chemical compound that has a hydroxyl group and an amine attached to the same carbon atom: −C(OH)(NR2)−. R can be hydrogen or an alkyl group. Hemiaminals are intermediates in imine formation from an amine and a carbonyl by alkylimino-de-oxo-bisubstitution. Hemiaminals can be viewed as a blend of aminals and geminal diol. They are a special case of amino alcohols.

Organic reductions or organic oxidations or organic redox reactions are redox reactions that take place with organic compounds. In organic chemistry oxidations and reductions are different from ordinary redox reactions, because many reactions carry the name but do not actually involve electron transfer. Instead the relevant criterion for organic oxidation is gain of oxygen and/or loss of hydrogen. Simple functional groups can be arranged in order of increasing oxidation state. The oxidation numbers are only an approximation:
Reductive amination is a form of amination that involves the conversion of a carbonyl group to an amine via an intermediate imine. The carbonyl group is most commonly a ketone or an aldehyde. It is a common method to make amines and is widely used in green chemistry since it can be done catalytically in one-pot under mild conditions. In biochemistry, dehydrogenase enzymes use reductive amination to produce the amino acid, glutamate. Additionally, there is ongoing research on alternative synthesis mechanisms with various metal catalysts which allow the reaction to be less energy taxing, and require milder reaction conditions. Investigation into biocatalysts, such as imine reductases, have allowed for higher selectivity in the reduction of chiral amines which is an important factor in pharmaceutical synthesis.

The Povarov reaction is an organic reaction described as a formal cycloaddition between an aromatic imine and an alkene. The imine in this organic reaction is a condensation reaction product from an aniline type compound and a benzaldehyde type compound. The alkene must be electron rich which means that functional groups attached to the alkene must be able to donate electrons. Such alkenes are enol ethers and enamines. The reaction product in the original Povarov reaction is a quinoline. Because the reactions can be carried out with the three components premixed in one reactor it is an example of a multi-component reaction.
Ketenimines are a group of organic compounds sharing a common functional group with the general structure R1R2C=C=NR3. A ketenimine is a cumulated alkene and imine and is related to an allene and a ketene.
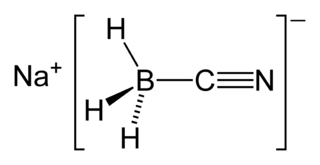
Sodium cyanoborohydride is a chemical compound with the formula Na[BH3(CN)]. It is a colourless salt used in organic synthesis for chemical reduction including that of imines and carbonyls. Sodium cyanoborohydride is a milder reductant than other conventional reducing agents.
In chemistry, mesoionic compounds are one in which a heterocyclic structure is dipolar and where both the negative and the positive charges are delocalized. A completely uncharged structure cannot be written and mesoionic compounds cannot be represented satisfactorily by any one mesomeric structure. Mesoionic compounds are a subclass of betaines. Examples are sydnones and sydnone imines, münchnones, and mesoionic carbenes.
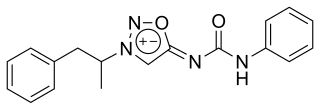
Mesocarb, sold under the brand name Sidnocarb or Sydnocarb and known by the developmental code name MLR-1017, is a psychostimulant medication which has been used in the treatment of psychiatric disorders and for a number of other indications in the Soviet Union and Russia. It is currently under development for the treatment of Parkinson's disease and sleep disorders. It is taken by mouth.
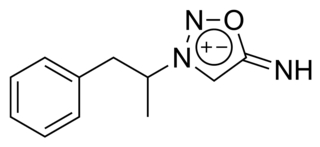
Feprosidnine (Sydnophen) is a stimulant drug which was developed in the USSR in the 1970s. It is structurally related to another Russian drug mesocarb but unlike mesocarb, was withdrawn earlier from production. In comparison with mesocarb it has own antidepressant activity, which makes it useful in treating depressions. Indications of feprosidnine included apathic, asthenic depressions, fatigue, apathic syndrome, narcolepsy and other similar conditions. Therapeutic range of doses: 10-50mg a day. Sydnophen has multiple mechanisms of action, the relative importance of which has not been clearly established. Effects on the body include reversible monoamine oxidase inhibition, cholinergic, adrenergic, opioid and nitric oxide donating actions, all of which may contribute to its pharmacological effects to some extent.

Sydnones are mesoionic heterocyclic chemical compounds possessing a 1,2,3-oxadiazole core with a keto group in the 5 position. Like other mesoionic compounds they are di-polar, possessing both positive and negative charges which are delocalized across the ring. Recent computational studies have indicated that sydnones and other similar mesoionic compounds are nonaromatic, "though well-stabilized in two separate regions by electron and charge delocalization." Sydnones are heterocyclic compounds named after the city of Sydney, Australia.

Molsidomine is an orally active, long acting vasodilating drug used to treat angina pectoris. Molsidomine is metabolized in the liver to the active metabolite linsidomine. Linsidomine is an unstable compound that releases nitric oxide (NO) upon decay as the actual vasodilating compound.
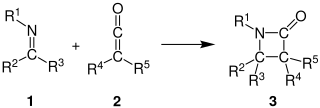
The Staudinger synthesis, also called the Staudinger ketene-imine cycloaddition, is a chemical synthesis in which an imine 1 reacts with a ketene 2 through a non-photochemical 2+2 cycloaddition to produce a β-lactam3. The reaction carries particular importance in the synthesis of β-lactam antibiotics. The Staudinger synthesis should not be confused with the Staudinger reaction, a phosphine or phosphite reaction used to reduce azides to amines.
Münchnone (synonyms: 1,3-oxazolium-5-oxide; 1,3-oxazolium-5-olate; anhydro-5-hydroxy-1,3-oxazolium hydroxide; 5-hydroxy-1,3-oxazolium hydroxide, inner salt; oxido-oxazolium) is a mesoionic heterocyclic aromatic chemical compound, with the molecular formula C3H3NO2. The name refers to the city of Munich, Germany (German: München), where the compound and its derivatives were first discovered and studied.
Montréalone is a mesoionic heterocyclic chemical compound. It is named for the city of Montréal, Canada, which is the location of McGill University, where it was first discovered.

The nitro-Mannich reaction is the nucleophilic addition of a nitroalkane to an imine, resulting in the formation of a beta-nitroamine. With the reaction involving the addition of an acidic carbon nucleophile to a carbon-heteroatom double bond, the nitro-Mannich reaction is related to some of the most fundamental carbon-carbon bond forming reactions in organic chemistry, including the aldol reaction, Henry reaction and Mannich reaction.