Related Research Articles

Ecdysis is the moulting of the cuticle in many invertebrates of the clade Ecdysozoa. Since the cuticle of these animals typically forms a largely inelastic exoskeleton, it is shed during growth and a new, larger covering is formed. The remnants of the old, empty exoskeleton are called exuviae.

Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column, which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordate subphylum Vertebrata, i.e. vertebrates. Well-known phyla of invertebrates include arthropods, mollusks, annelids, echinoderms, flatworms, cnidarians, and sponges.

The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all animals lungs. The trachea extends from the larynx and branches into the two primary bronchi. At the top of the trachea, the cricoid cartilage attaches it to the larynx. The trachea is formed by a number of horseshoe-shaped rings, joined together vertically by overlying ligaments, and by the trachealis muscle at their ends. The epiglottis closes the opening to the larynx during swallowing.

Arachnids are arthropods in the class Arachnida of the subphylum Chelicerata. Arachnida includes, among others, spiders, scorpions, ticks, mites, pseudoscorpions, harvestmen, camel spiders, whip spiders and vinegaroons.
Aquatic insects or water insects live some portion of their life cycle in the water. They feed in the same ways as other insects. Some diving insects, such as predatory diving beetles, can hunt for food underwater where land-living insects cannot compete.

Tracheole (trā'kē-ōl') is a fine respiratory tube of the trachea of an insect or a spider, part of the respiratory system.
Entomopathogenic fungi are parasitic unicellular or multicellular microorganisms belonging to the kingdom of Fungi, that can infect and seriously disable or kill insects. Entomopathogenicity is not limited to a particular class of fungi and is found in six divisions in the fungal kingdom. Some fungal entomopathogens are opportunistic whereas some have evolved into highly specific pathogens of insects.

Insect wings are adult outgrowths of the insect exoskeleton that enable insects to fly. They are found on the second and third thoracic segments, and the two pairs are often referred to as the forewings and hindwings, respectively, though a few insects lack hindwings, even rudiments. The wings are strengthened by a number of longitudinal veins, which often have cross-connections that form closed "cells" in the membrane. The patterns resulting from the fusion and cross-connection of the wing veins are often diagnostic for different evolutionary lineages and can be used for identification to the family or even genus level in many orders of insects.
Perrin's cave beetle, Siettitia balsetensis, is an extinct freshwater beetle from France. It and Siettitia ayenionensis are the only two species in the genus Siettitia.
Insect physiology includes the physiology and biochemistry of insect organ systems.

Leiobunum rotundum is a species of harvestman that is found within the western portion of the Old World.

Arthropods are covered with a tough, resilient integument, cuticle or exoskeleton of chitin. Generally the exoskeleton will have thickened areas in which the chitin is reinforced or stiffened by materials such as minerals or hardened proteins. This happens in parts of the body where there is a need for rigidity or elasticity. Typically the mineral crystals, mainly calcium carbonate, are deposited among the chitin and protein molecules in a process called biomineralization. The crystals and fibres interpenetrate and reinforce each other, the minerals supplying the hardness and resistance to compression, while the chitin supplies the tensile strength. Biomineralization occurs mainly in crustaceans. In insects and arachnids, the main reinforcing materials are various proteins hardened by linking the fibres in processes called sclerotisation and the hardened proteins are called sclerotin. The dorsal tergum, ventral sternum, and the lateral pleura form the hardened plates or sclerites of a typical body segment.
A cuticle, or cuticula, is any of a variety of tough but flexible, non-mineral outer coverings of an organism, or parts of an organism, that provide protection. Various types of "cuticle" are non-homologous, differing in their origin, structure, function, and chemical composition.

Arthropods are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (metameric) segments, and paired jointed appendages. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. They form an extremely diverse group of up to ten million species.
Desiccation tolerance refers to the ability of an organism to withstand or endure extreme dryness, or drought-like conditions. Plants and animals living in arid or periodically arid environments such as temporary streams or ponds may face the challenge of desiccation, therefore physiological or behavioral adaptations to withstand these periods are necessary to ensure survival. In particular, insects occupy a wide range of ecologically diverse niches and, so, exhibit a variety of strategies to avoid desiccation.

The tymbal is the corrugated exoskeletal structure used to produce sounds in insects. In male cicadas, the tymbals are membranes in the abdomen, responsible for the characteristic sound produced by the insect. In tiger moths, the tymbals are modified regions of the thorax and produce high-frequency clicks. In lesser wax moths the left and right tymbals emit high-frequency pulses that are used as mating calls.

Insects are hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body, three pairs of jointed legs, compound eyes, and a pair of antennae. Insects are the most diverse group of animals, with more than a million described species; they represent more than half of all animal species.

Insect morphology is the study and description of the physical form of insects. The terminology used to describe insects is similar to that used for other arthropods due to their shared evolutionary history. Three physical features separate insects from other arthropods: they have a body divided into three regions, three pairs of legs, and mouthparts located outside of the head capsule. This position of the mouthparts divides them from their closest relatives, the non-insect hexapods, which include Protura, Diplura, and Collembola.
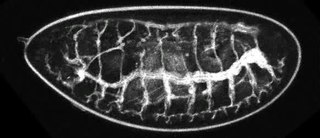
An insect's respiratory system is the system with which it introduces respiratory gases to its interior and performs gas exchange.

Isaria fumosorosea is an entomopathogenic fungus, formerly known as Paecilomyces fumosoroseus. It shows promise as a biological pesticide with an extensive host range.
References
- Mill, P.J., Tracheae and TracheolesMicroscopic Anatomy of Invertebrates, 11A, pp. 303–336, 1998.