| Look up tangent in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
A tangent , in geometry, is a straight line through a point on a curve that has the same direction at that point as the curve.
Contents
Tangent may also refer to:
| Look up tangent in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
A tangent , in geometry, is a straight line through a point on a curve that has the same direction at that point as the curve.
Tangent may also refer to:

In classical mathematics, analytic geometry, also known as coordinate geometry or Cartesian geometry, is the study of geometry using a coordinate system. This contrasts with synthetic geometry.

The clavichord is a Western European stringed rectangular keyboard instrument that was used largely in the Late Middle Ages, through the Renaissance, Baroque and Classical eras. Historically, it was mostly used as a practice instrument and as an aid to composition, not being loud enough for larger performances. The clavichord produces sound by striking brass or iron strings with small metal blades called tangents. Vibrations are transmitted through the bridge(s) to the soundboard.
Origin, origins, or original may refer to:
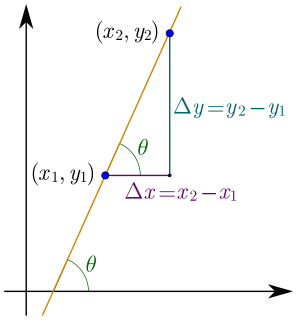
In mathematics, the slope or gradient of a line is a number that describes both the direction and the steepness of the line. Slope is often denoted by the letter m; there is no clear answer to the question why the letter m is used for slope, but its earliest use in English appears in O'Brien (1844) who wrote the equation of a straight line as "y = mx + b" and it can also be found in Todhunter (1888) who wrote it as "y = mx + c".

In geometry, the tangent line to a plane curve at a given point is the straight line that "just touches" the curve at that point. Leibniz defined it as the line through a pair of infinitely close points on the curve. More precisely, a straight line is said to be a tangent of a curve y = f(x) at a point x = c if the line passes through the point (c, f ) on the curve and has slope f'(c), where f' is the derivative of f. A similar definition applies to space curves and curves in n-dimensional Euclidean space.
Stargate SG-1 is a Canadian-American military science fiction adventure television series and part of Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer's Stargate franchise. The show, created by Brad Wright and Jonathan Glassner, is based on the 1994 science fiction film Stargate by Dean Devlin and Roland Emmerich. The television series was filmed in and around the city of Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. The series premiered on Showtime on July 27, 1997 and moved to the Sci Fi Channel on June 7, 2002; the final episode first aired on Sky1 on March 13, 2007.
In mathematics, curvature is any of several strongly related concepts in geometry. Intuitively, the curvature is the amount by which a curve deviates from being a straight line, or a surface deviates from being a plane.

In elementary geometry, two geometric objects are perpendicular if they intersect at a right angle.
In geometry, a secant is a line that intersects a curve at a minimum of two distinct points. The word secant comes from the Latin word secare, meaning to cut. In the case of a circle, a secant intersects the circle at exactly two points. A chord is the line segment determined by the two points, that is, the interval on the secant whose ends are the two points.
Moebius, Möbius or Mobius may refer to:
Differential geometry of curves is the branch of geometry that deals with smooth curves in the plane and the Euclidean space by methods of differential and integral calculus.
Stargate is an adventure military science fiction franchise.

A Stargate is an Einstein–Rosen bridge portal device within the Stargate fictional universe that allows practical, rapid travel between two distant locations. The devices first appear in the 1994 Roland Emmerich film Stargate, and thereafter in the television series Stargate SG-1, Stargate Atlantis, and Stargate Universe. In these productions, the Stargate functions as a plot device, allowing the main characters to visit alien planets without the need for spaceships or any other type of technology. The device allows for near-instantaneous travel across both interstellar and extragalactic distances.
Stargate is a military science fiction media franchise based on the film directed by Roland Emmerich, which he co-wrote with producer Dean Devlin. The franchise is based on the idea of an alien Einstein–Rosen bridge device that enables nearly instantaneous travel across the cosmos. The franchise began with the film Stargate, released on October 28, 1994, by Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer and Carolco, which grossed US$197 million worldwide. In 1997, Brad Wright and Jonathan Glassner created a television series titled Stargate SG-1 as a sequel to the film. This show was joined by Stargate Atlantis in 2004, Stargate Universe in 2009, and a prequel web series, Stargate Origins, in 2018. Also consistent with the same story are a variety of books, video games and comic books, as well as the direct-to-DVD movies Stargate: Children of the Gods, Stargate: The Ark of Truth, and Stargate: Continuum, which concluded the first television show after 10 seasons.
In law, a legacy is something held and transferred to someone as their inheritance, as by will and testament. Personal effects, family property, marriage property or collective property gained by will of real property.
The mythology of the Stargate franchise is the historical backstory of the series' premise.

Stargateliterature comprises the novels and short stories in the Stargate franchise fictional universe as well as non-fiction devoted to the franchise. Stargate literary works follow no strict continuity with the series or each other, and are often considered to be non-canon. This is evident in the fact that there is a period of roughly a year between the original idea for a novel and the finalised product, causing problems for authors as they are unaware as to how the franchise will develop and change during the writing process. Despite this, the editors of Stargate literature function as the medium between the author and the production company.

In geometry, a centre of an object is a point in some sense in the middle of the object. According to the specific definition of center taken into consideration, an object might have no center. If geometry is regarded as the study of isometry groups then a center is a fixed point of all the isometries which move the object onto itself.

In hyperbolic geometry, a horocycle is a curve whose normal or perpendicular geodesics all converge asymptotically in the same direction. It is the two-dimensional case of a horosphere.

In geometry, a convex curve is a simple curve in the Euclidean plane which lies completely on one side of each and every one of its tangent lines.