Related Research Articles
The Boii were a Celtic tribe of the later Iron Age, attested at various times in Cisalpine Gaul, Pannonia, present-day Bavaria, in and around present-day Bohemia, parts of present-day Slovakia and Poland, and Gallia Narbonensis.

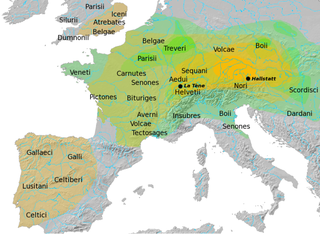
The Celts or Celtic peoples were a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia, identified by their use of Celtic languages and other cultural similarities. Major Celtic groups included the Gauls; the Celtiberians and Gallaeci of Iberia; the Britons, Picts, and Gaels of Britain and Ireland; the Boii; and the Galatians. The relation between ethnicity, language and culture in the Celtic world is unclear and debated; for example over the ways in which the Iron Age people of Britain and Ireland should be called Celts. In current scholarship, 'Celt' primarily refers to 'speakers of Celtic languages' rather than to a single ethnic group.

Gaul was a region of Western Europe first clearly described by the Romans, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, and parts of Switzerland, the Netherlands, Germany, and Northern Italy. It covered an area of 494,000 km2 (191,000 sq mi). According to Julius Caesar, who took control of the region on behalf of the Roman Republic, Gaul was divided into three parts: Gallia Celtica, Belgica, and Aquitania.

Commentarii de Bello Gallico, also Bellum Gallicum, is Julius Caesar's firsthand account of the Gallic Wars, written as a third-person narrative. In it Caesar describes the battles and intrigues that took place in the nine years he spent fighting the Celtic and Germanic peoples in Gaul that opposed Roman conquest.

Terence Graham Parry Jones was a Welsh actor, comedian, director, historian, writer and member of the Monty Python comedy troupe.
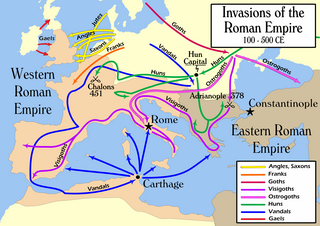
The Migration Period, also known as the Barbarian Invasions, was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories by various tribes, and the establishment of the post-Roman kingdoms.
Terry Jones' Medieval Lives is a 2004 television documentary series produced for the BBC. Written and hosted by Terry Jones, each half-hour episode examines a particular medieval personality, with the intent of separating myth from reality.

Roman Gaul refers to Gaul under provincial rule in the Roman Empire from the 1st century BC to the 5th century AD.
"The Stolen Eagle" is the series premiere of the British-American historical drama television series Rome. Written by series creator Bruno Heller and directed by Michael Apted, the episode first aired in the United States on Home Box Office (HBO) on August 28, 2005, and on the BBC in the United Kingdom and Ireland on November 2. Rome was given a budget of $100 million, making it the largest amount both networks had ever spent on a series. Heller centered the series' narrative on the perspectives of two common soldiers, similar to Rosencrantz and Guildenstern from Shakespeare's Hamlet. Apted shot the episode at Cinecittà, the Roman studio where the epic films Ben-Hur and Cleopatra were filmed. On the set, realism and authenticity were emphasized more than grandiosity, with depictions of a cosmopolitan city of all social classes.
Romanization or Latinization, in the historical and cultural meanings of both terms, indicate different historical processes, such as acculturation, integration and assimilation of newly incorporated and peripheral populations by the Roman Republic and the later Roman Empire. The terms were used in ancient Roman historiography and traditional Italian historiography until the Fascist period, when the various processes were called the "civilizing of barbarians".

The Battle of Vosges, also referred to as the Battle of Vesontio, was fought on September 14, 58 BC between the Germanic tribe of the Suebi, under the leadership of Ariovistus, and six Roman legions under the command of Gaius Julius Caesar. This encounter is the third major battle of the Gallic Wars. Germanic tribes crossed the Rhine, seeking a home in Gaul.

Ancient Rome: The Rise and Fall of an Empire is a 2006 BBC One docudrama series, with each episode looking at a different key turning point in the history of the Roman Republic and Empire. This docudrama focuses on the Latin western half of the Roman Empire.

Ancient Celtic warfare refers to the historical methods of warfare employed by various Celtic people and tribes from Classical antiquity through the Migration period.

Alan Ereira is a British author, historian and documentary filmmaker. He is a Professor of Practice at the University of Wales, Trinity St. David.

The Gauls were a group of Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age and the Roman period. Their homeland was known as Gaul (Gallia). They spoke Gaulish, a continental Celtic language.
Gaius Valerius Troucillus or Procillus was a Helvian Celt who served as an interpreter and envoy for Julius Caesar in the first year of the Gallic Wars. Troucillus was a second-generation Roman citizen, and is one of the few ethnic Celts who can be identified both as a citizen and by affiliation with a Celtic polity. His father, Caburus, and a brother are named in Book 7 of Caesar's Bellum Gallicum as defenders of Helvian territory against a force sent by Vercingetorix in 52 BC. Troucillus plays a role in two episodes from the first book of Caesar's war commentaries, as an interpreter for the druid Diviciacus and as an envoy to the Suebian king Ariovistus, who accuses him of spying and has him thrown in chains.

Celtic mythology is the body of myths belonging to the Celtic peoples. Like other Iron Age Europeans, Celtic peoples followed a polytheistic religion, having many gods and goddesses. The mythologies of continental Celtic peoples, such as the Gauls and Celtiberians, did not survive their conquest by the Roman Empire, the loss of their Celtic languages and their subsequent conversion to Christianity. Only remnants are found in Greco-Roman sources and archaeology. Most surviving Celtic mythology belongs to the Insular Celtic peoples. They preserved some of their myths in oral lore, which were eventually written down by Christian scribes in the Middle Ages. Irish mythology has the largest written body of myths, followed by Welsh mythology.
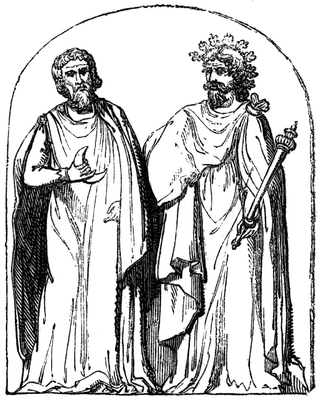
A druid was a member of the high-ranking priestly class in ancient Celtic cultures. Druids were religious leaders as well as legal authorities, adjudicators, lorekeepers, medical professionals and political advisors. Druids left no written accounts. While they were reported to have been literate, they are believed to have been prevented by doctrine from recording their knowledge in written form. Their beliefs and practices are attested in some detail by their contemporaries from other cultures, such as the Romans and the Greeks.
Onomaris was a Celtic queen regnant. She is described in the anonymous collection of Greek stories known in Latin as Tractatus De Mulieribus Claris en Bello. She is the first celtic woman mentioned in classical records.

The Battle of Histria, c. 62–61 B.C., was fought between the Bastarnae peoples of Scythia Minor and the Roman Consul Gaius Antonius Hybrida. The Bastarnae emerged victorious from the battle after successfully launching a surprise attack on the Roman troops; Hybrida escaped alongside his cavalry forces leaving behind the infantry to be massacred by the Bastarnian-Scythian attackers.
References
- ↑ "Decline and fall of the Roman myth". The Times. London. 7 May 2006.