Tetrachloroethane may refer to either of two isomeric chemical compounds:

Barium is a chemical element with the symbol Ba and atomic number 56. It is the fifth element in group 2 and is a soft, silvery alkaline earth metal. Because of its high chemical reactivity, barium is never found in nature as a free element.
A chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and plus (+) and minus (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name, and it contains no words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae.
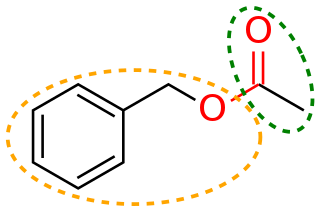
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a substituent or moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the rest of the molecule's composition. This enables systematic prediction of chemical reactions and behavior of chemical compounds and the design of chemical synthesis. The reactivity of a functional group can be modified by other functional groups nearby. Functional group interconversion can be used in retrosynthetic analysis to plan organic synthesis.
In chemistry, a hydrate is a substance that contains water or its constituent elements. The chemical state of the water varies widely between different classes of hydrates, some of which were so labeled before their chemical structure was understood.
In chemistry, the molar mass of a chemical compound is defined as the mass of a sample of that compound divided by the amount of substance in that sample, measured in moles. It is the mass of 1 mole of the substance or 6.022×1023 particles, expressed in grams. The molar mass is a bulk, not molecular, property of a substance. The molar mass is an average of many instances of the compound, which often vary in mass due to the presence of isotopes. Most commonly, the molar mass is computed from the standard atomic weights and is thus a terrestrial average and a function of the relative abundance of the isotopes of the constituent atoms on Earth. The molar mass is appropriate for converting between the mass of a substance and the amount of a substance for bulk quantities.

In chemistry, an enantiomer is one of two stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other that are non-superposable, much as one's left and right hands are mirror images of each other that cannot appear identical simply by reorientation. A single chiral atom or similar structural feature in a compound causes that compound to have two possible structures which are non-superposable, each a mirror image of the other. Each member of the pair is termed an enantiomorph ; the structural property is termed enantiomerism. The presence of multiple chiral features in a given compound increases the number of geometric forms possible, though there may still be some perfect-mirror-image pairs.

Sodium peroxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2O2. This yellowish solid is the product of sodium ignited in excess oxygen. It is a strong base. This metal peroxide exists in several hydrates and peroxyhydrates including Na2O2·2H2O2·4H2O, Na2O2·2H2O, Na2O2·2H2O2, and Na2O2·8H2O. The octahydrate, which is simple to prepare, is white, in contrast to the anhydrous material.

Chromium carbonyl, also known as chromium hexacarbonyl, is the chemical compound with the formula Cr(CO)6. At room temperature the solid is stable to air, although it does have a high vapor pressure and sublimes readily. Cr(CO)6 is zerovalent, meaning that Cr has an oxidation state of zero, and it is a homoleptic complex, which means that all the ligands are identical. The complex is octahedral with Cr–C and C–O distances of 1.91 and 1.14 Å, respectively.

Borneol is a bicyclic organic compound and a terpene derivative. The hydroxyl group in this compound is placed in an endo position. Being chiral, borneol exists as two enantiomers. Both (+)-borneol and (−)-borneol (l-borneol) are found in nature.

tert-Butyllithium is a chemical compound with the formula (CH3)3CLi. As an organolithium compound, it has applications in organic synthesis since it is a strong base, capable of deprotonating many carbon acids, including benzene. tert-Butyllithium is available commercially as hydrocarbon solutions; it is not usually prepared in the laboratory. Its synthesis was first reported by R. B. Woodward in 1941.

Mercury selenide (HgSe) is a chemical compound of mercury and selenium. It is a grey-black crystalline solid semi-metal with a sphalerite structure. The lattice constant is 0.608 nm.

Antimony triiodide is the chemical compound with the formula SbI3. This ruby-red solid is the only characterized "binary" iodide of antimony, i.e. the sole compound isolated with the formula SbxIy. It contains antimony in its +3 oxidation state. Like many iodides of the heavier main group elements, its structure depends on the phase. Gaseous SbI3 is a molecular, pyramidal species as anticipated by VSEPR theory. In the solid state, however, the Sb center is surrounded by an octahedron of six iodide ligands, three of which are closer and three more distant. For the related compound BiI3, all six Bi—I distances are equal.

A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., without breaking chemical bonds. Chemical substances can be simple substances, chemical compounds, or alloys. Chemical elements may or may not be included in the definition, depending on expert viewpoint.

1,1,2,2-Tetrachloroethane is a chlorinated derivative of ethane. It has the highest solvent power of any chlorinated hydrocarbon. As a refrigerant, it is used under the name R-130.
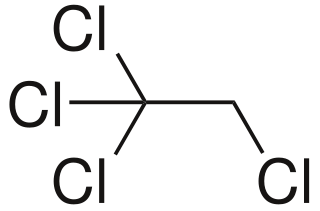
1,1,1,2-Tetrachloroethane is a chlorinated hydrocarbon. It is a colorless liquid with a sweet chloroform-like odor. It is used as a solvent and in the production of wood stains and varnishes.
Dioxin may refer to:

A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules composed of atoms from more than one element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element is therefore not a compound.
Aluminium(I) oxide is a compound of aluminium and oxygen with the chemical formula Al2O. It can be prepared by heating the stable oxide Al2O3 with elemental silicon at 1800 °C under vacuum.

Cannabicyclohexanol is a cannabinoid receptor agonist drug, developed by Pfizer in 1979. On 19 January 2009, the University of Freiburg in Germany announced that an analog of CP 47,497 was the main active ingredient in the herbal incense product Spice, specifically the 1,1-dimethyloctyl homologue of CP 47,497, which is now known as cannabicyclohexanol. The 1,1-dimethyloctyl homologue of CP 47,497 is in fact several times more potent than the parent compound, which is somewhat unexpected as the 1,1-dimethylheptyl is the most potent substituent in classical cannabinoid compounds such as HU-210.
An acid anhydride is a type of chemical compound derived by the removal of water molecules from an acid.