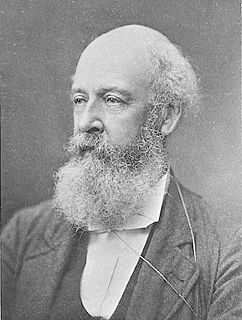Cauterization is a medical practice or technique of burning a part of a body to remove or close off a part of it. It destroys some tissue in an attempt to mitigate bleeding and damage, remove an undesired growth, or minimize other potential medical harm, such as infections when antibiotics are unavailable.

James Harvey Robinson was an American historian, who co-founded New History, which greatly broadened the scope of historical scholarship in relation to the social sciences. Jay Green concludes:
Albany Medical College (AMC) is a medical school located in Albany, New York, United States. It was founded in 1839 by Alden March and James H. Armsby and is one of the oldest medical schools in the nation. The college is part of the Albany Medical Center, which includes the Albany Medical Center Hospital.
Albert Warren Ferris was an American psychiatrist, born in Brooklyn, New York.

First published in 1981 by Elsevier, Principles of Neural Science is an influential neuroscience textbook edited by Eric R. Kandel, James H. Schwartz, and Thomas M. Jessell. The original edition was 468 pages; now on the fifth edition, the book has grown to 1747 pages. The second edition was published in 1985, third in 1991, fourth in 2000. The fifth and latest edition was published on October 26th, 2012 and includes Steven A. Siegelbaum and A.J. Hudspeth as editors. It has been hailed as the "Bible of Neuroscience" having been co-written by the "Father of Neuroscience", Eric Kandel.

William Henry Welch was an American physician, pathologist, bacteriologist, and medical school administrator. He was one of the "Big Four" founding professors at the Johns Hopkins Hospital. He was the first dean of the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine and was also the founder of the Johns Hopkins School of Hygiene and Public Health, the first school of public health in the country. Welch was more known for his cogent summations of current scientific work, than his own scientific research. The Johns Hopkins medical school library is also named after Welch. In his lifetime, he was called the "Dean of American Medicine" and received various awards and honors throughout his lifetime, and posthumously.

Perry's Chemical Engineers' Handbook was first published in 1934 and the most current ninth edition was published in July 2018. It has been a source of chemical engineering knowledge for chemical engineers, and a wide variety of other engineers and scientists, through seven previous editions spanning more than 70 years.

Marcia Angell is an American physician, author, and the first woman to serve as editor-in-chief of the New England Journal of Medicine. She is currently a Senior Lecturer in the Department of Global Health and Social Medicine at Harvard Medical School in Boston, Massachusetts.

Alfred Lebbeus Loomis was an American physician who served as president of the Association of American Physicians.
Paul Oscar Blocq (1860–1896) was a French pathologist who is remembered for his neuropathological work done with Jean-Martin Charcot (1825-1893) and Gheorghe Marinescu (1863-1938) at the Salpêtrière in Paris.

The National Physicians Alliance (NPA) is a 501(c)(3) national, multi-specialty medical organization founded in 2005. The organization's mission statement reads: "The National Physicians Alliance creates research and education programs that promote health and foster active engagement of physicians with their communities to achieve high quality, affordable health care for all. The NPA offers a professional home to physicians across medical specialties who share a commitment to professional integrity and health justice."
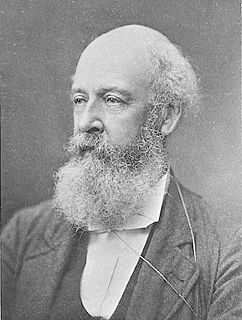
Charles Badham, FRS was a physician from London, England who gave bronchitis its name.
Jean-Pierre or Pierre Blaud , often seen as P. Blaud of/de Beaucaire was a French doctor of medicine who in 1832 introduced and started the use of Blaud's pills or iron pills as a medication for patients suffering from anemia. Blaud of Beaucaire was one of the leading physicians at the Hospital of Beaucaire in France.
The Michigan State Medical Society (MSMS) is a professional association representing more than 15,000 physicians in Michigan. Incorporated on June 5, 1866, MSMS is a non-profit, membership organization of physicians, graduates completing residency programs, and medical school students. The headquarters is located in East Lansing, Michigan, near Michigan State University and the capital city of Lansing. MSMS is the state affiliate of the American Medical Association.
The history of medicine in the United States encompasses a variety of periods and approaches to health care in the United States from colonial days to the present, ranging from early folk remedies to the increasing professionalization and managed care of modern medicine.
George Rosen (1910–1977) was an American physician, public health administrator, journal editor, and medical historian. His major interests were in the relationship of social, economic and cultural factors upon health.

Elise Depew Strang L'Esperance (1878–1958) was an American pathologist and physician, a pioneer in establishing a preventive model of cancer treatment. She was a pathologist noted for establishing cancer prevention clinics in New York. She founded two clinics: the Strang Tumor Clinic in 1932 and the Strang Cancer Prevention Clinic in 1937, which operated out of the New York Infirmary. In 1940, L'Esperance opened a second branch of the Strang Cancer Prevention Clinic at the Memorial Center for Cancer and Allied Diseases. During her medical career, L'Esperance published her research prolifically, credited for approximately 30 articles in medical journals.
Primary anemia may refer to:
George Argale Harrop was an American physician, nutritionist and writer.