
Mysia was a region in the northwest of ancient Asia Minor. It was located on the south coast of the Sea of Marmara. It was bounded by Bithynia on the east, Phrygia on the southeast, Lydia on the south, Aeolis on the southwest, Troad on the west and by the Propontis on the north. In ancient times it was inhabited by the Mysians, Phrygians, Aeolian Greeks and other groups.

The Phrygians were an ancient Indo-European people, initially dwelling in the southern Balkans – according to Herodotus – under the name of Bryges (Briges), changing it to Phryges after their final migration to Anatolia, via the Hellespont.

The Roman province of Asia or Asiana, in Byzantine times called Phrygia, was an administrative unit added to the late Republic. It was a Senatorial province governed by a proconsul. The arrangement was unchanged in the reorganization of the Roman Empire in 211.

Bolvadin is a city and district of Afyonkarahisar Province in Turkey. It covers an area of 1,108 km² and has an altitude of 1,016 m. The population of the district center is 31,387 (2010). The mayor is Fatih Kayacan.

Buldan is a town and a district of Denizli Province in the inner Aegean Region of Turkey. Buldan district area neighbors to the east and the south three other districts of the same province, namely Güney, Akköy and Sarayköy, and to the west by the areas of three districts of Aydın Province, Buharkent, Kuyucak and Karacasu, and to the northwest by Sarıgöl district of Manisa Province.

Apamea Cibotus, Apamea ad Maeandrum, Apamea or Apameia was an ancient city in Anatolia founded in the 3rd century BC by Antiochus I Soter, who named it after his mother Apama. It was in Hellenistic Phrygia, but became part of the Roman province of Pisidia. It was near, but on lower ground than, Celaenae (Kelainai).

Tripolis on the Meander – also Neapolis, Apollonia, and Antoniopolis – was an ancient city on the borders of Phrygia, Caria and Lydia, on the northern bank of the upper course of the Maeander, and on the road leading from Sardes by Philadelphia to Laodicea ad Lycum. It was situated 20 km to the northwest of Hierapolis.

Docimium, Docimia or Docimeium was an ancient city of Phrygia, Asia Minor where there were famous marble quarries.

Yenicekent is a depending township in Buldan district, Denizli Province in southwestern Turkey. The region is notable for its high plains covered with dense forests. Yenicekent is also the site of ancient Tripolis of Phrygia.
Synaus was a city in the Roman province of Phrygia Pacatiana, now Simav, Kütahya Province, Turkey.

Tiberiopolis was a town in the Roman province of Phrygia Pacatiana, mentioned by Ptolemy, Socrates of Constantinople and Hierocles.
Eucarpia or Eukarpia was a city in Phrygia and a bishopric in the late Roman province of Phrygia Salutaris, in Asia Minor.
Attuda, whose site was at present-day Hisarköy, Sarayköy District, Denizli Province, Turkey, was a city in the Roman province of Phrygia Pacatiana.
Traianopolis, Trajanopolis, Tranopolis, or Tranupolis was a Roman and Byzantine city in Phrygia Pacatiana Prima.
Trapezopolis was a city in the late Roman province of Phrygia Pacatiana Prima.

Pharnaces II ruled the satrapy of Hellespontine Phrygia under the Achaemenid Dynasty of Persia. Hellespontine Phrygia comprised the lands of Troad, Mysia and Bithynia and had its seat at Daskyleion, south of Cyzicus, Mysia.
Isba was a city on the border of ancient Pamphylia. It has been identified with the modern village of Kiesme.
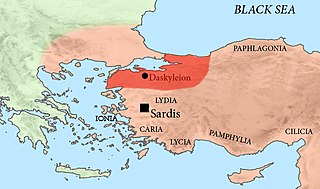
Hellespontine Phrygia or Lesser Phrygia was a Persian satrapy (province) in northwestern Anatolia, directly southeast of the Hellespont. Its capital was Dascylium, and for most of its existence it was ruled by the hereditary Persian Pharnacid dynasty. Together with Greater Phrygia, it made up the administrative provinces of the wider Phrygia region.












