A ship burial or boat grave is a burial in which a ship or boat is used either as a container for the dead and the grave goods, or as a part of the grave goods itself. If the ship is very small, it is called a boat grave. This style of burial was used among the Germanic peoples, particularly by Viking Age Norsemen. According to the Boxer Codex, ship burials were also practiced by the indigenous peoples of the Philippines.

Møn is an island in south-eastern Denmark. Until 1 January 2007, it was a municipality in its own right but it is now part of the municipality of Vordingborg, after merging with the former municipalities of Langebæk, Præstø, and Vordingborg. This has created a municipality with an area of 615 km2 (237 sq mi) and a total population of 46,307 (2005). It belongs to the Region Sjælland. Møn is one of Denmark's most popular destinations for tourists with its white chalk cliffs, countryside, sandy beaches and the market town of Stege. In June 2017, UNESCO designated Møn as Denmark's first biosphere reserve, consisting of "a series of islands and islets in the southern Baltic Sea, over approximately 45,118 hectares. Its landscapes include woodlands, grasslands, meadows, wetlands, coastal areas, ponds and steep hills."

Vestfold[²vɛstfɔl](listen) is a county in Norway, on the western shore of the Oslofjord. It borders Buskerud and Telemark. The county administration is in Tønsberg, Norway's oldest city, and the largest city is Sandefjord. With the exception of the city-county of Oslo, Vestfold is the smallest county in Norway by area.

Loppa is a municipality in Finnmark county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the village of Øksfjord. Other villages in Loppa include Andsnes, Bergsfjord, Langfjordhamn, Loppa, Nuvsvåg, Øksfjordbotn, Sandland, and Sør-Tverrfjord.

Levanger is a municipality in Trøndelag county, Norway. It is part of the district of Innherred. The administrative centre of the municipality is the town of Levanger. Some of the notable villages in the municipality include Alstadhaug, Ekne, Hokstad, Markabygd, Momarka, Frol, Mule, Nesset, Okkenhaug, Ronglan, Skogn, and Åsen.

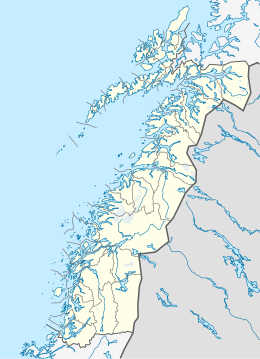
Alstahaug is a municipality in Nordland county, Norway. It is part of the Helgeland region. The administrative centre of the municipality is the town of Sandnessjøen. Some of the villages in Alstahaug include Søvika and Tjøtta.

Leirfjord is a municipality in Nordland county, Norway. It is part of the Helgeland traditional region. The administrative centre of the municipality is the village of Leland. Other villages in Leirfjord include Bardalssjøen and Sundøy. The large Helgeland Bridge is partly located in the municipality, connecting it to Alstahaug Municipality and the town of Sandnessjøen.

A tumulus is a mound of earth and stones raised over a grave or graves. Tumuli are also known as barrows, burial mounds or kurgans, and may be found throughout much of the world. A cairn, which is a mound of stones built for various purposes, may also originally have been a tumulus.

Alsta is an island in the municipalities of Alstahaug and Leirfjord in Nordland county, Norway. The island is surrounded by the Vefsnfjorden to the east, the Leirfjorden to the north, and the Alstenfjorden to the south and west. The eastern part of the island is dominated by the Seven Sisters mountain range which has five mountains that are more than 1,000 metres (3,300 ft) tall, while the western part of the island is relatively flat and it is the location of the town of Sandnessjøen and the village of Søvika in the south.

The Oseberg ship is a well-preserved Viking ship discovered in a large burial mound at the Oseberg farm near Tønsberg in Vestfold county, Norway. This ship is commonly acknowledged to be among the finer artifacts to have survived from the Viking Era. The ship and some of its contents are displayed at the Viking Ship Museum at Bygdøy on the western side of Oslo, Norway.

Lake Jackson Mounds Archaeological State Park (8LE1) is one of the most important archaeological sites in Florida, the capital of chiefdom and ceremonial center of the Fort Walton Culture inhabited from 1050–1500. The complex originally included seven earthwork mounds, a public plaza and numerous individual village residences.

The stone ship or ship setting was an early burial custom in Scandinavia, Northern Germany and the Baltic states. The grave or cremation burial was surrounded by slabs or stones in the shape of a ship. The ships vary in size and were erected from c. 1000 BC to 1000 AD.

Avaldsnes is a village in Karmøy municipality in Rogaland county, Norway. The village is located on the northeastern part of the island of Karmøy, along the Karmsundet strait, just south of the town of Haugesund. The village was an ancient centre of power on the west coast of Norway and is the site of one of Norway’s more important areas of cultural history. The trading port of Notow and the Avaldsnes Church are two notable historic sites in Avaldsnes.

Stord is an island in Hordaland county, Norway. Located in the traditional district of Sunnhordland, the island is part of the municipalities of Stord and Fitjar. The largest settlements on the island are the town of Leirvik and the villages of Sagvåg and Fitjar.

Battlegore Burial Chamber is a Bronze Age burial chamber located in Williton, Somerset. It is composed of three round barrows and possibly a long, chambered barrow. The site was excavated in 1931 by George Gray. The name "Battlegore" comes from this site being attributed to the location of a Danish raid in 918 AD or 988 AD. At least as early as the 14th century, the site was referred to as "Bytelgore", a predecessor of the word "Battlegore". Along with three nearby round barrows it has been scheduled as an ancient monument.

Loppa, is an island in Loppa Municipality in Finnmark county, Norway. The 12-square-kilometre (4.6 sq mi) island lies in the Lopphavet Sea in the western part of the municipality, west of the island of Silda. The small island has one village area on the southeastern coast. This village used to be the administrative centre of Loppa and an important fishing village for the municipality, but all of the administration of the village was moved to Øksfjord on the mainland. Today, Loppa Church is still located in this village, but there are only a few residents remaining on the island. In 1983, a seabird reserve was established along the western cliffs.
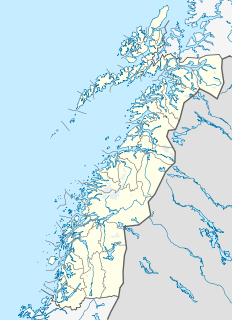
Vega is an island in Vega Municipality in Nordland county, Norway. The 108-square-kilometre (42 sq mi) island is the largest island in the 6,500 islands in the Vegaøyan archipelago, all of which is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The island lies in the Norwegian Sea, about 18 kilometres (11 mi) west of the mainland of Norway. The islands of Igerøya and Ylvingen lie between Vega and the mainland. The main villages on the island are Gladstad, the administrative centre of the municipality, and Holand.
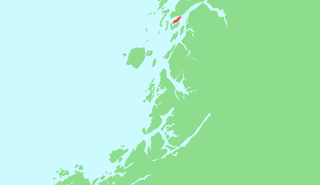
Offersøya or Offersøy is an island in Alstahaug Municipality in Nordland county, Norway. The 6.7-square-kilometre (2.6 sq mi) island lies directly between the large island of Alsta and the smaller island of Tjøtta at the mouth of the Vefsnfjorden. The Norwegian County Road 17 runs across the island connecting Alsta and Tjøtta. The island is relatively flat, with the highest point only reaching 43 metres (141 ft) above sea level. In 2016, there were 61 residents living on the island.

Altra is an island in Alstahaug Municipality in Nordland county, Norway. The 0.24-square-kilometre (59-acre) island lies between the large island of Alsta and the small island of Tenna. The flat island is rather unique in the area because it is about 12 kilometres (7.5 mi) long and at most about 2 kilometres (6,600 ft) wide at the northern end. Most of the island is very narrow, and in some places, it is only about 60 metres (200 ft) wide.