
Canadian football, or simply football, is a sport in Canada in which two teams of 12 players each compete on a field 110 yards (101 m) long and 65 yards (59 m) wide, attempting to advance a pointed oval-shaped ball into the opposing team's end zone.

Offside is one of the laws in association football, codified in Law 11 of the Laws of the Game. The law states that a player is in an offside position if any of their body parts, except the hands and arms, are in the opponents' half of the pitch, and closer to the opponents' goal line than both the ball and the second-last opponent.

A referee is an official, in a variety of sports and competition, responsible for enforcing the rules of the sport, including sportsmanship decisions such as ejection. The official tasked with this job may be known by a variety of other titles depending on the sport, including umpire, judge, arbiter (chess), commissaire, or technical official. Referees may be assisted by umpires, linesmen, timekeepers, touch judges, or video assistant referees.

A try is a way of scoring points in rugby union and rugby league football. A try is scored by grounding the ball in the opposition's in-goal area. Rugby union and league differ slightly in defining "grounding the ball" and the "in-goal" area. In rugby union a try is worth 5 points, and in rugby league a try is worth 4 points.
The Laws of the Game are the codified rules of association football. The laws mention the number of players a team should have, the game length, the size of the field and ball, the type and nature of fouls that referees may penalise, the offside law, and many other laws that define the sport. During a match, it is the task of the referee to interpret and enforce the Laws of the Game.
In rugby football, the penalty is the main disciplinary sanction available to the referee to penalise players who commit deliberate infringements. The team who did not commit the infringement are given possession of the ball and may either kick it towards touch, attempt a place kick at goal, or tap the ball with their foot and run it. It is also sometimes used as shorthand for penalty goal.

A corner kick, commonly known as a corner, is the method of restarting play in a game of association football when the ball goes out of play over the goal line, without a goal being scored and having last been touched by a member of the defending team. The kick is taken from the corner of the field of play nearest to the place where the ball crossed the goal line.

Like most forms of modern football, rugby league football is played outdoors on a rectangular grass field with goals at each end that are attacked and defended by two opposing teams. The rules of rugby league have changed significantly over the decades since rugby football split into the league and union codes. This article details the modern form of the game and how it is generally played today, although rules do vary slightly between specific competitions.

The ball in and out of play is the ninth law of the Laws of the Game of association football, and describes to the two basic states of play in the game.

A comparison of American football and rugby union is possible because of the games' shared origins, despite their dissimilarities.
The experimental law variations (ELVs) were a proposed set of amendments to the laws of rugby union. They were proposed by the sport's governing body, the International Rugby Board (IRB), and trialled games at Stellenbosch University in 2006. In 2008 thirteen of the 23 variations trialled were played globally including; greater responsibility for assistant referees, corner posts no longer considered to touch in-goal, no gain in ground if the ball is moved into the 22-metre line by a player from the same team as the kicker, quick throw ins can travel backwards, no restrictions to players in the lineout, restrictions on where receivers and opposition hookers can stand in a lineout, pregripping and lifting allowed, mauls can be pulled down and players can enter with their head and shoulders lower than their hips, offside line is five metres away from the scrum for the backs and scrum half must be positioned close to the scrum, all offences apart from foul play and offsides are a free kick, and unplayable rucks and mauls are restarted with a free kick. In 2009 the IRB approved ten of the laws, rejecting the laws relating to mauls, numbers in a lineout and the increase in sanctions punishable by free kicks.
This is a general glossary of the terminology used in the sport of rugby union. Where words in a sentence are also defined elsewhere in this article, they appear in italics.
Rugby league football has accrued considerable jargon to describe aspects of the game. Many terms originate in the Laws of the Game. Some aspects of the game have more than one term referring to them. Different terms have become popularly used to describe an aspect of the game in different places, with notable differences between the Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
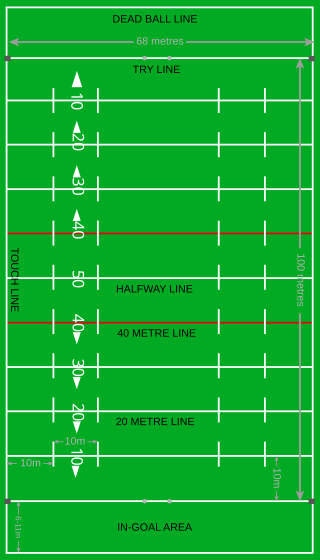
The rugby league playing field, also referred to as a pitch or paddock, is the playing surface for the sport of rugby league football and is surfaced exclusively with grass.

Rugby league match officials are responsible for fairly enforcing the Laws of the Game from a neutral point of view during a match of rugby league football and imposing penalties for deliberate breaches of these Laws. The most senior match official is the referee. They may be assisted by a range of other officials depending on the level and rules of the competition.
In rugby league football, the Laws of the Game are the rules governing how the sport is played. The Laws are the responsibility of the Rugby League International Federation, and cover the play, officiating, equipment and procedures of the game.

Rugby union match officials are responsible for enforcing the laws of rugby union during a match. "Every match is under the control of match officials who consist of the referee and two touch judges or assistant referees." Further officials can be authorised depending on the level and form of the game.

The laws of Rugby Union are defined by World Rugby and dictate how the game should be played. They are enforced by a referee, generally with the help of two assistant referees.

Comparison of association football (football/soccer) and rugby union is possible because of the games' similarities and shared origins.

Futsal began in the 1930s in South America as a version of association football, taking elements of its parent game into an indoor format so players could still play during inclement weather. Over the years, both sports have developed, creating a situation where the two sports share common traits while also hosting various differences.