A Touchstone file was originally a proprietary file format for the eponymous frequency-domain linear circuit simulator [1] from EEsof, launched in 1984 and acquired by HP. The simulator has been called HP/EEsof, then its engine has been successively included in the jOmega and ADS software suites and it is now owned by Keysight.
EEsof, today known as Keysight EEsof EDA, is a provider of electronic design automation (EDA) software that helps engineers design products such as cellular phones, wireless networks, radar, satellite communications systems, and high-speed digital wireline infrastructure. Applications include electronic system level (ESL), high-speed digital, RF-Mixed signal, device modeling, RF and Microwave design for commercial wireless, aerospace, and defense markets.
The Touchstone simulator has long since been superseded, [2] but its file format lives on.
A Touchstone file (also known as an SnP file after its set of file extensions [3] ) is an ASCII text file used for documenting the n-port network parameter data and noise data of linear active devices, passive filters, passive devices, or interconnect networks. An example of the format of the S-parameter section is given in the article about S-parameters. In addition to S-parameters, other representations such as Y-parameters and Z-parameters can be recorded.
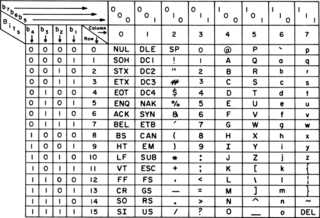
ASCII, abbreviated from American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard for electronic communication. ASCII codes represent text in computers, telecommunications equipment, and other devices. Most modern character-encoding schemes are based on ASCII, although they support many additional characters.
Scattering parameters or S-parameters describe the electrical behavior of linear electrical networks when undergoing various steady state stimuli by electrical signals.
It later became a de facto industry-standard file format not only for circuit simulators but also for measurement equipment (e.g. vector network analyzers, or VNAs), then later still an EIA standard as part of the Input/output Buffer Information Specification (IBIS) project. [4] On April 24, 2009, the IBIS Open Forum ratified version 2.0, [5] superseding Version 1.1. [6] Version 2.0 adds IBIS-style keywords such as [Reference], which permits per-port definition of the reference environment.
A de facto standard is a custom or convention that has achieved a dominant position by public acceptance or market forces. De facto is a Latin phrase that means in fact in the sense of "in practice but not necessarily ordained by law" or "in practice or actuality, but not officially established", as opposed to de jure.

A network analyzer is an instrument that measures the network parameters of electrical networks. Today, network analyzers commonly measure s–parameters because reflection and transmission of electrical networks are easy to measure at high frequencies, but there are other network parameter sets such as y-parameters, z-parameters, and h-parameters. Network analyzers are often used to characterize two-port networks such as amplifiers and filters, but they can be used on networks with an arbitrary number of ports.

The Electronic Industries Alliance was a standards and trade organization composed as an alliance of trade associations for electronics manufacturers in the United States. They developed standards to ensure the equipment of different manufacturers was compatible and interchangeable. The EIA ceased operations on February 11, 2011, but the former sectors continue to serve the constituencies of EIA.
Several further enhancements to the file format that allow description of the non-linear behavior of the component have been developed under the P2D and S2D pair of formats, [7] but these two have been superseded by the X-parameters functionality.

X-parameters are a generalization of S-parameters and are used for characterizing the amplitudes and relative phase of harmonics generated by nonlinear components under large input power levels. X-parameters are also referred to as the parameters of the Poly-Harmonic Distortion (PHD) nonlinear behavioral model.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
The Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) is a network protocol for delivering audio and video over IP networks. RTP is used in communication and entertainment systems that involve streaming media, such as telephony, video teleconference applications including WebRTC, television services and web-based push-to-talk features.
An optical switch is a device that enables optical signals to be selectively switched-on and -off or switched from one channel to another. The former is known as an optical (time-domain) switch or an optical modulator, while the latter can be specifically called an optical space switch or an optical router. In its ways to be switched temporally or spatially, it can be seen as physical analogies to the one-way or two-way switches in electrical circuits. In general, optical modulators and routers can be made from each other.
The File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard network protocol used for the transfer of computer files between a client and server on a computer network.
Speex is an audio compression format specifically tuned for the reproduction of human speech and also a free software speech codec that may be used on VoIP applications and podcasts. It is based on the CELP speech coding algorithm. Speex claims to be free of any patent restrictions and is licensed under the revised (3-clause) BSD license. It may be used with the Ogg container format or directly transmitted over UDP/RTP. It may also be used with the FLV container format.
A Controller Area Network is a robust vehicle bus standard designed to allow microcontrollers and devices to communicate with each other in applications without a host computer. It is a message-based protocol, designed originally for multiplex electrical wiring within automobiles to save on copper, but is also used in many other contexts.
Network congestion in data networking and queueing theory is the reduced quality of service that occurs when a network node or link is carrying more data than it can handle. Typical effects include queueing delay, packet loss or the blocking of new connections. A consequence of congestion is that an incremental increase in offered load leads either only to a small increase or even a decrease in network throughput.

In computing, the Preboot eXecution Environment specification describes a standardized client-server environment that boots a software assembly, retrieved from a network, on PXE-enabled clients. On the client side it requires only a PXE-capable network interface controller (NIC), and uses a small set of industry-standard network protocols such as DHCP and TFTP.
Input/output Buffer Information Specification or IBIS is a specification of a method for integrated circuit vendors to provide information about the input/output buffers of their product to their prospective customers without revealing the intellectual property of their implementation and without requiring proprietary encryption keys. From version 5.0, specification contains two separate types of models, "traditional IBIS" and "IBIS-AMI." The traditional model is generated in text format and consists of a number of tables that captures current vs. voltage (IV) and voltage vs. time (Vt) characteristics of the buffer, as well as the values of certain parasitic components. It is a standard data exchange format for exchanging modeling information among semiconductor device suppliers, simulation software suppliers, and end users.
Transistors are simple devices with complicated behavior. In order to ensure the reliable operation of circuits employing transistors, it is necessary to scientifically model the physical phenomena observed in their operation using transistor models. There exists a variety of different models that range in complexity and in purpose. Transistor models divide into two major groups: models for device design and models for circuit design.
Ngspice is a mixed-level/mixed-signal circuit simulator. It is the open-source successor of Spice3f5. A small group of maintainers and the user community contribute to the ngspice project by providing new features, enhancements and bug fixes.
The IBIS Interconnect Modeling Specification (ICM) is a behavioral, ASCII-based file format for distributing passive interconnect modeling information. The format and style of ICM are highly similar to the Input Output Buffer Information Specification (IBIS), and both specifications are managed by the same organization, the IBIS Open Forum. Interconnects under ICM may be represented through tabular frequency-dependent RLGC matrices or through S-parameters in separate Touchstone files. ICM models define interconnects as consisting of one or more segments. Segment topologies are described in terms of the arrangements of their nodes relative to pin or port lists. The electrical behaviors for each segment are then defined. Interconnects may be grouped into families with similar characteristics or sharing identical segment definitions.

Quite Universal Circuit Simulator (Qucs) is a free-software electronics circuit simulator software released under GPL. It gives you the ability to set up a circuit with a graphical user interface and simulate the large-signal, small-signal and noise behaviour of the circuit. Pure digital simulations are also supported using VHDL and/or Verilog.
G.984, commonly known as GPON, is a standard for passive optical networks (PON) published by the ITU-T. It is commonly used to implement the last kilometre of Fibre To The Premises (FTTP) services.

Electronic circuit simulation uses mathematical models to replicate the behavior of an actual electronic device or circuit.
Simulation software allows for modeling of circuit operation and is an invaluable analysis tool. Due to its highly accurate modeling capability, many colleges and universities use this type of software for the teaching of electronics technician and electronics engineering programs. Electronics simulation software engages the user by integrating him or her into the learning experience. These kinds of interactions actively engage learners to analyze, synthesize, organize, and evaluate content and result in learners constructing their own knowledge.
Compact Software was the first commercially successful microwave computer-aided design (CAD) company. The company was founded in 1973 by Les Besser to commercialize his eponymous program COMPACT, released when he was at Farinon Electric Company.
Passivity is a property of engineering systems, used in a variety of engineering disciplines, but most commonly found in analog electronics and control systems. A passive component, depending on field, may be either a component that consumes but does not produce energy or a component that is incapable of power gain.






