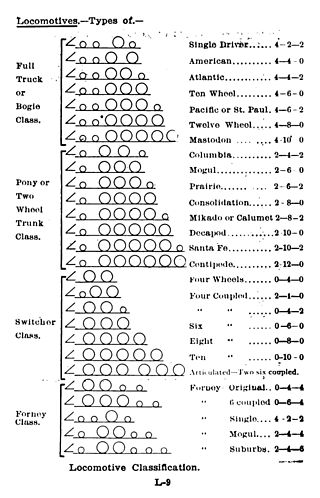
The Whyte notation is a classification method for steam locomotives, and some internal combustion locomotives and electric locomotives, by wheel arrangement. It was devised by Frederick Methvan Whyte, and came into use in the early twentieth century following a December 1900 editorial in American Engineer and Railroad Journal.
The UIC classification of locomotive axle arrangements, sometimes known as the German classification or German system, describes the wheel arrangement of locomotives, multiple units and trams. It is used in much of the world, notable exceptions being the United Kingdom, which uses a slightly simplified form of UIC, and in North America, where the AAR wheel arrangement system is used to describe diesel and electric locomotives. In North America, Whyte notation is only used for steam locomotives.

Four-wheel drive, also called 4×4 or 4WD, refers to a two-axled vehicle drivetrain capable of providing torque to all of its wheels simultaneously. It may be full-time or on-demand, and is typically linked via a transfer case providing an additional output drive shaft and, in many instances, additional gear ranges.

Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-6-0 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles and no trailing wheels. This arrangement is commonly called a Mogul.
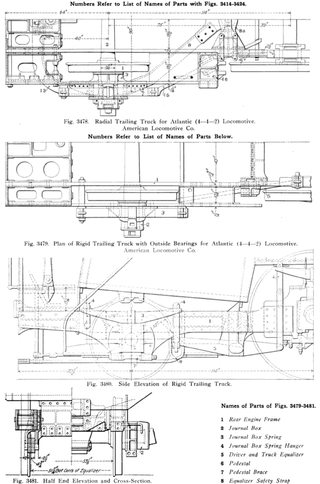
On a steam locomotive, a trailing wheel or trailing axle is generally an unpowered wheel or axle (wheelset) located behind the driving wheels. The axle of the trailing wheels is usually located in a trailing truck. On some large locomotives, a booster engine was mounted on the trailing truck to provide extra tractive effort when starting a heavy train and at low speeds on gradients.

The Union Pacific Railroad 9000 Class was a class of 88 steam locomotives, built by ALCO for the Union Pacific between 1926 and 1930.

The AA20 was a one-off steam locomotive constructed by the Soviet Union.

The Indian Railways primarily operates a fleet of electric and diesel locomotives, along with several compressed natural gas (CNG) locomotives. Steam locomotives are operated on a few World Heritage Sites and also run occasionally as heritage trains. A locomotive is also known as a loco or more popularly as an engine. The country's first steam locomotive ran on the Red Hill Railway from Red Hills to the Chintadripet bridge in Madras in 1837.
PKP classification system is a system of assigning letters and numbers to series and individual locomotives used by the PKP - Polish national railroad operator.
In Whyte notation, a 4-6-6-2 is a steam locomotive with four leading wheels in an unpowered bogie at the front of the locomotive followed by two sets of driving wheels with six wheels each, followed by two unpowered trailing wheels at the rear of the locomotive.
This page explains the numbering and classification schemes for locomotives employed by the Japanese Government Railways, the Japanese National Railways and the Japan Railways Group.

For more than a century, the Swiss locomotive, multiple unit, motor coach and railcar classification system, in either its original or updated forms, has been used to name and classify the rolling stock operated on the railways of Switzerland. It started out as a uniform system for the classification and naming of all rolling stock, powered and unpowered, but had been replaced and amended by the UIC classification of goods wagons.
Under the French classification system for locomotive wheel arrangements, the system is slightly different for steam and electric/diesel vehicles.
Railway coaches are classified under an international system developed by the UIC. This UIC classification of railway coaches replaced earlier national classification schemes in many countries, such as Germany. The coach class is expressed as a combination of letters. It is sometimes followed, for example in the Deutsche Bahn AG, by a three-figure class number. In a broader sense the vehicle number displayed on the coach is also part of its classification, because it encodes other technical details such as the top speed or the type of heating system used.
The leading wheel or leading axle or pilot wheel of a steam locomotive is an unpowered wheel or axle located in front of the driving wheels. The axle or axles of the leading wheels are normally located on a leading truck. Leading wheels are used to help the locomotive negotiate curves and to support the front portion of the boiler.

The Natal Government Railways Class I 2-6-0 of 1902 was a South African steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in the Colony of Natal.
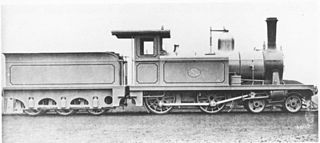
The Cape Government Railways 1st Class 4-4-0TT of 1881 was a South African steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in the Cape of Good Hope.

The Cape Government Railways 4th Class 4-6-0TT of 1884 was a South African steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in the Cape of Good Hope.

The Cape Government Railways NG 0-4-0T was a South African steam locomotive from the pre-Union era in the Cape of Good Hope.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.













