
The foreign relations of North Macedonia since its independence in 1991 have been characterized by the country's efforts to gain membership in international organizations such as NATO and the European Union and to gain international recognition under its previous constitutional name, overshadowed by a long-standing, dead-locked dispute with neighboring Greece. Greek objections to the country's name had led to it being admitted to the United Nations and several other international fora only under the provisional designation Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia until its official and erga omnes renaming to North Macedonia, a name under which it is now universally recognised.

The member states of the United Nations comprise 193 sovereign states. The United Nations (UN) is the world's largest intergovernmental organization. All members have equal representation in the UN General Assembly.
Succession of states is a concept in international relations regarding a successor state that has become a sovereign state over a territory that was previously under the sovereignty of another state. The theory has its roots in 19th-century diplomacy. A successor state often acquires a new international legal personality, which is distinct from a continuing state, also known as a continuator or historical heir, which despite changes to its borders retains the same legal personality and possess all its existing rights and obligations.

The flag of North Macedonia depicts a stylized yellow sun on a red field, with eight broadening rays extending from the center to the edge of the field. It was created by Miroslav Grčev and was adopted on 5 October 1995.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1244, adopted on 10 June 1999, after recalling resolutions 1160 (1998), 1199 (1998), 1203 (1998) and 1239 (1999), authorised an international civil and military presence in the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and established the United Nations Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo (UNMIK). It followed an agreement by Yugoslav President Slobodan Milošević to terms proposed by President of Finland Martti Ahtisaari and former Prime Minister of Russia Viktor Chernomyrdin on 8 June, involving withdrawal of all Yugoslav state forces from Kosovo.
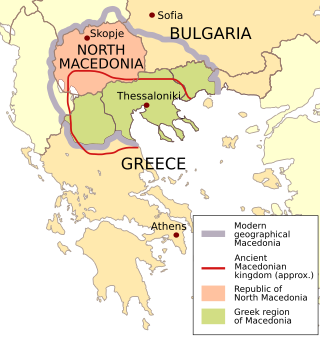
The use of the country name "Macedonia" was disputed between Greece and the Republic of Macedonia between 1991 and 2019. The dispute was a source of instability in the Western Balkans for 25 years. It was resolved through negotiations between the two countries, mediated by the United Nations, resulting in the Prespa Agreement, which was signed on 17 June 2018. Pertinent to its background is an early 20th-century multifaceted dispute and armed conflict that formed part of the background to the Balkan Wars. The specific naming dispute, although an existing issue in Yugoslav–Greek relations since World War II, was reignited after the breakup of Yugoslavia and the newly-gained independence of the former Socialist Republic of Macedonia in 1991. Since then, it was an ongoing issue in bilateral and international relations until it was settled with the Prespa agreement in June 2018, the subsequent ratification by the Macedonian and Greek parliaments in late 2018 and early 2019 respectively, and the official renaming of Macedonia to North Macedonia in February 2019.

Matthew Nimetz is an American diplomat and a former lawyer and retired managing director of a global private equity firm. He was the United Nations Special Representative for the naming dispute between Greece and the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia. He was also the Under Secretary of State for Security Assistance, Science, and Technology.

The accession of North Macedonia to the European Union has been on the current agenda for future enlargement of the EU since 2005, when it became an official candidate for accession. The then Republic of Macedonia submitted its membership application in 2004, thirteen years after its independence from Yugoslavia. It is one of nine current EU candidate countries, together with Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Georgia, Moldova, Montenegro, Serbia, Turkey and Ukraine.

United Nations Security Council resolution 753, adopted without a vote on 18 May 1992, after examining the application of the Republic of Croatia for membership in the United Nations, the Council recommended to the General Assembly that Croatia be admitted. The recommendation came amid the breakup of Yugoslavia.

United Nations Security Council resolution 755, adopted without a vote on 20 May 1992, after examining the application of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina for membership in the United Nations, the Council recommended to the General Assembly that Bosnia and Herzegovina be admitted. The recommendation came amid the breakup of Yugoslavia.
United Nations Security Council resolution 777, adopted unanimously on 19 September 1992, after reaffirming Resolution 713 (1992) and all subsequent resolutions on the topic, the Council considered that, as the state known as the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY) had ceased to exist, it noted that under Resolution 757 (1992), the claim by the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia to continue automatic membership in the United Nations was not widely accepted and so determined that membership of the SFRY in the United Nations could not continue. Therefore, the Council recommended to the General Assembly that the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia cease participation in the General Assembly and apply for membership in the United Nations.

United Nations Security Council resolution 821, adopted on 28 April 1993, after reaffirming Resolution 713 (1991) and all subsequent resolutions, the council also recalled resolutions 757 (1992), 777 (1992) and General Assembly Resolution 47/1 (1992) which stated that the state formerly known as the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia had ceased to exist and that it should apply for membership in the United Nations and until then should not participate in the General Assembly.

United Nations Security Council resolution 845, adopted unanimously on 18 June 1993, after recalling Resolution 817 (1993) and considering the secretary-General's report pursuant to it, the council urged both Greece and the Republic of Macedonia to continue efforts to settle the naming dispute.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1058, adopted on 30 May 1996, after recalling previous resolutions including resolutions 1027 (1995) and 1046 (1996), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Preventive Deployment Force (UNPREDEP) in Macedonia until 30 November 1996.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1082, adopted unanimously on 27 November 1996, after recalling previous resolutions including 1046 (1996) and 1058 (1996), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Preventive Deployment Force (UNPREDEP) in Macedonia until 31 May 1997 and reduced its size.
United Nations Security Council resolution 1105, adopted unanimously on 9 April 1997, after recalling Resolution 1082 (1996), the Council decided to suspend reduction of the military component of the United Nations Preventive Deployment Force (UNPREDEP) in Macedonia until the end of its current mandate, until 31 May 1997.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1142, adopted unanimously on 4 December 1997, after recalling resolutions 1105 (1997) and 1110 (1997), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Preventive Deployment Force (UNPREDEP) in Macedonia until 31 August 1998.

Democratic Federal Yugoslavia was a charter member of the United Nations from its establishment in 1945 as the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia until 1992 during the Yugoslav Wars. During its existence the country played a prominent role in the promotion of multilateralism and narrowing of the Cold War divisions in which various UN bodies were perceived as important vehicles. Yugoslavia was elected a non-permanent member of the United Nations Security Council on multiple occasions in periods between 1950 and 1951, 1956, 1972–1973, and 1988–1989, which was in total 7 years of Yugoslav membership in the organization. The country was also one of 17 original members of the Special Committee on Decolonization.

Albania and North Macedonia maintain diplomatic relations. Both countries are full members of the Council of Europe and of NATO. Both began European Union accession negotiations in March 2020. The Albanian language is an official language in Albania, while also being an official language in North Macedonia on a municipal level, if the ethnic Albanian population exceeds 20%, and ethnic Albanians make up the second largest community in North Macedonia.

The Agreement on Succession Issues of the Former Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia is an international agreement on shared state succession of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia reached among its former constituents republics following the breakup of the country in early 1990s.


















