
The major scale is one of the most commonly used musical scales, especially in Western music. It is one of the diatonic scales. Like many musical scales, it is made up of seven notes: the eighth duplicates the first at double its frequency so that it is called a higher octave of the same note.
In music theory, an interval is a difference in pitch between two sounds. An interval may be described as horizontal, linear, or melodic if it refers to successively sounding tones, such as two adjacent pitches in a melody, and vertical or harmonic if it pertains to simultaneously sounding tones, such as in a chord.

In music, a chord is a group of two or more notes played simultaneously, typically consisting of a root note, a third, and a fifth. Chords are the building blocks of harmony and form the harmonic foundation of a piece of music. They can be major, minor, diminished, augmented, or extended, depending on the intervals between the notes and their arrangement. Chords provide the harmonic support and coloration that accompany melodies and contribute to the overall sound and mood of a musical composition. For many practical and theoretical purposes, arpeggios and other types of broken chords may also be considered as chords in the right musical context.

In music, modulation is the change from one tonality to another. This may or may not be accompanied by a change in key signature. Modulations articulate or create the structure or form of many pieces, as well as add interest. Treatment of a chord as the tonic for less than a phrase is considered tonicization.
Modulation is the essential part of the art. Without it there is little music, for a piece derives its true beauty not from the large number of fixed modes which it embraces but rather from the subtle fabric of its modulation.
In music theory, a diminished triad is a triad consisting of two minor thirds above the root. It is a minor triad with a lowered (flattened) fifth. When using chord symbols, it may be indicated by the symbols "dim", "o", "m♭5", or "MI(♭5)". However, in most popular-music chord books, the symbol "dim" and "o" represents a diminished seventh chord, which in some modern jazz books and music theory books is represented by the "dim7" or "o7" symbols.

In music, the supertonic is the second degree of a diatonic scale, one whole step above the tonic. In the movable do solfège system, the supertonic note is sung as re.
In music, the subtonic is the degree of a musical scale which is a whole step below the tonic note. In a major key, it is a lowered, or flattened, seventh scale degree. It appears as the seventh scale degree in the natural minor and descending melodic minor scales but not in the major scale. In major keys, the subtonic sometimes appears in borrowed chords. In the movable do solfège system, the subtonic note is sung as te.
The diminished seventh chord is a four-note chord composed of a root note, together with a minor third, a diminished fifth, and a diminished seventh above the root:. For example, the diminished seventh chord built on B, commonly written as Bo7, has pitches B-D-F-A♭:
In music, a minor seventh chord is a seventh chord composed of a root note, a minor third, a perfect fifth, and a minor seventh. In other words, one could think of it as a minor triad with a minor seventh attached to it.
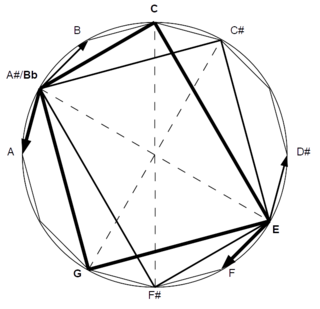
In music theory, chord substitution is the technique of using a chord in place of another in a progression of chords, or a chord progression. Much of the European classical repertoire and the vast majority of blues, jazz and rock music songs are based on chord progressions. "A chord substitution occurs when a chord is replaced by another that is made to function like the original. Usually substituted chords possess two pitches in common with the triad that they are replacing."

Jazz harmony is the theory and practice of how chords are used in jazz music. Jazz bears certain similarities to other practices in the tradition of Western harmony, such as many chord progressions, and the incorporation of the major and minor scales as a basis for chordal construction. In jazz, chords are often arranged vertically in major or minor thirds, although stacked fourths are also quite common. Also, jazz music tends to favor certain harmonic progressions and includes the addition of tensions, intervals such as 9ths, 11ths, and 13ths to chords. Additionally, scales unique to style are used as the basis of many harmonic elements found in jazz. Jazz harmony is notable for the use of seventh chords as the basic harmonic unit more often than triads, as in classical music. In the words of Robert Rawlins and Nor Eddine Bahha, "7th chords provide the building blocks of jazz harmony."

Rhythm changes is a common 32-bar jazz chord progression derived from George Gershwin's "I Got Rhythm". The progression is in AABA form, with each A section based on repetitions of the ubiquitous I–vi–ii–V sequence (or variants such as iii–vi–ii–V), and the B section using a circle of fifths sequence based on III7–VI7–II7–V7, a progression which is sometimes given passing chords.
The harmonic minor scale is a musical scale derived from the natural minor scale, with the minor seventh degree raised by one semitone to a major seventh, creating an augmented second between the sixth and seventh degrees.
In music theory, the half-diminished seventh chord is a seventh chord composed of a root note, together with a minor third, a diminished fifth, and a minor seventh. For example, the half-diminished seventh chord built on B, commonly written as Bm7(♭5), or Bø7, has pitches B-D-F-A:
The Nashville Number System is a method of transcribing music by denoting the scale degree on which a chord is built. It was developed by Neal Matthews Jr in the late 1950s as a simplified system for the Jordanaires to use in the studio and further developed by Charlie McCoy. It resembles the Roman numeral and figured bass systems traditionally used to transcribe a chord progression since the 1700s. The Nashville Number System was compiled and published in a book by Chas. Williams in 1988.
The Nashville Number System is a trick that musicians use to figure out chord progressions on the fly. It is an easy tool to use if you understand how music works. It has been around for about four hundred years, but sometime during the past fifty years [approximately 1953–2003], Nashville got the credit.
The Nashville numbering system provided us the shorthand that we needed so that we could depend on our ears rather than a written arrangement. It took far less time to jot the chords, and once you had the chart written, it applied to any key. The beauty of the system is that we don't have to read. We don't get locked into an arrangement that we may feel is not as good as one we can improvise.
In music, harmonization is the chordal accompaniment to a line or melody: "Using chords and melodies together, making harmony by stacking scale tones as triads".
In music theory, Roman numeral analysis is a type of harmonic analysis in which chords are represented by Roman numerals, which encode the chord's degree and harmonic function within a given musical key.
Musicians use various kinds of chord names and symbols in different contexts to represent musical chords. In most genres of popular music, including jazz, pop, and rock, a chord name and its corresponding symbol typically indicate one or more of the following:
- the root note,
- the chord quality,
- whether the chord is a triad, seventh chord, or an extended chord,
- any altered notes,
- any added tones, and
- the bass note if it is not the root.
The jazz minor scale or ascending melodic minor scale is a derivative of the melodic minor scale, except only the ascending form of the scale is used. As the name implies, it is primarily used in jazz, although it may be found in other types of music as well. It may be derived from the major scale with a minor third, making it a synthetic scale, and features a dominant seventh chord on the fifth degree (V) like the harmonic minor scale. It can also be derived from the diatonic Dorian mode with a major seventh.

The Royal Road progression (王道進行, ōdō shinkō), also known as the IVM7–V7–iii7–vi progression or koakuma chord progression (小悪魔コード進行, koakuma kōdo shinkō), is a common chord progression within contemporary Japanese pop music.






