Related Research Articles
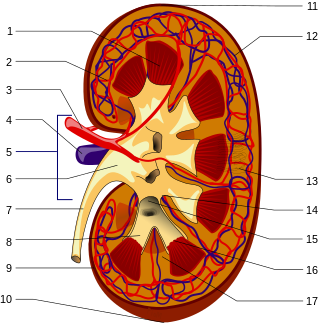
Nephrology is a specialty for both adult internal medicine and pediatric medicine that concerns the study of the kidneys, specifically normal kidney function and kidney disease, the preservation of kidney health, and the treatment of kidney disease, from diet and medication to renal replacement therapy. The word "renal" is an adjective meaning "relating to the kidneys", and its roots are French or late Latin. Whereas according to some opinions, "renal" and "nephro" should be replaced with "kidney" in scientific writings such as "kidney medicine" or "kidney replacement therapy", other experts have advocated preserving the use of renal and nephro as appropriate including in "nephrology" and "renal replacement therapy", respectively.
Albuminuria is a pathological condition wherein the protein albumin is abnormally present in the urine. It is a type of proteinuria. Albumin is a major plasma protein ; in healthy people, only trace amounts of it are present in urine, whereas larger amounts occur in the urine of patients with kidney disease. For a number of reasons, clinical terminology is changing to focus on albuminuria more than proteinuria.

Creatinine is a breakdown product of creatine phosphate from muscle and protein metabolism. It is released at a constant rate by the body.

Proteinuria is the presence of excess proteins in the urine. In healthy persons, urine contains very little protein, less than 150 mg/day; an excess is suggestive of illness. Excess protein in the urine often causes the urine to become foamy. Severe proteinuria can cause nephrotic syndrome in which there is worsening swelling of the body.

Nephrotic syndrome is a collection of symptoms due to kidney damage. This includes protein in the urine, low blood albumin levels, high blood lipids, and significant swelling. Other symptoms may include weight gain, feeling tired, and foamy urine. Complications may include blood clots, infections, and high blood pressure.

Kidney failure, also known as end-stage renal disease (ESRD), is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as either acute kidney failure, which develops rapidly and may resolve; and chronic kidney failure, which develops slowly and can often be irreversible. Symptoms may include leg swelling, feeling tired, vomiting, loss of appetite, and confusion. Complications of acute and chronic failure include uremia, hyperkalemia, and volume overload. Complications of chronic failure also include heart disease, high blood pressure, and anaemia.

Renal functions include maintaining an acid–base balance; regulating fluid balance; regulating sodium, potassium, and other electrolytes; clearing toxins; absorption of glucose, amino acids, and other small molecules; regulation of blood pressure; production of various hormones, such as erythropoietin; and activation of vitamin D.

Urinalysis, a portmanteau of the words urine and analysis, is a panel of medical tests that includes physical (macroscopic) examination of the urine, chemical evaluation using urine test strips, and microscopic examination. Macroscopic examination targets parameters such as color, clarity, odor, and specific gravity; urine test strips measure chemical properties such as pH, glucose concentration, and protein levels; and microscopy is performed to identify elements such as cells, urinary casts, crystals, and organisms.

Assessment of kidney function occurs in different ways, using the presence of symptoms and signs, as well as measurements using urine tests, blood tests, and medical imaging.

Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a type of kidney disease in which a gradual loss of kidney function occurs over a period of months to years. Initially generally no symptoms are seen, but later symptoms may include leg swelling, feeling tired, vomiting, loss of appetite, and confusion. Complications can relate to hormonal dysfunction of the kidneys and include high blood pressure, bone disease, and anemia. Additionally CKD patients have markedly increased cardiovascular complications with increased risks of death and hospitalization.

Cystinuria is an inherited autosomal recessive disease characterized by high concentrations of the amino acid cystine in the urine, leading to the formation of cystine stones in the kidneys, ureters, and bladder. It is a type of aminoaciduria. "Cystine", not "cysteine," is implicated in this disease; the former is a dimer of the latter.

Diabetic nephropathy, also known as diabetic kidney disease, is the chronic loss of kidney function occurring in those with diabetes mellitus. Diabetic nephropathy is the leading causes of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and end-stage renal disease (ESRD) globally. The triad of protein leaking into the urine, rising blood pressure with hypertension and then falling renal function is common to many forms of CKD. Protein loss in the urine due to damage of the glomeruli may become massive, and cause a low serum albumin with resulting generalized body swelling (edema) so called nephrotic syndrome. Likewise, the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) may progressively fall from a normal of over 90 ml/min/1.73m2 to less than 15, at which point the patient is said to have end-stage renal disease. It usually is slowly progressive over years.

Hypertensive kidney disease is a medical condition referring to damage to the kidney due to chronic high blood pressure. It manifests as hypertensive nephrosclerosis. It should be distinguished from renovascular hypertension, which is a form of secondary hypertension, and thus has opposite direction of causation.
Protein toxicity is the effect of the buildup of protein metabolic waste compounds, like urea, uric acid, ammonia, and creatinine. Protein toxicity has many causes, including urea cycle disorders, genetic mutations, excessive protein intake, and insufficient kidney function, such as chronic kidney disease and acute kidney injury. Symptoms of protein toxicity include unexplained vomiting and loss of appetite. Untreated protein toxicity can lead to serious complications such as seizures, encephalopathy, further kidney damage, and even death.

Nephritic syndrome is a syndrome comprising signs of nephritis, which is kidney disease involving inflammation. It often occurs in the glomerulus, where it is called glomerulonephritis. Glomerulonephritis is characterized by inflammation and thinning of the glomerular basement membrane and the occurrence of small pores in the podocytes of the glomerulus. These pores become large enough to permit both proteins and red blood cells to pass into the urine. By contrast, nephrotic syndrome is characterized by proteinuria and a constellation of other symptoms that specifically do not include hematuria. Nephritic syndrome, like nephrotic syndrome, may involve low level of albumin in the blood due to the protein albumin moving from the blood to the urine.
Microalbuminuria is a term to describe a moderate increase in the level of urine albumin. It occurs when the kidney leaks small amounts of albumin into the urine, in other words, when an abnormally high permeability for albumin in the glomerulus of the kidney occurs. Normally, the kidneys filter albumin, so if albumin is found in the urine, then it is a marker of kidney disease. The term microalbuminuria is now discouraged by Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes and has been replaced by moderately increased albuminuria.
The fractional excretion of sodium (FENa) is the percentage of the sodium filtered by the kidney which is excreted in the urine. It is measured in terms of plasma and urine sodium, rather than by the interpretation of urinary sodium concentration alone, as urinary sodium concentrations can vary with water reabsorption. Therefore, the urinary and plasma concentrations of sodium must be compared to get an accurate picture of kidney clearance. In clinical use, the fractional excretion of sodium can be calculated as part of the evaluation of acute kidney failure in order to determine if hypovolemia or decreased effective circulating plasma volume is a contributor to the kidney failure.
Glomerulonephrosis is a non-inflammatory disease of the kidney (nephrosis) presenting primarily in the glomerulus as nephrotic syndrome. The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney and it contains the glomerulus, which acts as a filter for blood to retain proteins and blood lipids. Damage to these filtration units results in important blood contents being released as waste in urine. This disease can be characterized by symptoms such as fatigue, swelling, and foamy urine, and can lead to chronic kidney disease and ultimately end-stage renal disease, as well as cardiovascular diseases. Glomerulonephrosis can present as either primary glomerulonephrosis or secondary glomerulonephrosis.

Orthostatic albuminuria, also known as orthostatic proteinuria is defined by raised levels of urine protein excretion while in an upright position. In orthostatic albuminuria urine protein excretion returns to normal while in a supine position, such as laying down. Orthostatic albuminuria is the most common cause of isolated proteinuria in those under 20. The prevalence of orthostatic albuminuria is suspected to be between 2 and 5%, however some studies suggest that it is more common. Orthostatic albuminuria is diagnosed if urine protein levels are normal in a morning urine sample and there are no other obvious causes of albuminuria. Patients with orthostatic albuminuria are often asymptomatic and there is no indication for any type of treatment or interventions.
A renal diet is a diet aimed at keeping levels of fluids, electrolytes, and minerals balanced in the body in individuals with chronic kidney disease or who are on dialysis. Dietary changes may include the restriction of fluid intake, protein, and electrolytes including sodium, phosphorus, and potassium. Calories may also be supplemented if the individual is losing weight undesirably.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Yang, Chih-Yu; Chen, Fu-An; Chen, Chun-Fan; Liu, Wen-Sheng; Shih, Chia-Jen; Ou, Shuo-Ming; Yang, Wu-Chang; Lin, Chih-Ching; Yang, An-Hang (2015-09-09). Kim, Jayoung (ed.). "Diagnostic Accuracy of Urine Protein/Creatinine Ratio Is Influenced by Urine Concentration". PLOS ONE. 10 (9). Public Library of Science (PLoS): e0137460. Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1037460Y. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137460 . ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 4564100 . PMID 26353117.
- ↑ "Protein urine test: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia". MedlinePlus. 2019-05-08. Retrieved 2019-05-21.
- ↑ "Protein in Urine: MedlinePlus Lab Test Information". MedlinePlus. 2019-04-15. Retrieved 2019-05-21.
- ↑ National Kidney Foundation (2002), "K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification", American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 39 (2 Suppl 1): S1–266, ISSN 0272-6386, PMID 11904577
- ↑ Ginsberg, Jay M.; Chang, Bruce S.; Matarese, Richard A.; Garella, Serafino (1983-12-22). "Use of Single Voided Urine Samples to Estimate Quantitative Proteinuria". The New England Journal of Medicine. 309 (25). Massachusetts Medical Society: 1543–1546. doi:10.1056/nejm198312223092503. ISSN 0028-4793. PMID 6656849.
- 1 2 3 "Urine Protein". Lab Tests Online. Retrieved 2019-05-21.
- ↑ "Summary of Recommendation Statements". Kidney International Supplements. 3 (1). Elsevier BV: 5–14. 2013. doi:10.1038/kisup.2012.77. ISSN 2157-1716. PMC 4284512 . PMID 25598998.