Related Research Articles
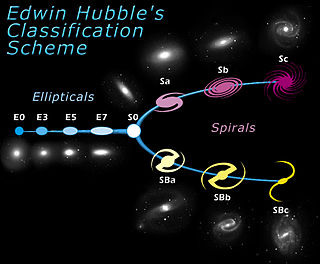
The Hubble sequence is a morphological classification scheme for galaxies invented by Edwin Hubble in 1926. It is often colloquially known as the Hubble tuning fork diagram because the shape in which it is traditionally represented resembles a tuning fork.

The New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars is an astronomical catalogue of deep-sky objects compiled by John Louis Emil Dreyer in 1888. The NGC contains 7,840 objects, including galaxies, star clusters and emission nebulae. Dreyer published two supplements to the NGC in 1895 and 1908, known as the Index Catalogues, describing a further 5,386 astronomical objects. Thousands of these objects are best known by their NGC or IC numbers, which remain in widespread use.

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the first high-precision measurements of the intrinsic brightnesses, proper motions, and parallaxes of stars, enabling better calculations of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial velocity measurements from spectroscopy, astrophysicists were able to finally measure all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.
VV, V V, or v. v. may refer to:

Halton Christian "Chip" Arp was an American astronomer. He was known for his 1966 Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies, which catalogues many examples of interacting and merging galaxies, though Arp disputed the idea, claiming apparent associations were prime examples of ejections. Arp was also known as a critic of the Big Bang theory and for advocating a non-standard cosmology incorporating intrinsic redshift.

Boris Aleksandrovich Vorontsov-Velyaminov was a Russian astrophysicist. His name is sometimes given as Vorontsov-Vel'yaminov.
The Third Cambridge Catalogue of Radio Sources (3C) is an astronomical catalogue of celestial radio sources detected originally at 159 MHz, and subsequently at 178 MHz.

An astronomical survey is a general map or image of a region of the sky that lacks a specific observational target. Alternatively, an astronomical survey may comprise a set of images, spectra, or other observations of objects that share a common type or feature. Surveys are often restricted to one band of the electromagnetic spectrum due to instrumental limitations, although multiwavelength surveys can be made by using multiple detectors, each sensitive to a different bandwidth.
The Astronomical Observatory of Belogradchik or Belogradchik Observatory is an astronomical observatory owned and operated by the Institute of Astronomy of the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences. It is located near the town of Belogradchik in northwestern Bulgaria, at the foot of the Western Balkan Mountains. The other observatory operated by the same institute is the Rozhen Observatory.

A tidal tail is a thin, elongated region of stars and interstellar gas that extends into space from a galaxy. Tidal tails occur as a result of galactic tide forces between interacting galaxies. Examples of galaxies with tidal tails include the Tadpole Galaxy and the Mice Galaxies. Tidal forces can eject a significant amount of a galaxy's gas into the tail; within the Antennae Galaxies, for example, nearly half of the observed gaseous matter is found within the tail structures. Within those galaxies which have tidal tails, approximately 10% of the galaxy's stellar formation takes place in the tail. Overall, roughly 1% of all stellar formation in the known universe occurs within tidal tails.
The Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg is a data centre which collects and distributes astronomical information . It was established in 1972 under the name Centre de Données Stellaires by the National Institute of Astronomy and Geophysics (INAG). The on-line services currently provided by the CDS include:

Arp 104, also known as Keenan's system, is entry 104 in Halton Arp's Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies catalog for spiral galaxy NGC 5216 and globular galaxy NGC 5218. The two galaxies are joined by a bridge of galactic material spanning 22 000 light years.
The Morphological Catalogue of Galaxies(MCG) or Morfologiceskij Katalog Galaktik, is a Russian catalogue of 30,642 galaxies compiled by Boris Vorontsov-Velyaminov and V. P. Arkhipova. It is based on scrutiny of prints of the Palomar Sky Survey plates, and putatively complete to a photographic magnitude of 15. Including galaxies to magnitude 16 would have resulted in an unmanageably large dataset.

An astronomical catalog or catalogue is a list or tabulation of astronomical objects, typically grouped together because they share a common type, morphology, origin, means of detection, or method of discovery. The oldest and largest are star catalogues. Hundreds have been published, including general ones and special ones for such items as infrared stars, variable stars, giant stars, multiple star systems, star clusters, and so forth.

NGC 5238 is an irregular galaxy in the constellation Canes Venatici. Located at a comoving distance of 4.51 Mpc, it is 64.4 arcseconds in diameter. It has sometimes been classified as a blue compact dwarf galaxy. Although some authors have hypothesized it to be a member of the M101 Group of galaxies, it is currently believed to be an isolated galaxy.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to galaxies:

NGC 965 is a spiral galaxy approximately 294 million light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Cetus. It was discovered by American astronomer Ormond Stone in 1886 with the 26" refractor at Leander McCormick Observatory.

NGC 4513 is a lenticular galaxy and a ring galaxy located about 110 million light-years away in the constellation Draco. It was discovered by astronomer Heinrich d'Arrest on October 16, 1866.
References
- ↑ Vorontsov-Velyaminov, B.A. (1959). Atlas and Catalogue of interacting galaxies. Part 1. Moscow: SAI. OCLC 657642954.
- ↑ Vorontsov-Velyaminov B.A. (1977). "Atlas of interacting galaxies, part II and the concept of fragmentation of galaxies". Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 28: 1–117. Bibcode:1977A&AS...28....1V.