Alternative or alternate may refer to:

The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) is an intergovernmental organization within the United Nations Secretariat that promotes the interests of developing countries in world trade. It was established in 1964 by the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) and reports to that body and the United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC). UNCTAD is composed of 195 member states and works with nongovernmental organizations worldwide; its permanent secretariat is in Geneva, Switzerland.
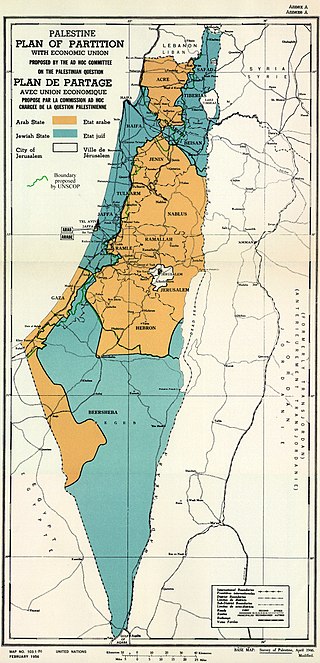
The United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine was a proposal by the United Nations, which recommended a partition of Mandatory Palestine at the end of the British Mandate. On 29 November 1947, the UN General Assembly adopted the Plan as Resolution 181 (II).
Ticket or tickets may refer to:
A white paper is a report or guide that informs readers concisely about a complex issue and presents the issuing body's philosophy on the matter. It is meant to help readers understand an issue, solve a problem, or make a decision. A white paper is the first document researchers should read to better understand a core concept or idea. Since the 1990s, this type of document has proliferated in business. Today, a business-to-business (B2B) white paper is closer to a marketing presentation, a form of content meant to persuade customers and partners and promote a certain product or viewpoint. That makes B2B white papers a type of grey literature.

The Churchill White Paper of 3 June 1922 was drafted at the request of Winston Churchill, then Secretary of State for the Colonies, partly in response to the 1921 Jaffa Riots. The official name of the document was Palestine: Correspondence with the Palestine Arab Delegation and the Zionist Organisation. The white paper was made up of nine documents and "Churchill's memorandum" was an enclosure to document number 5. While maintaining Britain's commitment to the Balfour Declaration and its promise of a Jewish national home in Mandatory Palestine, the paper emphasized that the establishment of a national home would not impose a Jewish nationality on the Arab inhabitants of Palestine. To reduce tensions between the Arabs and Jews in Palestine the paper called for a limitation of Jewish immigration to the economic capacity of the country to absorb new arrivals. This limitation was considered a great setback to many in the Zionist movement, though it acknowledged that the Jews should be able to increase their numbers through immigration rather than sufferance.
Salvador, meaning "salvation" in Catalan, Spanish, and Portuguese may refer to:

The White Paper of 1939 was a policy paper issued by the British government, led by Neville Chamberlain, in response to the 1936–1939 Arab revolt in Palestine. After its formal approval in the House of Commons on 23 May 1939, it acted as the governing policy for Mandatory Palestine from 1939 to the 1948 British departure. After the war, the Mandate was referred to the United Nations.
The colón was the currency of El Salvador from 1892 until 2001, when it was replaced by the U.S. dollar during the presidency of Francisco Flores. The colón was subdivided into 100 centavos and its ISO 4217 code was SVC. The plural is "colones" in Spanish and the currency was named after Christopher Columbus, known as Cristóbal Colón in Spanish.
Paper is a thin, flat material produced by the compression of fibres.
Green Book or The Green Book may refer to:

The Salvadoran Civil War was a twelve-year period of civil war in El Salvador that was fought between the government of El Salvador and the Farabundo Martí National Liberation Front (FMLN), a coalition or "umbrella organization" of left-wing groups backed by the Cuban regime of Fidel Castro as well as the Soviet Union. A coup on 15 October 1979 followed by government killings of anti-coup protesters is widely seen as the start of civil war. The war did not formally end until 16 January 1992 with the signing of the Chapultepec Peace Accords in Mexico City.
El Salvador is a country in Central America.

Jon David Glassman is a former U.S. State Department official. He is best known for having authored the "White Paper" on Communist intervention in El Salvador published by the U.S. State Department in 1981. Glassman also served as Deputy National Security Advisor for former Vice President Dan Quayle.
On February 23, 1981, the U.S. State Department released a document titled "Communist Interference in El Salvador: Documents Demonstrating Communist Support of the Salvadoran Insurgency", also known as "the White Paper". The document was used as justification for U.S. intervention in Nicaragua. Critics charged that the technique deployed by the White Paper was to correlate events in El Salvador into alleged examples of Soviet and Cuban military involvement. The White Paper was claimed to be part of a propaganda effort to divert attention from U.S. support for a repressive regime by creating a false threat of communist insurgency.
The Palestine white papers are the British government statements of policy presented to Parliament regarding Mandatory Palestine, issued between 1922 and 1946.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.





