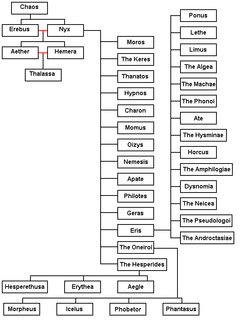
In Greek mythology, Erebus, or Erebos, was often conceived as a primordial deity, representing the personification of darkness; for instance, Hesiod's Theogony identifies him as one of the first five beings in existence, born of Chaos.

A thunderbolt or lightning bolt is a symbolic representation of lightning when accompanied by a loud thunderclap. In Indo-European mythology, the thunderbolt was identified with the 'Sky Father'; this association is also found in later Hellenic representations of Zeus and Vedic descriptions of the vajra wielded by the god Indra. It may have been a symbol of cosmic order, as expressed in the fragment from Heraclitus describing "the Thunderbolt that steers the course of all things".
In Norse mythology, Jörmungandr, also known as the Midgard Serpent or World Serpent, is a sea serpent, the middle child of Loki and the giantess Angrboða. According to the Prose Edda, Odin took Loki's three children by Angrboða—the wolf Fenrir, Hel, and Jörmungandr—and tossed Jörmungandr into the great ocean that encircles Midgard. The serpent grew so large that it was able to surround the Earth and grasp its own tail. As a result, it received the name of World Serpent. When it releases its tail, Ragnarök will begin. Jörmungandr's arch-enemy is the thunder-god, Thor. It is an example of an ouroboros.

Hindu mythology are found in Hindu texts such as the Vedic literature, epics like Mahabharata and Ramayana, the Puranas, and regional literature like the Tamil Periya Puranam and the Mangal Kavya of Bengal. Hindu mythology is also found in widely translated popular texts such as the fables of the Panchatantra and the Hitopadesha, as well as in Southeast Asian texts.

Chinese mythology is mythology that has been passed down in oral form or recorded in literature in the geographic area now known as "China". Chinese mythology includes many varied myths from regional and cultural traditions. Much of the mythology involves exciting stories full of fantastic people and beings, the use of magical powers, often taking place in an exotic mythological place or time. Like many mythologies, Chinese mythology has in the past been believed to be, at least in part, a factual recording of history. Along with Chinese folklore, Chinese mythology forms an important part of Chinese folk religion. Many stories regarding characters and events of the distant past have a double tradition: ones which present a more historicized or euhemerized version and ones which presents a more mythological version.

Germanic mythology consists of the body of myths native to the Germanic peoples. The category includes Norse mythology, Anglo-Saxon mythology, and Continental Germanic mythology. It was a key element of Germanic paganism.

Persian mythology or Iranian mythology is the body of the myths originally told by ancient Persians and other Iranian peoples, and a genre of Ancient Persian folklore. These stories concern the origin and nature of the world, the lives and activities of deities, heroes, and mythological creatures, and the origins and significance of the ancient Persians' own cult and ritual practices. Modern scholars study the myths to shed light on the religious and political institutions of not only modern-day Iran but the Greater Iran, which includes regions of West Asia, Central Asia, South Asia and Transcaucasia where Iranian culture has had significant influence. Historically, these were regions long ruled by dynasties of various Iranian empires, that incorporated considerable aspects of Persian culture through extensive contact with them, or where sufficient Iranian peoples settled to still maintain communities who patronize their respective cultures. It roughly corresponds to the Iranian plateau and its bordering plains. The Encyclopædia Iranica uses the term Iranian Cultural Continent for this region.

Philippine mythology is the body of stories and epics originating from, and part of, the indigenous Philippine folk religions, which include various ethnic faiths distinct from one another. Philippine mythology is incorporated from various sources, having similarities with Indonesian and Malay myths, as well as Hindu, Muslim, Shinto, Buddhist, and Christian traditions, such as the notion of heaven, hell, and the human soul. Philippine mythology attempts to explain the nature of the world through the lives and actions of heroes, deities, and mythological creatures. The majority of these myths were passed on through oral tradition, and preserved through the aid of community spiritual leaders or shamans and community elders.

Virgo (♍︎) is the sixth astrological sign in the Zodiac. It spans the 150–180th degree of the zodiac. Under the tropical zodiac, the Sun transits this area on average between August 23 and September 22, and the Sun transits the constellation Virgo from approximately September 16 to October 30. Individuals born during these dates, depending on which system of astrology they subscribe to, may be called Virgos or Virgoans; they are also represented in newspaper horoscopes with other astrological signs. The symbol of the maiden is based on Astraea. In Greek mythology, she was the last immortal to abandon Earth at the end of the Silver Age, when the gods fled to Olympus – hence the sign's association with Earth.

In mythology and the study of folklore and religion, a trickster is a character in a story who exhibits a great degree of intellect or secret knowledge and uses it to play tricks or otherwise disobey normal rules and defy conventional behavior.

Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the origin and nature of the world, the lives and activities of deities, heroes, and mythological creatures, and the origins and significance of the ancient Greeks' own cult and ritual practices. Modern scholars study the myths to shed light on the religious and political institutions of ancient Greece, and to better understand the nature of myth-making itself.

Norse mythology is the body of myths of the North Germanic peoples, stemming from Norse paganism and continuing after the Christianization of Scandinavia, and into the Scandinavian folklore of the modern period. The northernmost extension of Germanic mythology, Norse mythology consists of tales of various deities, beings, and heroes derived from numerous sources from both before and after the pagan period, including medieval manuscripts, archaeological representations, and folk tradition.
Myth is a folklore genre consisting of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society, such as foundational tales or origin myths. The main characters in myths are usually non-humans, such as gods, demigods, and other supernatural figures. However, others also include humans, animals, or combinations in their classificiation of myth. Stories of everyday human beings, although often of leaders of some type, are usually contained in legends, as opposed to myths. Myths are sometimes distinguished from legends in that myths deal with gods, usually have no historical basis, and are set in a world of the remote past, very different from that of the present.

Roman mythology is the body of myths of ancient Rome as represented in the literature and visual arts of the Romans. One of a wide variety of genres of Roman folklore, Roman mythology may also refer to the modern study of these representations, and to the subject matter as represented in the literature and art of other cultures in any period. Roman mythology draws from the mythology of the Italic peoples and ultimately from Proto-Indo-European mythology.

Celtic is the mythology of Celtic polytheism, the religion of the Iron Age Celts. Like other Iron Age Europeans, the early Celts maintained a polytheistic mythology and religious structure. For Celts in close contact with Ancient Rome, such as the Gauls and Celtiberians, their mythology did not survive the Roman Empire, their subsequent conversion to Christianity and the loss of their Celtic languages. It is mostly through contemporary Roman and Christian sources that their mythology has been preserved. The Celtic peoples who maintained either political or linguistic identities left vestigial remnants of their ancestral mythologies that were put into written form during the Middle Ages.












