Yeast extract agar is a growth medium containing yeast extract. It may refer to:
- The nonselective yeast extract agar of Windle Taylor
- YM (selective medium), for yeasts and molds
- Buffered charcoal yeast extract agar, for Legionella
Yeast extract agar is a growth medium containing yeast extract. It may refer to:

Yeast extracts consist of the cell contents of yeast without the cell walls; they are used as food additives or flavorings, or as nutrients for bacterial culture media. They are often used to create savory flavors and umami taste sensations, and can be found in a large variety of packaged food, including frozen meals, crackers, snack foods, gravy, stock and more. They are rich in B vitamins, and so are of particular importance to vegans and vegetarians. Yeast extracts and fermented foods contain glutamic acid, an amino acid which adds an umami flavor. Glutamic acid is found in meat, cheese, fungi, and vegetables—such as broccoli, and tomatoes.

An agar plate is a Petri dish that contains a growth medium solidified with agar, used to culture microorganisms. Sometimes selective compounds are added to influence growth, such as antibiotics.

A growth medium or culture medium is a solid, liquid, or semi-solid designed to support the growth of a population of microorganisms or cells via the process of cell proliferation or small plants like the moss Physcomitrella patens. Different types of media are used for growing different types of cells.

YEPD or yeast extract peptone dextrose, also often abbreviated as YPD, is a complete medium for yeast growth. It contains yeast extract, peptone, double-distilled water, and glucose (dextrose). It can be used as solid medium by including agar. The yeast extract will typically contain all the amino acids necessary for growth. By being a complete medium, YEPD cannot be used as a selection medium to test for auxotrophs. Instead, YEPD is used as a growth medium to grow yeast cultures.

Lysogeny broth (LB) is a nutritionally rich medium primarily used for the growth of bacteria. Its creator, Giuseppe Bertani, intended LB to stand for lysogeny broth, but LB has also come to colloquially mean Luria broth, Lennox broth, life broth or Luria–Bertani medium. The formula of the LB medium was published in 1951 in the first paper of Bertani on lysogeny. In this article he described the modified single-burst experiment and the isolation of the phages P1, P2, and P3. He had developed the LB medium to optimize Shigella growth and plaque formation.
YEM may refer to:
YMG may refer to:

Potato dextrose agar and potato dextrose broth are common microbiological growth media made from potato infusion and dextrose. Potato dextrose agar is the most widely used medium for growing fungi and bacteria.
Buffered charcoal yeast extract (BCYE) agar is a selective growth medium used to culture or grow certain types of bacteria, particularly the Gram-negative species Legionella pneumophila. It has also been used for the laboratory diagnosis of Acanthamoeba keratitis, Francisella and Nocardia.
Plate Count Agar (PCA), also called Standard Methods Agar (SMA), is a microbiological growth medium commonly used to assess or to monitor "total" or viable bacterial growth of a sample. PCA is not a selective medium.
R2A agar is a culture medium developed to study bacteria which normally inhabit potable water. These bacteria tend to be slow-growing species and would quickly be suppressed by faster-growing species on a richer culture medium.
De Man, Rogosa and Sharpe agar, often abbreviated to MRS, is a selective culture medium designed to favour the luxuriant growth of Lactobacilli for lab study. Developed in 1960, this medium was named for its inventors, Johannes Cornelis de Man, Morrison Rogosa and Margaret Elisabeth Sharpe. It contains sodium acetate, which suppresses the growth of many competing bacteria. This medium has a clear brown colour.
YM Agar and Broth, is a selective growth medium with low pH useful for cultivating yeasts, molds, or other acid-tolerant or acidophilic organisms, while deterring growth of most bacteria and other acid intolerant organisms. It is Malt extract medium modified by the addition of Yeast extract and peptone.

Nutrient agar is a general purpose medium supporting growth of a wide range of non-fastidious organisms. It typically contains (mass/volume):

Sabouraud agar or Sabouraud dextrose agar (SDA) is a type of agar growth medium containing peptones. It is used to cultivate dermatophytes and other types of fungi, and can also grow filamentous bacteria such as Nocardia. It has utility for research and clinical care.
TSBV is the acronym for tryptic soy-serum-bacitracin-vancomycin, a type of agar plate medium used in microbiological testing to select for Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans (A.a.). It was described by Jørgen Slots in 1982, who also discovered the role of A.a. in periodontitis.
This bacterial growth medium was developed in 1971 for Lactococcus species isolated from milk products. It was originally called M16 medium, but in 1975 Terzaghi and Sandine added disodium-β-glycerophosphate to the medium as a buffer, and named the new growth medium M17 medium. It was later found that the addition of disodium-β-glycerophosphate inhibits the growth of many Lactobacillus species.
C.D.V. agar is a nutrient medium prepared using Cicer arietinum, Daucus carota (carrot) and Vigna radiata by Mr. Vinay J. Rao and Mr. Keshava Murthy P. at Surana College, Bangalore, India under the guidance of their botany lecturers, Prof. B.R Chandrashekarappa, Mrs. Sharada H.C., and with the aid of their classmates from Vijaya College, Bangalore.

The NYC medium or GC medium agar is used for isolating Gonococci.
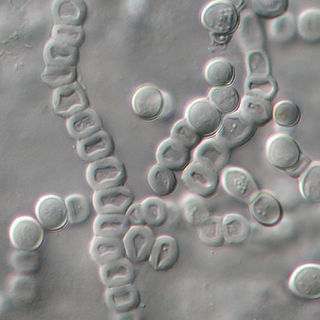
Trichophyton verrucosum, commonly known as the cattle ringworm fungus, is a dermatophyte largely responsible for fungal skin disease in cattle, but is also a common cause of ringworm in donkeys, dogs, goat, sheep, and horses. It has a worldwide distribution, however human infection is more common in rural areas where contact with animals is more frequent, and can cause severe inflammation of the afflicted region. Trichophyton verrucosum was first described by Emile Bodin in 1902.