Aromatic compounds are those chemical compounds that contain one or more rings with pi electrons delocalized all the way around them. In contrast to compounds that exhibit aromaticity, aliphatic compounds lack this delocalization. The term "aromatic" was assigned before the physical mechanism determining aromaticity was discovered, and referred simply to the fact that many such compounds have a sweet or pleasant odour; however, not all aromatic compounds have a sweet odour, and not all compounds with a sweet odour are aromatic compounds. Aromatic hydrocarbons, or arenes, are aromatic organic compounds containing solely carbon and hydrogen atoms. The configuration of six carbon atoms in aromatic compounds is called a "benzene ring", after the simple aromatic compound benzene, or a phenyl group when part of a larger compound.
Inorganic chemistry deals with synthesis and behavior of inorganic and organometallic compounds. This field covers chemical compounds that are not carbon-based, which are the subjects of organic chemistry. The distinction between the two disciplines is far from absolute, as there is much overlap in the subdiscipline of organometallic chemistry. It has applications in every aspect of the chemical industry, including catalysis, materials science, pigments, surfactants, coatings, medications, fuels, and agriculture.

In chemistry, a ketone is a functional group with the structure R2C=O, where R can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group (a carbon-oxygen double bond). The simplest ketone is acetone (R = R' = methyl), with the formula CH3C(O)CH3. Many ketones are of great importance in biology and in industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids (e.g., testosterone), and the solvent acetone.

In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate, millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds, along with a few other exceptions, are not classified as organic compounds and are considered inorganic. Other than those just named, little consensus exists among chemists on precisely which carbon-containing compounds are excluded, making any rigorous definition of an organic compound elusive.
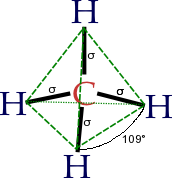
Organic chemistry is a branch of chemistry that studies the structure, properties and reactions of organic compounds, which contain carbon-carbon covalent bonds. Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes physical and chemical properties, and evaluation of chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical study.

In organic chemistry, the phenyl group, or phenyl ring, is a cyclic group of atoms with the formula C6H5. Phenyl groups are closely related to benzene and can be viewed as a benzene ring, minus a hydrogen, which may be replaced by some other element or compound to serve as a functional group. Phenyl groups have six carbon atoms bonded together in a hexagonal planar ring, five of which are bonded to individual hydrogen atoms, with the remaining carbon bonded to a substituent. Phenyl groups are commonplace in organic chemistry. Although often depicted with alternating double and single bonds, phenyl groups are chemically aromatic and have equal bond lengths between carbon atoms in the ring.

An oxidizing agent, also known as an oxidant or oxidizer, is a substance that has the ability to oxidize other substances — in other words to accept their electrons. Common oxidizing agents are oxygen, hydrogen peroxide and the halogens.
The quinones are a class of organic compounds that are formally "derived from aromatic compounds [such as benzene or naphthalene] by conversion of an even number of –CH= groups into –C(=O)– groups with any necessary rearrangement of double bonds, resulting in "a fully conjugated cyclic dione structure". The archetypical member of the class is 1,4-benzoquinone or cyclohexadienedione, often called simply "quinone". Other important examples are 1,2-benzoquinone (ortho-quinone), 1,4-naphthoquinone and 9,10-anthraquinone.
In environmental chemistry, the chemical oxygen demand (COD) is an indicative measure of the amount of oxygen that can be consumed by reactions in a measured solution. It is commonly expressed in mass of oxygen consumed over volume of solution which in SI units is milligrams per litre (mg/L). A COD test can be used to easily quantify the amount of organics in water. The most common application of COD is in quantifying the amount of oxidizable pollutants found in surface water or wastewater. COD is useful in terms of water quality by providing a metric to determine the effect an effluent will have on the receiving body, much like biochemical oxygen demand (BOD).

Organotin compounds or stannanes are chemical compounds based on tin with hydrocarbon substituents. Organotin chemistry is part of the wider field of organometallic chemistry. The first organotin compound was diethyltin diiodide ((C2H5)2SnI2), discovered by Edward Frankland in 1849. The area grew rapidly in the 1900s, especially after the discovery of the Grignard reagents, which are useful for producing Sn-C bonds. The area remains rich with many applications in industry and continuing activity in the research laboratory.

n-Butyllithium C4H9Li (abbreviated n-BuLi) is an organolithium reagent. It is widely used as a polymerization initiator in the production of elastomers such as polybutadiene or styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS). Also, it is broadly employed as a strong base (superbase) in the synthesis of organic compounds as in the pharmaceutical industry.

Organic peroxides are organic compounds containing the peroxide functional group (ROOR′). If the R′ is hydrogen, the compounds are called hydroperoxides, which are discussed in that article. Peresters are the peroxy analog of esters and have general structure RC(O)OOR. The O−O bond of peroxides easily breaks, producing free radicals of the form RO•. Thus, organic peroxides are useful as initiators for some types of polymerisation, such as the epoxy resins used in glass-reinforced plastics. MEKP and benzoyl peroxide are commonly used for this purpose. However, the same property also means that organic peroxides can either intentionally or unintentionally initiate explosive polymerisation in materials with unsaturated chemical bonds, and this process has been used in explosives. Organic peroxides, like their inorganic counterparts, are powerful bleaching agents.

Sodium dichromate is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2Cr2O7. However, the salt is usually handled as its dihydrate Na2Cr2O7·2H2O. Virtually all chromium ore is processed via conversion to sodium dichromate and virtually all compounds and materials based on chromium are prepared from this salt. In terms of reactivity and appearance, sodium dichromate and potassium dichromate are very similar. The sodium salt is, however, around twenty times more soluble in water than the potassium salt (49 g/L at 0 °C) and its equivalent weight is also lower, which is often desirable.

Organosilicon compounds are organometallic compounds containing carbon–silicon bonds. Organosilicon chemistry is the corresponding science of their preparation and properties. Most organosilicon compounds are similar to the ordinary organic compounds, being colourless, flammable, hydrophobic, and stable to air. Silicon carbide is an inorganic compound.
Organophosphorus compounds are organic compounds containing phosphorus. They are used primarily in pest control as an alternative to chlorinated hydrocarbons that persist in the environment. Some organophosphorus compounds are highly effective insecticides, although some are extremely toxic to humans, including sarin and VX nerve agents.

Diphenylmethane is an organic compound with the formula (C6H5)2CH2 (often abbreviated CH
2Ph
2). The compound consists of methane wherein two hydrogen atoms are replaced by two phenyl groups. It is a white solid.
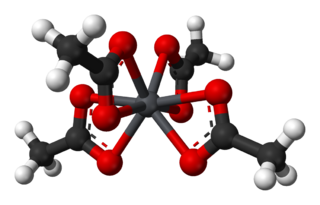
Lead(IV) acetate or lead tetraacetate is a chemical compound with chemical formula Pb(C2H3O2)4. It is a colorless solid that is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents, indicating that it is not a salt. It is degraded by moisture and is typically stored with additional acetic acid. The compound is used in organic synthesis.

Phenacyl bromide is the organic compound with the formula C6H5C(O)CH2Br. This colourless solid is a powerful lachrymator as well as a useful precursor to other organic compounds.
Organoiodine compounds are organic compounds that contain one or more carbon–iodine bonds. They occur widely in organic chemistry, but are relatively rare in nature. The thyroxine hormones are organoiodine compounds that are required for health and the reason for government-mandated iodization of salt.
Organosodium chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to sodium chemical bond. The application of organosodium compounds in chemistry is limited in part due to competition from organolithium compounds, which are commercially available and exhibit more convenient reactivity.












