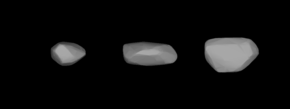
Arago, provisional designation 1923 OT, is a dark asteroid from the outer regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 55 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 5 September 1923, by Russian astronomer Sergey Belyavsky at the Simeiz Observatory on the Crimean peninsula. The asteroid was named after French mathematician François Arago.
1028 Lydina, provisional designation 1923 PG, is a carbonaceous background asteroid and member of the Cybele group from the outermost regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 82 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered at the Simeiz Observatory on the Crimean peninsula on 6 November 1923, by Soviet astronomer Vladimir Albitsky, who named it after his wife, Lydia Il'inichna Albitskaya. The dark C-type asteroid has a rotation period of 11.68 hours.
1031 Arctica, provisional designation 1924 RR, is a dark asteroid from the outer region of the asteroid belt, approximately 75 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 6 June 1924, by Soviet−Russian astronomer Sergey Belyavsky at Simeiz Observatory on the Crimean peninsula. It was named for the Arctic Sea.
1062 Ljuba, provisional designation 1925 TD, is a carbonaceous background asteroid from the outer regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 58 kilometers in diameter. The asteroid was discovered on 11 October 1925, by Soviet–Russian astronomer Sergey Belyavsky at the Simeiz Observatory on the Crimean peninsula. It was named after female paratrooper Ljuba Berlin, who died at an early age. The C-type asteroid has a longer-than average rotation period of 33.8 hours.
1074 Beljawskya, provisional designation 1925 BE, is a Themistian asteroid from the outer region of the asteroid belt, approximately 48 kilometers in diameter.
1112 Polonia, provisional designation 1928 PE, is an Eoan asteroid from the outer regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 38 kilometers in diameter. Discovered by Soviet astronomer Pelageya Shajn at Simeiz in 1928, it was the first asteroid discovery made by a woman. The L-type asteroid has a long rotation period of 82.5 hours, and was named for the country of Poland.
1113 Katja, provisional designation 1928 QC, is a background asteroid from the outer regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 39 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered by Pelageya Shajn at the Simeiz Observatory in 1928, and named after Ekaterina Iosko, a staff member at the discovering observatory.

1118 Hanskya is a large background asteroid, approximately 77 kilometers in diameter, located in the outer regions of the asteroid belt. Discovered by Sergey Belyavsky and Nikolaj Ivanov in 1927, it was named after Russian astronomer Aleksey Hansky. The presumed dark C-type asteroid has a rotation period of 15.6 hours.
1123 Shapleya, provisional designation 1928 ST, is a stony Florian asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 11 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 21 September 1928, by Russian astronomer Grigory Neujmin at Simeiz Observatory on the Crimean peninsula. It was named after American astronomer Harlow Shapley.

1129 Neujmina is an Eos asteroid from the outer regions of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 8 August 1929, by astronomer Praskoviya Parchomenko at the Simeiz Observatory on the Crimean peninsula. The stony S-type asteroid has a rotation period of 5.1 hours and measures approximately 34 kilometers in diameter. It was named after Soviet astronomer Grigory Neujmin.

1137 Raïssa is a stony background asteroid and slow rotator, approximately 22 kilometers in diameter, located in the inner regions of the asteroid belt. It was discovered by Grigory Neujmin at Simeiz Observatory in 1929, and named in memory of Raïssa Maseeva, who worked at the Pulkovo Observatory.
1149 Volga, provisional designation 1929 PF, is a dark background asteroid from the outer regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 55 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 1 August 1929, by Soviet astronomer Evgenij Skvorcov at the Simeiz Observatory on the Crimean peninsula. The asteroid was named after the Volga River.
1166 Sakuntala, provisional designation 1930 MA, is a stony background asteroid from the central regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 26 kilometers in diameter. Discovered by Praskovjya Parchomenko at Simeiz Observatory in 1930, the asteroid was named after the figure of Shakuntala from an ancient Indian drama.
2531 Cambridge, provisional designation 1980 LD, is a stony Eoan asteroid from the outer regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 20 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 11 June 1980, by American astronomer Edward Bowell at Lowell's Anderson Mesa Station in Arizona, United States. The asteroid was named for the Cambridge University.
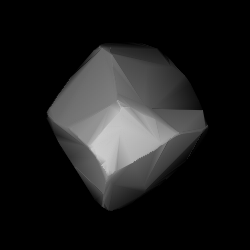
1283 Komsomolia is a metallic background asteroid and potentially slow rotator from the outer regions of the asteroid belt. Discovered by Vladimir Albitsky in 1925, it was later named after Komsomol, a political youth organization of the former Soviet Union. The M-type asteroid has roughly a rotation period 96 hours of and measures approximately 30 kilometers in diameter.
1255 Schilowa, provisional designation 1932 NC, is a background asteroid from the outer regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 34 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 8 July 1932, by Soviet astronomer Grigory Neujmin at the Simeiz Observatory on the Crimean peninsula. The asteroid has a longer-than average rotation period of 29.5 hours. It was named after Mariya Zhilova (Schilowa), who was Russia's first professional female astronomer.
1306 Scythia, provisional designation 1930 OB, is a dark Ursula asteroid from the outer regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 72 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 22 July 1930, by Soviet astronomer Grigory Neujmin at the Simeiz Observatory on the Crimean peninsula. The asteroid was named for the historic region of Scythia.
1266 Tone is a dark background asteroid from the outer regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 80 kilometers in diameter. Discovered by astronomer Okuro Oikawa at the Tokyo Observatory in 1927, it was assigned the provisional designation 1927 BD. The asteroid was later named after the Tone River, one of Japan's largest rivers.

1289 Kutaïssi is a stony Koronian asteroid from the outer region of the asteroid belt. Discovered by Grigory Neujmin at Simeiz Observatory in 1933, it was later named after the Georgian city of Kutaisi. The S-type asteroid has a rotation period of 3.6 hours and measures approximately 22 kilometers in diameter.
1535 Päijänne, provisional designation 1939 RC, is an asteroid from the outer region of the asteroid belt, approximately 25 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 9 September 1939, by Finnish astronomer Yrjö Väisälä at the Turku Observatory in Southwest Finland. It was later named for Lake Päijänne.