This article needs additional citations for verification .(January 2023) |
The 1180s BC is a decade which lasted from 1189 BC to 1180 BC.
| Millennium |
|---|
| 2nd millennium BC |
| Centuries |
| Decades |
| Years |
|
| Categories |
This article needs additional citations for verification .(January 2023) |
The 1180s BC is a decade which lasted from 1189 BC to 1180 BC.
| Millennium |
|---|
| 2nd millennium BC |
| Centuries |
| Decades |
| Years |
|
| Categories |
The Levant is the area in Southwest Asia, south of the Taurus Mountains, bounded by the Mediterranean Sea in the west, the Arabian Desert in the south, and Mesopotamia in the east. It stretches 400 mi (640 km) north to south from the Taurus Mountains to the Sinai desert, and 70–100 mi (110–160 km) east to west between the sea and the Arabian desert. The term is also sometimes used to refer to modern events or states in the region immediately bordering the eastern Mediterranean Sea: the Hatay Province of Turkey, Cyprus, Syria, Lebanon, Palestine, and Jordan.

The 7th century BC began the first day of 700 BC and ended the last day of 601 BC.
The 12th century BC is the period from 1200 to 1101 BC. The Late Bronze Age collapse in the ancient Near East and eastern Mediterranean is often considered to begin in this century.
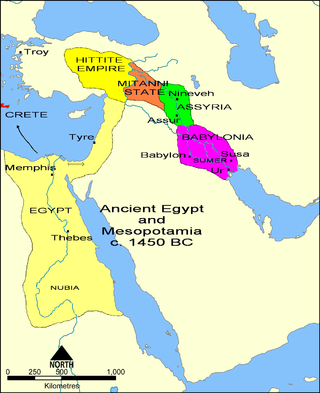
The 15th century BC was the century that lasted from 1500 BC to 1401 BC.
The 1150s BC is a decade which lasted from 1159 BC to 1150 BC.
The 1020s BC is a decade which lasted from 1029 BC to 1020 BC.
The 1170s BC is a decade which lasted from 1179 BC to 1170 BC.
The 1190s BC is a decade which lasted from 1199 BC to 1190 BC.

The 1250s BC is a decade which lasted from 1259 BC to 1250 BC.
Canaan was a Semitic-speaking civilization and region in the Ancient Near East during the late 2nd millennium BC. Canaan had significant geopolitical importance in the Late Bronze Age Amarna Period as the area where the spheres of interest of the Egyptian, Hittite, Mitanni and Assyrian Empires converged or overlapped. Much of present-day knowledge about Canaan stems from archaeological excavation in this area at sites such as Tel Hazor, Tel Megiddo, En Esur, and Gezer.

The 1400s BC is a decade which lasted from 1409 BC to 1400 BC.

Ugarit was an ancient port city in northern Syria, in the outskirts of modern Latakia, discovered by accident in 1928 together with the Ugaritic texts. Its ruins are often called Ras Shamra after the headland where they lie.
A vassal state is any state that has a mutual obligation to a superior state or empire, in a status similar to that of a vassal in the feudal system in medieval Europe. Vassal states were common among the empires of the Near East, dating back to the era of the Egyptian, Hittite and Mitanni conflict, as well as ancient China. The use of vassal states continued through the Middle Ages, with the last empire to use such states being the Ottoman Empire.

Alalakh is an ancient archaeological site approximately 20 kilometres (12 mi) northeast of Antakya in what is now Turkey's Hatay Province. It flourished, as an urban settlement, in the Middle and Late Bronze Age, c. 2000-1200 BC. The city contained palaces, temples, private houses and fortifications. The remains of Alalakh have formed an extensive mound covering around 22 hectares. In Late Bronze Age, Alalakh was the capital of the local kingdom of Mukiš.

Suppiluliuma II, the son of Tudḫaliya IV, was the last known king of the New Kingdom of the Hittite Empire, ruling c. 1207–1178 BC, contemporary with Tukulti-Ninurta I of the Middle Assyrian Empire.

The Late Bronze Age collapse was a time of widespread societal collapse during the 12th century BC, between c. 1200 and 1150. The collapse affected a large area of the Eastern Mediterranean and the Near East, in particular Egypt, eastern Libya, the Balkans, the Aegean, Anatolia, and the Caucasus. It was sudden, violent, and culturally disruptive for many Bronze Age civilizations, and it brought a sharp economic decline to regional powers, notably ushering in the Greek Dark Ages.

Ammurapi was the last Bronze Age ruler and king of the ancient Syrian city of Ugarit. Ammurapi was a contemporary of the Hittite King Suppiluliuma II. He wrote a preserved vivid letter RS 18.147 in response to a plea for assistance from the king of Alashiya.

The ancient Near East was the home of early civilizations within a region roughly corresponding to the modern Middle East: Mesopotamia, ancient Egypt, ancient Iran, Anatolia/Asia Minor and the Armenian highlands, the Levant, Cyprus and the Arabian Peninsula. The ancient Near East is studied in the fields of Ancient Near East studies, Near Eastern archaeology and ancient history.

The Yamhad dynasty was an ancient Amorite royal family founded in c. 1810 BC by Sumu-Epuh of Yamhad who had his capital in the city of Aleppo. Started as a local dynasty, the family expanded its influence through the actions of its energetic ruler Yarim-Lim I who turned it into the most influential family in the Levant through both diplomatic and military tools. At its height the dynasty controlled most of northern Syria and the modern Turkish province of Hatay with a cadet branch ruling in the city of Alalakh.