Related Research Articles
Inertia is the tendency of objects in motion to stay in motion and objects at rest to stay at rest, unless a force causes its speed or direction to change. It is one of the fundamental principles in classical physics, and described by Isaac Newton in his first law of motion. It is one of the primary manifestations of mass, one of the core quantitative properties of physical systems. Newton writes:
LAW I. Every object perseveres in its state of rest, or of uniform motion in a right line, except insofar as it is compelled to change that state by forces impressed thereon.

The Scientific Revolution was a series of events that marked the emergence of modern science during the early modern period, when developments in mathematics, physics, astronomy, biology and chemistry transformed the views of society about nature. The Scientific Revolution took place in Europe in the second half of the Renaissance period, with the 1543 Nicolaus Copernicus publication De revolutionibus orbium coelestium often cited as its beginning.
Galileo's ship refers to two physics experiments, a thought experiment and an actual experiment, by Galileo Galilei, the 16th- and 17th-century physicist and astronomer. The experiments were created to argue the idea of a rotating Earth as opposed to a stationary Earth around which rotated the Sun, planets, and stars.

The Discourses and Mathematical Demonstrations Relating to Two New Sciences published in 1638 was Galileo Galilei's final book and a scientific testament covering much of his work in physics over the preceding thirty years. It was written partly in Italian and partly in Latin.
The year 1633 in science and technology involved some significant events.

"And yet it moves" or "Although it does move" is a phrase attributed to the Italian mathematician, physicist and philosopher Galileo Galilei (1564–1642) in 1633 after being forced to recant his claims that the Earth moves around the Sun, rather than the converse. In this context, the implication of the phrase is: despite his recantation, the Inquisition’s proclamations to the contrary, or any other conviction or doctrine of men, the Earth does, in fact, move.

The Copernican Revolution was the paradigm shift from the Ptolemaic model of the heavens, which described the cosmos as having Earth stationary at the center of the universe, to the heliocentric model with the Sun at the center of the Solar System. This revolution consisted of two phases; the first being extremely mathematical in nature and the second phase starting in 1610 with the publication of a pamphlet by Galileo. Beginning with the 1543 publication of Nicolaus Copernicus’s De revolutionibus orbium coelestium, contributions to the “revolution” continued until finally ending with Isaac Newton’s work over a century later.

The Galileo affair began around 1610 and culminated with the trial and condemnation of Galileo Galilei by the Roman Catholic Inquisition in 1633. Galileo was prosecuted for his support of heliocentrism, the astronomical model in which the Earth and planets revolve around the Sun at the centre of the universe.

Dialogo de Cecco di Ronchitti da Bruzene in perpuosito de la stella Nuova is the title of an early 17th-century pseudonymous pamphlet ridiculing the views of an aspiring Aristotelian philosopher, Antonio Lorenzini da Montepulciano, on the nature and properties of Kepler's Supernova, which had appeared in October 1604. The pseudonymous Dialogue was written in the coarse language of a rustic Paduan dialect, and first published in about March, 1605, in Padua. A second edition was published later the same year in Verona. Antonio Favaro republished the contents of the pamphlet in its original language in 1881, with annotations and a commentary in Italian. He republished it again in Volume 2 of the National Edition of Galileo's works in 1891, along with a translation into standard Italian. An English translation was published by Stillman Drake in 1976.

The Assayer is a book by Galileo Galilei, published in Rome in October 1623. It is generally considered to be one of the pioneering works of the scientific method, first broaching the idea that the book of nature is to be read with mathematical tools rather than those of scholastic philosophy, as generally held at the time.
Stillman Drake, an American historian of science who moved to Canada in 1967 and acquired Canadian citizenship a few years later, is best known for his work on Galileo Galilei (1569–1642).
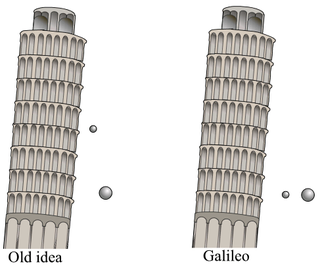
Between 1589 and 1592, the Italian scientist Galileo Galilei is said to have dropped "unequal weights of the same material" from the Leaning Tower of Pisa to demonstrate that their time of descent was independent of their mass, according to a biography by Galileo's pupil Vincenzo Viviani, composed in 1654 and published in 1717. The basic premise had already been demonstrated by Italian experimenters a few decades earlier.
Gasparo Berti was an Italian mathematician, astronomer and physicist. He was probably born in Mantua and spent most of his life in Rome. He is most famous today for his experiment in which he unknowingly created the first working barometer. Though he was best known for his work in mathematics and physics, little of his work in either survives.

The theory of impetus is an auxiliary or secondary theory of Aristotelian dynamics, put forth initially to explain projectile motion against gravity. It was introduced by John Philoponus in the 6th century, and elaborated by Nur ad-Din al-Bitruji at the end of the 12th century. The theory was modified by Avicenna in the 11th century and Abu'l-Barakāt al-Baghdādī in the 12th century, before it was later established in Western scientific thought by Jean Buridan in the 14th century. It is the intellectual precursor to the concepts of inertia, momentum and acceleration in classical mechanics.

Mario Guiducci was an Italian scholar and writer. A friend and colleague of Galileo, he collaborated with him on the Discourse on Comets in 1618.

Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei, commonly referred to as Galileo Galilei or simply Galileo, was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath. He was born in the city of Pisa, then part of the Duchy of Florence. Galileo has been called the father of observational astronomy, modern-era classical physics, the scientific method, and modern science.

Pietro Catena was an Italian astronomer, philosopher, mathematician, theologian and catholic priest, citizen of the Republic of Venice. He was a precursor of the Renaissance Scientific Revolution and investigated the relationships between mathematics, logic and philosophy. As a professor in Padua, Catena occupied the same mathematical chair later assigned to Galileo Galilei.

Lodovico delle Colombe was an Italian Aristotelian scholar, famous for his battles with Galileo Galilei in a series of controversies in physics and astronomy.
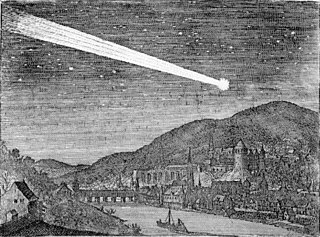
The Discourse on Comets was a pamphlet published in 1619 with Mario Guiducci as the named author, though in reality it was mostly the work of Galileo Galilei. In it Galileo conjectured that comets were not physical bodies but atmospheric effects like the aurora borealis.

Niccolò Arrighetti was Italian intellectual, pupil and associate of Galileo Galilei.