Events
This section is empty.You can help by adding to it.(January 2013) |
| |||
|---|---|---|---|
1890 in philosophy
This section is empty.You can help by adding to it.(January 2013) |

William Morris was a British textile designer, poet, novelist, translator, and socialist activist associated with the British Arts and Crafts Movement. He was a major contributor to the revival of traditional British textile arts and methods of production. His literary contributions helped to establish the modern fantasy genre, while he played a significant role propagating the early socialist movement in Britain.

News from Nowhere (1890) is a classic work combining utopian socialism and soft science fiction written by the artist, designer and socialist pioneer William Morris. It was first published in serial form in the Commonweal journal beginning on 11 January 1890. In the novel, the narrator, William Guest, falls asleep after returning from a meeting of the Socialist League and awakes to find himself in a future society based on common ownership and democratic control of the means of production. In this society there is no private property, no big cities, no authority, no monetary system, no divorce, no courts, no prisons, and no class systems. This agrarian society functions simply because the people find pleasure in nature, and therefore they find pleasure in their work.

William James (1842–1910) was an American philosopher and psychologist, and the first educator to offer a psychology course in the United States. James was a leading thinker of the late nineteenth century, one of the most influential U.S. philosophers, and has been labelled the "Father of American psychology".

Sir Charles Lyell, 1st Baronet, was a Scottish geologist who popularised the revolutionary work of James Hutton. He is best known as the author of Principles of Geology, which presented uniformitarianism–the idea that the Earth was shaped by the same scientific processes still in operation today–to the broad general public. Principles of Geology also challenged theories popularised by Georges Cuvier, which were the most accepted and circulated ideas about geology in Europe at the time.

Thomas Reid was a religiously trained British philosopher, a contemporary of David Hume as well as "Hume's earliest and fiercest critic". He was the founder of the Scottish School of Common Sense and played an integral role in the Scottish Enlightenment. In 1783 he was a joint founder of the Royal Society of Edinburgh.
The Democratic-Republican Party was an American political party formed by Thomas Jefferson and James Madison around 1792 to oppose the centralizing policies of the new Federalist Party run by Alexander Hamilton, who was Secretary of the Treasury and chief architect of George Washington's administration. From 1801 to 1825, the new party controlled the presidency and Congress as well as most states during the First Party System. It began in 1791 as one faction in Congress and included many politicians who had been opposed to the new constitution. They called themselves Republicans after their political philosophy, republicanism. They distrusted the Federalist tendency to centralize and loosely interpret the Constitution, believing these policies were signs of monarchism and anti-republican values. The party splintered in 1824, with the faction loyal to Andrew Jackson coalescing into the Jacksonian movement, the faction led by John Quincy Adams and Henry Clay forming the National Republican Party and some other groups going on to form the Anti-Masonic Party. The National Republicans, Anti-Masons, and other opponents of Andrew Jackson later formed themselves into the Whig Party.
The Whigs were a political faction and then a political party in the parliaments of England, Scotland, Great Britain, Ireland and the United Kingdom. Between the 1680s and 1850s, they contested power with their rivals, the Tories. The Whigs' origin lay in constitutional monarchism and opposition to absolute monarchy. The Whigs played a central role in the Glorious Revolution of 1688 and were the standing enemies of the Stuart kings and pretenders, who were Roman Catholic. The Whigs took full control of the government in 1715 and remained totally dominant until King George III, coming to the throne in 1760, allowed Tories back in. The Whig Supremacy (1715–1760) was enabled by the Hanoverian succession of George I in 1714 and the failed Jacobite rising of 1715 by Tory rebels. The Whigs thoroughly purged the Tories from all major positions in government, the army, the Church of England, the legal profession and local offices. The Party's hold on power was so strong and durable, historians call the period from roughly 1714 to 1783 the age of the Whig Oligarchy. The first great leader of the Whigs was Robert Walpole, who maintained control of the government through the period 1721–1742 and whose protégé Henry Pelham led from 1743 to 1754.

William III, also widely known as William of Orange, was sovereign Prince of Orange from birth, Stadtholder of Holland, Zeeland, Utrecht, Gelderland and Overijssel in the Dutch Republic from 1672 and King of England, Ireland and Scotland from 1689 until his death in 1702. As King of Scotland, he is known as William II. He is sometimes informally known in Northern Ireland and Scotland as "King Billy".

The Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood was a group of English painters, poets, and art critics, founded in 1848 by William Holman Hunt, John Everett Millais and Dante Gabriel Rossetti. The three founders were joined by William Michael Rossetti, James Collinson, Frederic George Stephens and Thomas Woolner to form the seven-member "brotherhood". Their principles were shared by other artists, including Ford Madox Brown, Arthur Hughes and Marie Spartali Stillman.

The Principles of Psychology is an 1890 book about psychology by William James, an American philosopher and psychologist who trained to be a physician before going into psychology. There are four methods from James' book: stream of consciousness ; emotion ; habit ; and will.
Whiggism is a historical political philosophy that grew out of the Parliamentarian faction in the Wars of the Three Kingdoms (1639–1651). The Whigs' key policy positions were the supremacy of Parliament, tolerance of Protestant dissenters and opposition to a "Papist" on the throne, especially James II or one of his descendants.

William Thompson was an Irish political and philosophical writer and social reformer, developing from utilitarianism into an early critic of capitalist exploitation whose ideas influenced the Cooperative, Trade Union and Chartist movements as well as Karl Marx. Born into the Anglo-Irish Ascendancy of wealthy landowners and merchants of Cork society, his attempt to will his estate to the cooperative movement after his death sparked a long court case as his family fought successfully to have the will annulled. According to E. T. Craig, this decision to will his estate to the cooperative movement was taken after a visit to the pioneering Ralahine Commune. Marxist James Connolly described him as the "first Irish socialist" and a forerunner to Marx.
The specious present is the time duration wherein one's perceptions are considered to be in the present. Time perception studies the sense of time, which differs from other senses since time cannot be directly perceived but must be reconstructed by the brain.

The stratum spinosum is a layer of the epidermis found between the stratum granulosum and stratum basale. Their spiny appearance is due to shrinking of the microfilaments between desmosomes that occurs when stained with H&E. Keratinization begins in the stratum spinosum. This layer is composed of polyhedral keratinocytes. They have large pale-staining nuclei as they are active in synthesizing fibrilar proteins, known as cytokeratin, which build up within the cells aggregating together forming tonofibrils. The tonofibrils go on to form the desmosomes, which allow for strong connections to form between adjacent keratinocytes.
Total Living Network (TLN) is a religious broadcasting channel based in Aurora, Illinois which carries a wide variety of family and ministry programs.
In heraldry, an avellane cross is a form of cross which resembles four hazel filberts in their husks or cases, joined together at the great end. The term comes from the Latin name for the hazel, originally Nux avellana. It was fairly rare in English heraldry.

James II and VII was King of England and Ireland as James II and King of Scotland as James VII, from 6 February 1685 until he was deposed in the Glorious Revolution of 1688. The last Roman Catholic monarch of England, Scotland and Ireland, his reign is now remembered primarily for struggles over religious tolerance. However, it also involved the principles of absolutism and divine right of kings and his deposition ended a century of political and civil strife by confirming the primacy of Parliament over the Crown.
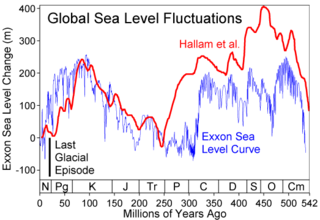
The sea-level curve is the representation of the changes of the sea level throughout the geological history.
Voluntary action is an anticipated goal-oriented movement. The concept arises in many areas of study, including cognitive psychology, operant conditioning, philosophy, neurology, and criminology among others, and it has various meanings depending on the context in which it is used. For example, operant psychology uses the term to refer to the actions that are modifiable by their consequences. A more cognitive account may refer to voluntary action as involving the identification of a desired outcome together with the action necessary to achieve that outcome. Voluntary action is often associated with consciousness and will. For example, Psychologist Charles Nuckolls holds that we control our voluntary behavior, and that it is not known how we come to plan what actions will be executed. Many psychologists, notably Tolman, apply the concept of voluntary action to both animal and human behavior, raising the issue of animal consciousness and its role in voluntary action.
African histoplasmosis is an infection caused by Histoplasma duboisii. Disease has been most often reported in Uganda, Nigeria, Zaire and Senegal. In human disease it manifests differently than histoplasmosis, most often involving the skin and bones and rarely involving the lungs.
Fredson Thayer Bowers was an American bibliographer and scholar of textual editing.
Events from the year 1757 in Scotland.