The "Republican Revolution", "Revolution of '94", or "Gingrich Revolution" are political slogans that refer to the Republican Party's (GOP) success in the 1994 U.S. mid-term elections, which resulted in a net gain of 54 seats in the House of Representatives, and a pick-up of eight seats in the Senate. It was led by Newt Gingrich.

The 1962 United States elections were held on November 6 to elect the members of the 88th United States Congress. The election occurred in the middle of Democratic President John F. Kennedy's term. The Republican Party picked up four seats in the House of Representatives. Still, the Democrats retained strong majorities in both houses of Congress.

The 2010 United States elections were held on Tuesday, November 2, 2010, in the middle of Democratic President Barack Obama's first term. Republicans ended unified Democratic control of Congress and the presidency by winning a majority in the House of Representatives and gained seats in the Senate despite Democrats holding Senate control. Despite the election being widely characterized as a "Republican wave" election, 2010 is the first midterm election since 1982 that the party of the incumbent president holds a chamber of Congress while simultaneously losing the other and the last time Democrats did so since 1886.

The 1980 United States elections were held on Tuesday, November 4. Republican presidential nominee Ronald Reagan defeated incumbent Democratic President Jimmy Carter in a landslide. Republicans picked up seats in both chambers of Congress and won control of the Senate, though Democrats retained a majority in the House of Representatives. The election is sometimes referred to as part of the "Reagan Revolution", a conservative realignment in U.S. politics and marked the start of the Reagan Era.

The 2002 United States elections were held on November 5, in the middle of Republican President George W. Bush's first term. Republicans won unified control of Congress, picking up seats in both chambers of Congress, making Bush the first President since Franklin D. Roosevelt in 1934 to gain seats in both houses of Congress. In the gubernatorial elections, Democrats won a net gain of one seat. The elections were held just a little under fourteen months after the September 11 attacks. Thus, the elections were heavily overshadowed by the War on Terror.

The 2000 United States elections were held on November 7, 2000. Republican Governor George W. Bush of Texas defeated Democratic Vice President Al Gore of Tennessee in the presidential election. Republicans retained control of both houses of Congress, giving the party unified control of Congress and the presidency for the first time since the 1954 elections.

The 1998 United States elections were held on November 3, 1998, in the middle of Democratic President Bill Clinton's second term and during impeachment proceedings against the president as a result of the Clinton–Lewinsky scandal. Though Republicans retained control of both chambers of Congress, the elections were unusual because this is the first midterm since 1934 that the president's party gained seats in the House of Representatives.

The 1994 United States elections were held on November 8, 1994. The elections occurred in the middle of Democratic President Bill Clinton's first term in office, and elected the members of 104th United States Congress. The elections have been described as the "Republican Revolution" because the Republican Party captured unified control of Congress for the first time since 1952. Republicans picked up eight seats in the Senate and won a net of 54 seats in the House of Representatives. Republicans also picked up a net of ten governorships and took control of many state legislative chambers. This is the first midterm election since 1946 that Republicans ended unified Democratic control of Congress in a midterm election under a Democratic president.

The 1986 United States elections were held on November 4 and elected the members of the 100th United States Congress. The elections occurred in the middle of Republican President Ronald Reagan's second term. Democrats regained unified control of both chambers of Congress for the first time since the 1980 elections.

The 1996 United States elections were held on November 5. Democratic President Bill Clinton won re-election, while the Republicans maintained their majorities in both houses of the United States Congress.
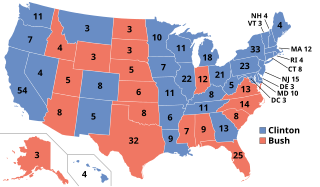
The 1992 United States elections elected state governors, the President of the United States, and members of the 103rd United States Congress. The election took place after the Soviet Union crumbled and the Cold War ended, as well as the redistricting that resulted from the 1990 census. Often considered "The Year Of The Woman," these elections brought an increased number of female politicians to Washington such as Dianne Feinstein (D-CA) and Carol Moseley Braun (D-IL). Governor Bill Clinton of Arkansas defeated incumbent President George H. W. Bush and businessman Ross Perot in the presidential election. The Democratic Party maintained their control of both chambers of Congress. This is the first Democratic trifecta since the Republican victory in the 1980 elections and the last one during the 20th century and the last one overall until 2008.
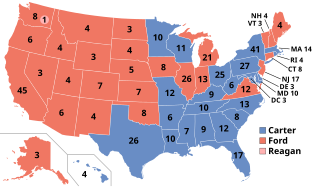
The 1976 United States elections were held on November 2, and elected the members of the 95th United States Congress. The Democratic Party won the presidential election and retained control of Congress.

The 1984 United States elections were held on November 6, and elected the members of the 99th United States Congress. Republicans won a landslide victory in the presidential election, picked up seats in the House of Representatives, and successfully defended their Senate majority.

The 1988 United States elections were held on November 8 and elected the President of the United States and members of the 101st United States Congress. Republican Vice President George H. W. Bush defeated Democratic Governor of Massachusetts Michael Dukakis. Despite Dukakis' defeat, the Democratic Party built on their majorities in Congress.

The 1972 United States elections were held on November 7, and elected the members of the 93rd United States Congress. The election took place during the later stages of the Vietnam War. The Republican Party won a landslide victory in the presidential election, and picked up seats in the House, but the Democratic Party easily retained control of Congress. This was the first election after the ratification of the 26th Amendment granted the right to vote to those aged 18–20.

The 1970 United States elections were held on November 3, and elected the members of the 92nd United States Congress. The election took place during the Vietnam War, in the middle of Republican President Richard Nixon's first term. The Democratic Party defended their control of Congress by retaining its Senate majority and increasing its majority in the House of Representatives.

The 1966 United States elections were held on November 8, 1966, and elected the members of the 90th United States Congress. The election was held in the middle of Democratic President Lyndon B. Johnson's second term, and during the Vietnam War. Johnson's Democrats lost forty-seven seats to the Republican Party in the House of Representatives. The Democrats also lost three seats in the U.S. Senate to the Republicans. Despite their losses, the Democrats retained control of both chambers of Congress. Republicans won a large victory in the gubernatorial elections, with a net gain of seven seats. This was the first election held after the passage of the Voting Rights Act of 1965, which led to a surge in African-American voter participation.

The 1946 United States elections were held on November 5, 1946, and elected the members of the 80th United States Congress. In the first election after World War II, incumbent President Harry S. Truman and the Democratic Party suffered large losses. After having been in the minority of both chambers of Congress since 1932, Republicans took control of both the House and the Senate.
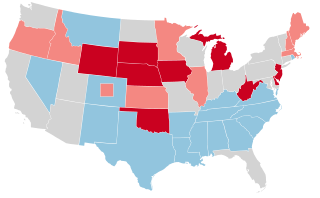
The 1942 United States elections were held on November 3, 1942, and elected the members of the 78th United States Congress. In Democratic President Franklin D. Roosevelt's unprecedented third mid-term election and during World War II, the Republican Party picked up seats in both chambers. Still, the Democrats retained control of Congress.

The 2018 United States elections were held on Tuesday, November 6, 2018. These midterm elections occurred during Incumbent Republican President Donald Trump's term. Although the Republican Party increased its majority in the Senate, unified Republican control of Congress and the White House was brought to an end when the Democratic Party won control of the House of Representatives in what was widely characterized as a "blue wave" election as Democrats also gained governorships, other statewide offices, and state legislative chambers.





















