1,4-Dichlorobenzene (1,4-DCB, p-DCB, or para-dichlorobenzene, sometimes abbreviated as PDCB or para) is an organic compound with the formula C6H4Cl2. This colorless solid has a strong odor. The molecule consists of a benzene ring with two chlorine atoms (replacing hydrogen atoms) on opposing sites of the ring.

Barium nitrate is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ba(NO3)2. It, like most barium salts, is colorless, toxic, and water-soluble. It burns with a green flame and is an oxidizer; the compound is commonly used in pyrotechnics.

Toluene diisocyanate (TDI) is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H3(NCO)2. Two of the six possible isomers are commercially important: 2,4-TDI (CAS: 584-84-9) and 2,6-TDI (CAS: 91-08-7). 2,4-TDI is produced in the pure state, but TDI is often marketed as 80/20 and 65/35 mixtures of the 2,4 and 2,6 isomers respectively. It is produced on a large scale, accounting for 34.1% of the global isocyanate market in 2000, second only to MDI. Approximately 1.4 billion kilograms were produced in 2000. All isomers of TDI are colorless, although commercial samples can appear yellow.

Methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI) is an aromatic diisocyanate. Three isomers are common, varying by the positions of the isocyanate groups around the rings: 2,2′-MDI, 2,4′-MDI, and 4,4′-MDI. The 4,4′ isomer is most widely used, and is also known as 4,4′-diphenylmethane diisocyanate. This isomer is also known as Pure MDI. MDI reacts with polyols in the manufacture of polyurethane. It is the most produced diisocyanate, accounting for 61.3% of the global market in the year 2000.

Chlorobenzene is an aromatic organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5Cl. This colorless, flammable liquid is a common solvent and a widely used intermediate in the manufacture of other chemicals.

o-Xylene (ortho-xylene) is an aromatic hydrocarbon with the formula C6H4(CH3)2. with two methyl substituents bonded to adjacent carbon atoms of a benzene ring (the ortho configuration). It is a constitutional isomer of m-xylene and p-xylene, the mixture being called xylene or xylenes. o-Xylene is a colorless slightly oily flammable liquid.
2-Chloroethanol is a chemical compound with the formula HOCH2CH2Cl and the simplest chlorohydrin. This colorless liquid has a pleasant ether-like odor. It is miscible with water. The molecule is bifunctional, consisting of both an alkyl chloride and an alcohol functional groups.
Benzyl chloride, or α-chlorotoluene, is an organic compound with the formula C6H5CH2Cl. This colorless liquid is a reactive organochlorine compound that is a widely used chemical building block.
Hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI or HMDI) is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)6(NCO)2. It is classified as an diisocyanate. It is a colorless liquid.

Crotonaldehyde is a chemical compound with the formula CH3CH=CHCHO. The compound is usually sold as a mixture of the E- and Z-isomers, which differ with respect to the relative position of the methyl and formyl groups. The E-isomer is more common (data given in Table is for the E-isomer). This lachrymatory liquid is moderately soluble in water and miscible in organic solvents. As an unsaturated aldehyde, crotonaldehyde is a versatile intermediate in organic synthesis. It occurs in a variety of foodstuffs, e.g. soybean oils.
4-Nitroaniline, p-nitroaniline or 1-amino-4-nitrobenzene is an organic compound with the formula C6H6N2O2. It is an organic chemical compound, consisting of a benzene ring in which an amino group is para to a nitro group. This chemical is commonly used as an intermediate in the synthesis of dyes, antioxidants, pharmaceuticals, gasoline, gum inhibitors, poultry medicines, and as a corrosion inhibitor.

o-Anisidine (2-anisidine) is an organic compound with the formula CH3OC6H4NH2. A colorless liquid, commercial samples can appear yellow owing to air oxidation. It is one of three isomers of the methoxy-containing aniline derivative.

4-Nitrochlorobenzene is the organic compound with the formula ClC6H4NO2. It is a pale yellow solid. 4-Nitrochlorobenzene is a common intermediate in the production of a number of industrially useful compounds, including common antioxidants found in rubber. Other isomers with the formula ClC6H4NO2 include 2-nitrochlorobenzene and 3-nitrochlorobenzene.
ortho-Cresol, also 2-methylphenol, is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H4(OH). It is a colourless solid that is widely used intermediate in the production of other chemicals. It is a derivative of phenol and is an isomer of p-cresol and m-cresol.
4,4′-Methylenedianiline (MDA) is an organic compound with the formula CH2(C6H4NH2)2. It is a light-brown solid. It is produced on industrial scale as a precursor to polyurethanes.
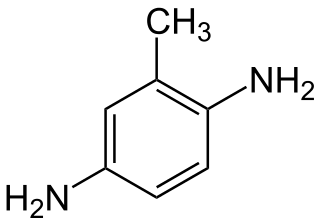
2,5-Diaminotoluene is an organic compound with the formula C6H3(NH2)2CH3. It is one isomer of six with this formula. 2,5-Diaminotoluene is a colorless crystalline solid, although commercial samples are often colored owing to air oxidation. It is commonly used in hair coloring.
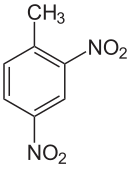
4-Nitrotoluene or para-nitrotoluene is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H4NO2. It is a pale yellow solid. It is one of three isomers of nitrotoluene.
3-Nitrotoluene or meta-nitrotoluene is a yellow liquid. It is used in the manufacture of meta-toluidine. It is an intermediate in the production of various dyes.
2-Nitrotoluene or ortho-nitrotoluene is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H4NO2. It is pale yellow liquid that crystallizes in two forms, called α (−9.27 °C) and β (−3.17 °C). It is mainly a precursor to o-toluidine, which is an intermediate in the production of various dyes.

2,4-Diaminotoluene is an organic compound with the formula C6H3(NH2)2CH3. It is one isomer of six with this formula. It is a white solid although commercial samples are often yellow-tan.