Related Research Articles

The economy of Mozambique is $14.396 billion by gross domestic product as of 2018, and has developed since the end of the Mozambican Civil War (1977–1992). In 1987, the government embarked on a series of macroeconomic reforms, which were designed to stabilize the economy. These steps, combined with donor assistance and with political stability since the multi-party elections in 1994, have led to dramatic improvements in the country's growth rate. Inflation was brought to single digits during the late 1990s, although it returned to double digits in 2000–02. Fiscal reforms, including the introduction of a value-added tax and reform of the customs service, have improved the government's revenue collection abilities.
The Cardiff Ely bread riots, or Ely petrol riots, was the outbreak of violence that occurred in the council suburb of Ely in the capital of Wales, Cardiff, during September 1991. The unrest was attributed to a dispute between two shopkeepers over who could sell bread and other food products which escalated into a riot involving up to 500 participants. An estimated 175 police officers were mobilised, including reinforcements called in from the Vale of Glamorgan, to deal with the unrest.

The Southern bread riots were events of civil unrest in the Confederacy during the American Civil War, perpetrated mostly by women in March and April 1863. During these riots, which occurred in cities throughout the South, hungry women and men invaded and looted various shops and stores.

Food riots may occur when there is a shortage and/or unequal distribution of food. Causes can be food price rises, harvest failures, incompetent food storage, transport problems, food speculation, hoarding, poisoning of food, or attacks by pests. Hence, the pathway between food related issues such as crop failure, price hike or volatility and an actual “riot” is often complex.

World food prices increased dramatically in 2007 and the first and second quarter of 2008, creating a global crisis and causing political and economic instability and social unrest in both poor and developed nations. Although the media spotlight focused on the riots that ensued in the face of high prices, the ongoing crisis of food insecurity had been years in the making. Systemic causes for the worldwide increases in food prices continue to be the subject of debate. After peaking in the second quarter of 2008, prices fell dramatically during the late-2000s recession but increased during late 2009 and 2010, reaching new heights in 2011 and 2012 at a level slightly higher than the level reached in 2008. Over the next years, prices fell, reaching a low in March 2016 with the deflated Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) food price index close to pre-crisis level of 2006.
Prior to 1994, immigrants from elsewhere faced discrimination and even violence in South Africa. After majority rule in 1994, contrary to expectations, the incidence of xenophobia increased. Between 2000 and March 2008, at least 67 people died in what were identified as xenophobic attacks. In May 2008, a series of attacks left 62 people dead; although 21 of those killed were South African citizens. The attacks were motivated by xenophobia. In 2015, another nationwide spike in xenophobic attacks against immigrants in general prompted a number of foreign governments to begin repatriating their citizens. A Pew Research poll conducted in 2018 showed that 62% of South Africans viewed immigrants as a burden on society by taking jobs and social benefits and that 61% of South Africans thought that immigrants were more responsible for crime than other groups. Between 2010 and 2017 the immigrant community in South Africa increased from 2 million people to 4 million people. The proportion of South Africa's total population that is foreign born increased from 2.8% in 2005 to 7% in 2019, according to the United Nations International Organization for Migration, in spite of widespread xenophobia in the country. This made South Africa the largest recipient of immigrants on the African continent in 2019.
Antonio Francisco Munguambe is a Mozambican politician.

The 2009 French Caribbean general strikes began in the French overseas region of Guadeloupe on 20 January 2009, and spread to neighbouring Martinique on 5 February 2009. Both islands are located in the Lesser Antilles of the Caribbean. The general strikes began over the cost of living, the prices of basic commodities, including fuel and food, and demands for an increase in the monthly salaries of low income workers.

The Jordanian protests were a series of protests in Jordan that began in January 2011, and resulted in the firing of the cabinet ministers of the government. In its early phase, protests in Jordan were initially against unemployment, inflation, corruption. along with demanding for real constitutional monarchy and electoral reforms.
On 11 April 2015, several South Africans attacked foreigners in a xenophobic attack in Durban, South Africa, which extended to some parts of Johannesburg. Several people, both foreign and South African alike, were killed with some of the killings captured on camera.
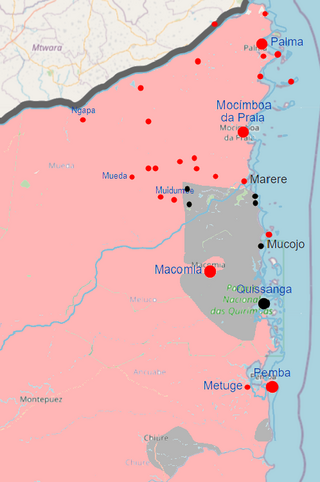
The insurgency in Cabo Delgado is an ongoing Islamist insurgency in Cabo Delgado Province, Mozambique, mainly fought between militant Islamists and jihadists attempting to establish an Islamic state in the region, and Mozambican security forces. Civilians have been the main targets of terrorist attacks by Islamist militants. The main insurgent faction is Ansar al-Sunna, a native extremist faction with tenuous international connections. From mid-2018, the Islamic State's Central Africa Province has allegedly become active in northern Mozambique as well, and claimed its first attack against Mozambican security forces in June 2019. In addition, bandits have exploited the rebellion to carry out raids. As of 2020, the insurgency intensified, as in the first half of 2020 there were nearly as many attacks carried out as in the whole of 2019.
The 2018 Tunisian protests were a series of protests occurring throughout Tunisia. Beginning January 2018, protests erupted in multiple towns and cities across Tunisia over issues related to the cost of living and taxes. As of January 9, the demonstrations had claimed at least one life, and revived worries about the fragile political situation in Tunisia.

The 2018–2022 Arab protests, known as Arab Spring 2.0 or Second Arab Spring, were a series of anti-government protests in several Arab countries, including Tunisia, Morocco, Jordan, Sudan, Algeria, Egypt, Iraq, Lebanon, Libya, Oman, and Syria. Economic protests also took place in the Gaza Strip.

The concept of human rights in Mozambique is an ongoing issue for the African country, officially named the Republic of Mozambique. For more than four centuries, Mozambique was ruled by the Portuguese. Following Mozambique’s independence from Portugal came 17 years of civil war, between RENAMO and FRELIMO, until 1992, when peace was finally reached. Armando Guebuza was then elected president in 2004 and re-elected in 2009, despite criticisms that he lacked honesty, transparency, and impartiality. This sparked a series of human rights incidents including unlawful killing, arbitrary arrests, inhumane prison conditions, and unfair trials. There were also many issues regarding freedom in relation to speech and media, internet freedom, freedom of peaceful assembly, and discrimination and abuse of women, children and people with disabilities. Many of these issues are ongoing and have become current human rights violation is for Mozambique.

The 2017–2021 Iranian protests were a series of political movements, civil disobedience, online activism, and demonstrations followed by government crackdowns that since the mid-2010s have erupted nationwide in Iran, in response to the Shiite political Islam and theocracy of the Islamic Republic of Iran, which began in 1979 following the Iranian Revolution.
The 1984 Egyptian intifada was a bloody uprising and civil resistance movement that rocked northern Egypt against food prices and Inflation that skyrocketed under the presidency of Hosni Mubarak. On 1 October, in Kafr-el-Dawwar, Riots rocked the city led by mostly workers against the prices of basic economic goods and prices. It would be the biggest and most bloodiest protests in Egypt since the 1977 Egyptian bread riots and the first and biggest political challenge in Hosni Mubarak’s presidency.
The 1990 Moroccan protests was a mass uprising and popular movement that consisted of violent demonstrations and massive anti-Gulf War protests in 1990–1991 in Morocco. Protesters rallied in cities nationwide, starting in Fez, where protesters marched in rioting against bread prices and the gulf war. Tens of thousands took to the streets in organised protests and planned strike actions, protests rallied that quickly turned into an uprising and popular Riots, calling on the fall of the regime. 5 days of massive demonstrations swept small cities in Morocco as they rose up to inflation and high prices. In Tangier, 20 days of strikes and general strikes was pulled out by thousands of workers calling on better wages. No deaths of fatalities was reported during the mass protests in Tangier. Huge student-led anti-government demonstrations and anti-Kuwait invasion protests was sweeping the Arab world, starting in Egypt and inspired protesters in Morocco. 33 were killed during the rioting and the protests was quickly suppressed by the army and the army was deployed to patrol the streets in case of any protest actions and movement. 127-240 were injured during the echoes of anger in the country. Huge marches in support of both sides of the Iraq-Kuwait conflict was held in January–February; at least 100,000+ protesters marched. After the December rioting in Fez, curfews was imposed to quell the mass uprising.

The Battle of Palma or the Battle for Palma was fought during late March and early April 2021 over control of the city of Palma in Mozambique, between the Mozambique Defence Armed Forces, other Mozambican security forces and private military contractors on one side, and Islamist rebels reportedly associated with the Islamic State (IS) on another side. The Islamists invaded the city, killing dozens of people before Mozambique regained control days later. Palma was left destroyed, and a major oil and gas company decided to suspend all operations in the area due to the battle. Researchers have described the battle as an overall success for the insurgents. The rebels also maintained their presence in the town's surroundings, and continued to raid Palma in the following weeks. The battle was part of the insurgency in Cabo Delgado, which started in 2017 and has resulted in the deaths of thousands of people, mainly local civilians.
References
- ↑ "Deadly riots in Mozambique over rising prices". BBC News. BBC. 1 September 2010.
- ↑ "Mozambique's food riots – the true face of global warming". TheGuardian.com . The Guardian. 4 September 2010.
- ↑ "Mozambique bread riots spread as police shoot protesters dead". TheGuardian.com . The Guardian. 2 September 2010.