Related Research Articles

Ab urbe condita, or anno urbis conditae, abbreviated as AUC or AVC, expresses a date in years since 753 BC, the traditional founding of Rome. It is an expression used in antiquity and by classical historians to refer to a given year in Ancient Rome. In reference to the traditional year of the foundation of Rome, the year 1 BC would be written AUC 753, whereas AD 1 would be AUC 754. The foundation of the Roman Empire in 27 BC would be AUC 727. The current year AD 2023 would be AUC 2776.
The Julian calendar is a solar calendar of 365 days in every year with an additional leap day every fourth year. The Julian calendar is still used in parts of the Eastern Orthodox Church and in parts of Oriental Orthodoxy as well as by the Berbers.

The Roman calendar was the calendar used by the Roman Kingdom and Roman Republic. Although primarily used of Rome's pre-Julian calendars, the term often includes the Julian calendar established by the reforms of the dictator Julius Caesar and emperor Augustus in the late 1st century BC.
Year 12 BC was either a common year starting on Saturday, Sunday or Monday or a leap year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar and a common year starting on Friday of the Proleptic Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Messalla and Quirinius. The denomination 12 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
AD 1 or 1 CE was the epoch year for the Anno Domini (AD) Christian calendar era and also the 1st year of the Common Era (CE) and the 1st millennium and of the 1st century of the Christian and the common era. It was a common year starting on Saturday or Sunday, a common year starting on Saturday by the proleptic Julian calendar, and a common year starting on Monday by the proleptic Gregorian calendar. In the Roman Empire, AD 1 was known as the Year of the Consulship of Caesar and Paullus, named after Roman consuls Gaius Caesar and Lucius Aemilius Paullus, and less frequently, as year AUC 754 within the Roman Empire. The denomination "AD 1" for this year has been in consistent use since the mid-medieval period when the Anno Domini (AD) calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. It was the beginning of the Christian era/common era. The preceding year is 1 BC; there is no year 0 in this numbering scheme. The Anno Domini dating system was devised in AD 525 by Dionysius Exiguus.
The proleptic Julian calendar is produced by extending the Julian calendar backwards to dates preceding AD 8 when the quadrennial leap year stabilized. The leap years that were actually observed between the implementation of the Julian calendar in 45 BC and AD 8 were erratic.
In chronology and periodization, an epoch or reference epoch is an instant in time chosen as the origin of a particular calendar era. The "epoch" serves as a reference point from which time is measured.
Year 8 BC was either a common year starting on Friday or Saturday or a leap year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar and a common year starting on Wednesday of the Proleptic Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Censorinus and Gaius Asinius. The denomination 8 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
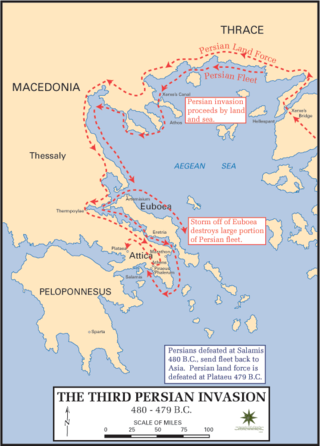
Year 480 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Vibulanus and Cincinnatus. The denomination 480 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 46 BC was the last year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Caesar and Lepidus. The denomination 46 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 45 BC was either a common year starting on Thursday, Friday or Saturday or a leap year starting on Friday or Saturday and the first year of the Julian calendar and a leap year starting on Friday of the Proleptic Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Caesar without Colleague. The denomination 45 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 212 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Flaccus and Pulcher. The denomination 212 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

The ancient Egyptian calendar – a civil calendar – was a solar calendar with a 365-day year. The year consisted of three seasons of 120 days each, plus an intercalary month of five epagomenal days treated as outside of the year proper. Each season was divided into four months of 30 days. These twelve months were initially numbered within each season but came to also be known by the names of their principal festivals. Each month was divided into three 10-day periods known as decans or decades. It has been suggested that during the Nineteenth Dynasty and the Twentieth Dynasty the last two days of each decan were usually treated as a kind of weekend for the royal craftsmen, with royal artisans free from work.
A calendar era is the period of time elapsed since one epoch of a calendar and, if it exists, before the next one. For example, it is the year 2023 as per the Gregorian calendar, which numbers its years in the Western Christian era.
The Attic calendar or Athenian calendar is the lunisolar calendar beginning in midsummer with the lunar month of Hekatombaion, in use in ancient Attica, the ancestral territory of the Athenian polis. It is sometimes called the Greek calendar because of Athens's cultural importance, but it is only one of many ancient Greek calendars.
The Era of the Martyrs, also known as the Diocletian era, is a method of numbering years based on the reign of Roman Emperor Diocletian who instigated the last major persecution against Christians in the Empire. It was used by the Church of Alexandria beginning in the 4th century AD/CE and it has been used by the Coptic Orthodox Church of Alexandria from the 5th century until the present. This era was used to number the year in Easter tables produced by the Church of Alexandria.

Anno Mundi, abbreviated as AM or A.M., or Year After Creation, is a calendar era based on the biblical accounts of the creation of the world and subsequent history. Two such calendar eras have seen notable use historically:
A year zero does not exist in the Anno Domini (AD) calendar year system commonly used to number years in the Gregorian calendar ; in this system, the year 1 BC is followed directly by year AD 1. However, there is a year zero in both the astronomical year numbering system, and the ISO 8601:2004 system, the interchange standard for all calendar numbering systems. There is also a year zero in most Buddhist and Hindu calendars.

The Byzantine calendar, also called the Roman calendar, the Creation Era of Constantinople or the Era of the World, was the calendar used by the Eastern Orthodox Church from c. 691 to 1728 in the Ecumenical Patriarchate. It was also the official calendar of the Byzantine Empire from 988 to 1453 and of Kievan Rus' and Russia from c. 988 to 1700. This calendar was used also in other areas of the Byzantine commonwealth such as in Serbia, where it is found in old Serbian legal documents such as Dušan's Code, thus being referred to as the Serbian Calendar as well. Since Byzantine is a historiographical term, the original name uses the adjective "Roman" as it was what the Eastern Roman Empire continued calling itself.
The Gregorian calendar is the calendar used in most parts of the world. It was introduced on February 24 with a papal bull, and went into effect in October 1582 by Pope Gregory XIII as a modification of, and replacement for, the Julian calendar. The principal change was to space leap years differently so as to make the average calendar year 365.2425 days long, more closely approximating the 365.2422-day 'tropical' or 'solar' year that is determined by the Earth's revolution around the Sun.