Related Research Articles

Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications, usually known by the acronym DECT, is a standard used for creating cordless telephone systems and for IoT systems. It originated in Europe, where it is the common standard, replacing earlier cordless phone standards, such as 900 MHz CT1 and CT2. The IoT usage relies on the new DECT-2020 standard.

A Faraday cage or Faraday shield is an enclosure used to block electromagnetic fields. A Faraday shield may be formed by a continuous covering of conductive material, or in the case of a Faraday cage, by a mesh of such materials. Faraday cages are named after scientist Michael Faraday, who first constructed one in 1836.

TEMPEST is a U.S. National Security Agency specification and a NATO certification referring to spying on information systems through leaking emanations, including unintentional radio or electrical signals, sounds, and vibrations. TEMPEST covers both methods to spy upon others and how to shield equipment against such spying. The protection efforts are also known as emission security (EMSEC), which is a subset of communications security (COMSEC).

A flash drive is a data storage device that includes flash memory with an integrated USB interface. A typical USB drive is removable, rewritable, and smaller than an optical disc, and usually weighs less than 30 g (1 oz). Since first offered for sale in late 2000, the storage capacities of USB drives range from 8 to 256 gigabytes (GB), 512 GB and 1 terabyte (TB). As of 2023, 2 TB flash drives were the largest currently in production. Some allow up to 100,000 write/erase cycles, depending on the exact type of memory chip used, and are thought to physically last between 10 and 100 years under normal circumstances.

The SAM Lock Tool, better known as Syskey, is a discontinued component of Windows NT that encrypts the Security Account Manager (SAM) database using a 128-bit RC4 encryption key.

Crystal healing is a pseudoscientific alternative-medicine practice that uses semiprecious stones and crystals such as quartz, agate, amethyst or opal. Adherents of the practice claim that these have healing powers, but there is no scientific basis for this claim. Practitioners of crystal healing believe they can boost low energy, prevent bad energy, release blocked energy, and transform a body's aura.

The antennas contained in mobile phones, including smartphones, emit radiofrequency (RF) radiation ; the parts of the head or body nearest to the antenna can absorb this energy and convert it to heat. Since at least the 1990s, scientists have researched whether the now-ubiquitous radiation associated with mobile phone antennas or cell phone towers is affecting human health. Mobile phone networks use various bands of RF radiation, some of which overlap with the microwave range. Other digital wireless systems, such as data communication networks, produce similar radiation.

Wireless USB (Universal Serial Bus) is a short-range, high-bandwidth wireless radio communication protocol created by the Wireless USB Promoter Group, which is intended to increase the availability of general USB-based technologies. It is unrelated to Wi-Fi and different from the Cypress Wireless USB offerings. It was maintained by the WiMedia Alliance which ceased operations in 2009. Wireless USB is sometimes abbreviated as WUSB, although the USB Implementers Forum discouraged this practice and instead prefers to call the technology Certified Wireless USB to distinguish it from the competing UWB standard.
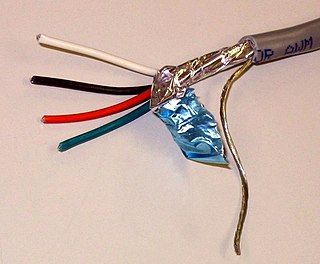
A shielded cable or screened cable is an electrical cable that has a common conductive layer around its conductors for electromagnetic shielding. This shield is usually covered by an outermost layer of the cable. Common types of cable shielding can most broadly be categorized as foil type, contraspiralling wire strands or both. A longitudinal wire may be necessary with dielectric spiral foils to short out each turn.
In computing, external storage refers to non-volatile (secondary) data storage outside a computer's own internal hardware, and thus can be readily disconnected and accessed elsewhere. Such storage devices may refer to removable media, compact flash drives, portable storage devices, or network-attached storage. Web-based cloud storage is the latest technology for external storage.
Electromagnetic hypersensitivity (EHS) is a claimed sensitivity to electromagnetic fields, to which negative symptoms are attributed. EHS has no scientific basis and is not a recognized medical diagnosis, although it is generally accepted that the experience of EHS symptoms is of psychosomatic origin. Claims are characterized by a "variety of non-specific symptoms, which afflicted individuals attribute to exposure to electromagnetic fields". Attempts to justify the claim that EHS is caused by exposure to electromagnetic fields have amounted to pseudoscience.

In telecommunications, 5G is the fifth-generation technology standard for cellular networks, which cellular phone companies began deploying worldwide in 2019, and is the successor to 4G technology that provides connectivity to most current mobile phones.

Trek 2000 International Limited is a Singaporean technology company that is listed on the Singapore Exchange (SGX:TREK). The company claims to be the inventor of the ThumbDrive, a USB data storage device. The company owns a library of more than 600 patents, with 360 granted patents. It has also developed numerous other products in the same consumer electronics market segments including the Ai-Ball and offers products such as SSDs and Flash Drives. The ThumbDrive trademark is registered by Trek 2000 International in international markets, although the original inventors of the USB flash drive and the related patents are the subjects of multiple disputes.

A dongle is a small piece of computer hardware that connects to a port on another device to provide it with additional functionality, or enable a pass-through to such a device that adds functionality.

Windows To Go is a feature in Windows 8 Enterprise, Windows 8.1 Enterprise, Windows 10 Education and Windows 10 Enterprise versions prior to the May 2020 update, that allows the system to boot and run from certain USB mass storage devices such as USB flash drives and external hard disk drives which have been certified by Microsoft as compatible. It is a fully manageable corporate Windows environment. The development of Windows To Go was discontinued by Microsoft in 2019, and is no longer available in Windows 10 as of the May 2020 update.

Shungite is either a diverse group of metamorphosed Precambrian rocks all of which contain pyrobitumen, or the pyrobitumen within those rocks. It was first described from a deposit near Shunga village, in Karelia, Russia, from where it gets its name. Shungite is most widely known for pseudoscientific and quack medical claims about its uses in medicine and technology, where it is claimed to have properties ranging from nebulous health benefits to blocking 5G radiation.

The YubiKey is a hardware authentication device manufactured by Yubico to protect access to computers, networks, and online services that supports one-time passwords (OTP), public-key cryptography, and authentication, and the Universal 2nd Factor (U2F) and FIDO2 protocols developed by the FIDO Alliance. It allows users to securely log into their accounts by emitting one-time passwords or using a FIDO-based public/private key pair generated by the device. YubiKey also allows storing static passwords for use at sites that do not support one-time passwords. Google, Amazon, Microsoft, Twitter, and Facebook use YubiKey devices to secure employee accounts as well as end-user accounts. Some password managers support YubiKey. Yubico also manufactures the Security Key, a similar lower-cost device with only FIDO2/WebAuthn and FIDO/U2F support.
In cryptography, electromagnetic attacks are side-channel attacks performed by measuring the electromagnetic radiation emitted from a device and performing signal analysis on it. These attacks are a more specific type of what is sometimes referred to as Van Eck phreaking, with the intention to capture encryption keys. Electromagnetic attacks are typically non-invasive and passive, meaning that these attacks are able to be performed by observing the normal functioning of the target device without causing physical damage. However, an attacker may get a better signal with less noise by depackaging the chip and collecting the signal closer to the source. These attacks are successful against cryptographic implementations that perform different operations based on the data currently being processed, such as the square-and-multiply implementation of RSA. Different operations emit different amounts of radiation and an electromagnetic trace of encryption may show the exact operations being performed, allowing an attacker to retrieve full or partial private keys.

Karsten Nohl is a German cryptography expert and hacker. His areas of research include Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) security, radio-frequency identification (RFID) security, and privacy protection.
Simon Jean Paul Sasha Adams, known as Sacha Stone, is a British New Age influencer and conspiracy theorist. He is marketing 5GBioShield, a fake anti-radiation protection device. He is also known for founding The International Tribunal for Natural Justice, The New Earth Project and the New Earth Festival which he hosts at his private resort, Akasha New Earth Haven, in Ubud, Bali.
References
- 1 2 Cellan-Jones, Rory (28 May 2020). "Trading Standards squad targets anti-5G USB stick". BBC News .
Cyber-security experts say the £339 5GBioShield appears to no more than a basic USB drive. 'We consider it to be a scam,' Stephen Knight, operations director for London Trading Standards told the BBC.
- ↑ Koetsier, John. "$350 '5G Bioshield' Radiation Protection Device Is A ... $6 USB Stick". Forbes. Retrieved 19 December 2021.
- 1 2 "Reverse Engineering a 5 g 'Bioshield'". Pen Test Partners. Archived from the original on 28 May 2020.
The circular area on the main casing looked like it might be where the "quantum holographic catalyzer technology" transmitter might be. Carefully taking that off, not to damage the key components and, with crushing disappointment, it looked exactly like a regular sticker.
- ↑ Wright, Tom (16 June 2020). "The 5G Con That Could Make You Sick" (PDF). File on Four .
I have explained that until now, I explained the scientific base of my invention and you should understand also, anybody should understand that these love protection, very high frequency, the highest frequency in the universe is a frequency of love. And when you protect something with that highest frequency, nothing what is lower can penetrate it. My technology is a, is a, made in a new energy, very simple, easy, cheap and efficient. That is a simple sticker where I need three nano layers. One nano layer is a glue, the other is PVC and the third one is colour.
- ↑ Taylor, Michael (20 May 2020). "Glastonbury 5G row: Report slammed as 'farcical' for coronavirus and expensive Bioshield claims". Somerset Live.
- ↑ "'5GBioShield' cited in council's 5G report described as 'nothing more than a £5 USB key with a sticker on'". Somerset Live.
- ↑ Koetsier, John (28 May 2020). "$350 '5G Bioshield' Radiation Protection Device Is A ... $6 USB Stick". Forbes . Archived from the original on 10 June 2021.
A $350 USB stick is being marketed as a "5G Bioshield" for credulous 5G conspiracy theorists, says a security service that specializes in electronic security.