Related Research Articles

Abortion in the United Kingdom is de facto available under the terms of the Abortion Act 1967 in Great Britain and the Abortion (No.2) Regulations 2020 in Northern Ireland. The procurement of an abortion remains a criminal offence in Great Britain under the Offences Against the Person Act 1861, although the Abortion Act provides a legal defence for both the pregnant woman and her doctor in certain cases. Although a number of abortions did take place before the 1967 Act, there have been around 10 million abortions in the United Kingdom. Around 200,000 abortions are carried out in England and Wales each year and just under 14,000 in Scotland; the most common reason cited under the ICD-10 classification system for around 98% of all abortions is "risk to woman's mental health."
Abortion in Ireland is regulated by the Health Act 2018. Abortion is permitted in Ireland during the first twelve weeks of pregnancy, and later in cases where the pregnant woman's life or health is at risk, or in the cases of a fatal foetal abnormality. Abortion services commenced on 1 January 2019, following its legalisation by the aforementioned Act, which became law on 20 December 2018. Previously, the 8th Constitutional Amendment had given the life of the unborn foetus the same value as that of its mother, but the 36th constitutional amendment, approved by referendum in May 2018, replaced this with a clause permitting the Oireachtas (parliament) to legislate for the termination of pregnancies.

Teenage pregnancy, also known as adolescent pregnancy, is pregnancy in a female adolescent or young adult under the age of 20. Worldwide, pregnancy complications are the leading cause of death for women and girls 15 to 19 years old. The definition of teenage pregnancy includes those who are legally considered adults in their country. The WHO defines adolescence as the period between the ages of 10 and 19 years. Pregnancy can occur with sexual intercourse after the start of ovulation, which can happen before the first menstrual period (menarche). In healthy, well-nourished girls, the first period usually takes place between the ages of 12 and 13.

Abortion is a divisive issue in the United States. The issue of abortion is prevalent in American politics and culture wars, though a majority of Americans support continued access to abortion. There are widely different abortion laws depending on state, although there are no federal laws.

Abortion laws vary widely among countries and territories, and have changed over time. Such laws range from abortion being freely available on request, to regulation or restrictions of various kinds, to outright prohibition in all circumstances. Many countries and territories that allow abortion have gestational limits for the procedure depending on the reason; with the majority being up to 12 weeks for abortion on request, up to 24 weeks for rape, incest, or socioeconomic reasons, and more for fetal impairment or risk to the woman's health or life. As of 2022, countries that legally allow abortion on request or for socioeconomic reasons comprise about 60% of the world's population. In 2024, France became the first country to explicitly protect abortion rights in its constitution.
Abortion in Australia is legal. There are no federal abortion laws, and full decriminalisation of the procedure has been enacted in all jurisdictions. Access to abortion varies between the states and territories: Surgical abortions are readily available on request within the first 22 to 24 weeks of pregnancy in most jurisdictions, and up to 16 weeks in Tasmania. Later-term abortions can be obtained with the approval of two doctors, although the Australian Capital Territory only requires a single physician's approval.

Sexual and reproductive health (SRH) is a field of research, health care, and social activism that explores the health of an individual's reproductive system and sexual well-being during all stages of their life. Sexual and reproductive health is more commonly defined as sexual and reproductive health and rights, to encompass individual agency to make choices about their sexual and reproductive lives.
Many jurisdictions have laws applying to minors and abortion. These parental involvement laws require that one or more parents consent or be informed before their minor daughter may legally have an abortion.

Abortion in South Africa is legal by request when the pregnancy is under 13 weeks. It is also legal to terminate a pregnancy between week 13 and week 20 under the following conditions: the continued pregnancy would significantly affect the pregnant person's social or economic circumstances, the continued pregnancy poses a risk of injury to the pregnant person's physical or mental health, there is a substantial risk that the foetus would suffer from a severe physical or mental abnormality, or the pregnancy resulted from rape or incest. If the pregnancy is more than 20 weeks, a termination is legal if the foetus' life is in danger, or there is a likelihood of serious birth defects.
Abortion has been legal in India under various circumstances with the introduction of the Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) Act, 1971. The Medical Termination of Pregnancy Regulations, 2003 were issued under the Act to enable women to access safe and legal abortion services.

Abortion in Andorra is illegal in all cases; the Co-Princes of Andorra are the President of France and the Bishop of Urgell, who is required to adhere to Roman Catholic teaching on pregnancy. Around 88% of its population identifies as Roman Catholic.

The legality of abortion in the United States and the various restrictions imposed on the procedure vary significantly depending on the laws of each state or other jurisdiction, although there is no uniform federal law. Some states prohibit abortion at all stages of pregnancy with few exceptions, others permit it up to a certain point in a woman's pregnancy, while others allow abortion throughout a woman's pregnancy. In states where abortion is legal, several classes of restrictions on the procedure may exist, such as parental consent or notification laws, requirements that patients be shown an ultrasound before obtaining an abortion, mandatory waiting periods, and counseling requirements.
Abortion in Costa Rica is severely restricted by criminal law. Currently, abortions are allowed in Costa Rica only in order to preserve the life or physical health of the woman. Abortions are illegal in almost all cases, including when the pregnancy is a result of rape or incest and when the foetus suffers from medical problems or birth defects. Both social and economic factors have led to this legal status. It remains unclear whether abortions are legal to preserve the mental health of the woman, though the 2013 United Nations abortion report says Costa Rica does allow abortions concerning the mental health of a woman.
Reproductive coercion is a collection of behaviors that interfere with decision-making related to reproductive health. These behaviors are meant to maintain power and control related to reproductive health by a current, former, or hopeful intimate or romantic partner, but they can also be perpetrated by parents or in-laws. Coercive behaviors infringe on individuals' reproductive rights and reduce their reproductive autonomy.
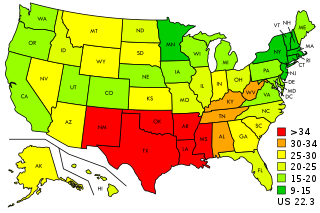
Teenage pregnancy in the United States occurs mostly unintentionally and out of wedlock but has been declining almost continuously since the 1990s. In 2022, the teenage birth rate fell to 13.5 per 1,000 girls aged 15 to 19, the lowest on record. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), this decline is due to abstinence and the use of contraception. However, the averages conceal significant ethnic or geographic differences within the nation. The birth rates for Hispanic and African-American teens were more than double those of European-American teens, while Asian-American adolescents have the lowest pregnancy and birth rates of all. As of 2015, New Mexico, Texas, Oklahoma, Arkansas, Louisiana, and Mississippi had the highest adolescent birth rates in the Union.
Abortion in Benin is legally permitted "upon the request of the pregnant woman, voluntary termination of pregnancy can be allowed when the pregnancy is likely to aggravate or cause a situation of material, educational, professional or moral distress incompatible with the interest of the woman and/or the unborn child…" in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy.
Abortion in Thailand is legal and available on-request up to 20 weeks of pregnancy. Abortion has been legal up to at least 12 weeks of pregnancy since 7 February 2021. Following a 2020 ruling of the Constitutional Court which declared a portion of the abortion statutes unconstitutional, the Parliament removed first-term abortion from the criminal code. Once strict, over time laws have been relaxed to take into account high rates of teen pregnancy, women who lack the means or will to raise children, and the consequences of illegal abortion.

Abortion in South Korea was decriminalized, effective 1 January 2021, by a 2019 order of the Constitutional Court of Korea. It is currently legal throughout pregnancy, as no new law has been enacted. Thus there are no gestational limits or other restrictions.

The Health Act 2018 is an Act of the Oireachtas which defines the circumstances and processes within which abortion may be legally performed in Ireland. It permits termination under medical supervision, generally up to 12 weeks' pregnancy, and later if pregnancy poses a serious health risk or there is a fatal foetal abnormality.

A referendum on partially legalising abortion was held in Gibraltar on 24 June 2021. The referendum question was whether to enact the Crimes (Amendment) Act 2019, which allows abortions up to 12 weeks if the woman's mental or physical health is at risk. It also allows abortion later if the woman's life is at risk, to prevent "grave permanent" mental or physical injury, or there is a fatal fetal abnormality. It had originally been scheduled for 19 March 2020, but was postponed on 12 March 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The proposal was approved by 63% of voters.
References
- ↑ Thanabouasy, Phayboune (21 July 2021). "Authorities Draft New Legislation on Surrogacy and Abortion in Laos". The Laotian Times. Retrieved 25 October 2023.
- ↑ "ຂໍ້ຕົກລົງ ວ່າດ້ວຍ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ການໃຫ້ຖືພາແທນ ແລະ ການໃຫ້ຫຼຸລູກ" [Decision on the Management of Surrogacy and Abortion]. Decision No. 2077 of 8 July 2021 (in Lao). Ministry of Health of Laos. Archived from the original on 17 November 2021. Retrieved 25 October 2023.
- ↑ Vongxay, Viengnakhone; Chaleunvong, Kongmany; Essink, Dirk R.; Durham, Jo; Sychareun, Vanphanom (30 July 2020). "Knowledge of and attitudes towards abortion among adolescents in Lao PDR". Global Health Action. 13 (sup2): 1791413. doi: 10.1080/16549716.2020.1791413 . PMC 7480451 . PMID 32741348.