Related Research Articles

Boracay is a resort island in the Western Visayas region of the Philippines, located 0.8 kilometers (0.50 mi) off the northwest coast of Panay. It has a total land area of 10.32 square kilometers (3.98 sq mi), under the jurisdiction of three barangays in Malay, Aklan, and had a population of 37,802 in 2020.

A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side.
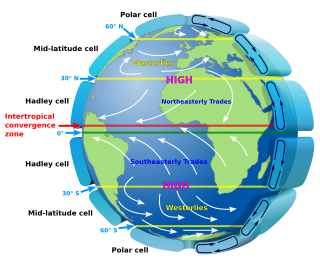
In meteorology, prevailing wind in a region of the Earth's surface is a surface wind that blows predominantly from a particular direction. The dominant winds are the trends in direction of wind with the highest speed over a particular point on the Earth's surface at any given time. A region's prevailing and dominant winds are the result of global patterns of movement in the Earth's atmosphere. In general, winds are predominantly easterly at low latitudes globally. In the mid-latitudes, westerly winds are dominant, and their strength is largely determined by the polar cyclone. In areas where winds tend to be light, the sea breeze/land breeze cycle is the most important cause of the prevailing wind; in areas which have variable terrain, mountain and valley breezes dominate the wind pattern. Highly elevated surfaces can induce a thermal low, which then augments the environmental wind flow.

Sofronio Española, officially the Municipality of Sofronio Española, is a 2nd class municipality in the province of Palawan, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 37,416 people.

Esperanza, officially the Municipality of Esperanza, is a 5th class municipality in the province of Masbate, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 17,534 people.

The 2003 Pacific typhoon season was a slightly below average yearlong period of tropical cyclogenesis exhibiting the development of 45 tropical depressions, of which 21 became named storms; of those, 14 became typhoons. Though every month with the exception of February and March featured tropical activity, most storms developed from May through October. During the season, tropical cyclones affected the Philippines, Japan, China, the Korean Peninsula, Indochina, and various islands in the western Pacific.

The 1993 Pacific typhoon season has no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1993, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between May and November. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.

The Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration is the National Meteorological and Hydrological Services (NMHS) agency of the Philippines mandated to provide protection against natural calamities and to ensure the safety, well-being and economic security of all the people, and for the promotion of national progress by undertaking scientific and technological services in meteorology, hydrology, climatology, astronomy and other geophysical sciences. Created on December 8, 1972, by reorganizing the Weather Bureau, PAGASA now serves as one of the Scientific and Technological Services Institutes of the Department of Science and Technology.
The Philippines is a typhoon-prone country, with approximately 20 typhoons entering its area of responsibility each year. Locally known generally as bagyo, typhoons regularly form in the Philippine Sea and less regularly, in the South China Sea, with the months of June to September being the most active, August being the month with the most activity. Each year, at least ten typhoons are expected to hit the island nation, with five expected to be destructive and powerful. In 2013, Time declared the country as the "most exposed country in the world to tropical storms".
The 1939 Pacific typhoon season has no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1939, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between May and November. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.
Amihan is a genderless deity that is depicted as a bird in the Philippine mythology. According to the Tagalog folklore, Amihan is the first creature to inhabit the universe, along with the gods called Bathala and Aman Sinaya. In the legend Amihan is described as a bird who saves the first human beings, Malakas and Maganda from a bamboo plant.

In Philippine mythology, the Tigmamanukan was believed by the Tagalog people to be an omen or augural bird. Although the behaviors of numerous birds and lizards were said to be omens, particular attention was paid to the tigmamanukan. Before Christianisation, the Tagalogs believed that the tigmamanukan was sent by Bathala to give hints to mankind whether they needed to proceed on a journey or not. In some Philippine creation myths, the tigmamanukan bird was sent by Bathala to crack open the primordial bamboo whence the first man and woman came out.

The North American monsoon, variously known as the Southwest monsoon, the Mexican monsoon, the New Mexican monsoon, or the Arizona monsoon is a pattern of pronounced increase in thunderstorms and rainfall over large areas of the southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico, centered roughly on the Rio Grande Valley, and typically occurring between June and mid-September. During the monsoon, thunderstorms are fueled by daytime heating and build up during the late afternoon and early evening. Typically, these storms dissipate by late night, and the next day starts out fair, with the cycle repeating daily. The monsoon typically loses its energy by mid-September when much drier conditions are reestablished over the region. Geographically, the North American monsoon precipitation region is centered over the Sierra Madre Occidental in the Mexican states of Sinaloa, Durango, Sonora and Chihuahua.

The Philippines has five types of climates: tropical rainforest, tropical monsoon, tropical savanna, humid subtropical and oceanic characterized by relatively high temperature, oppressive humidity and plenty of rainfall. There are two seasons in the country, the wet season and the dry season, based upon the amount of rainfall. This is also dependent on location in the country as some areas experience rain all throughout the year. Based on temperature, the warmest months of the year are March through October; the winter monsoon brings cooler air from November to February. May is the warmest month, and January, the coolest.
The 2012 Luzon southwest monsoon floods, was an eight-day period of torrential rain and thunderstorms in Luzon in the Philippines from August 1 to August 8, 2012. Its effects centered on Metro Manila, the surrounding provinces of the Calabarzon region and the provinces of Central Luzon. Not a typhoon in its own right, the storm was a strong movement of the southwest monsoon caused by the pull of Typhoon Saola (Gener) from August 1–3, strengthened by Typhoon Haikui. It caused typhoon-like damage: the most damage caused by rain since September 2009, when Typhoon Ketsana (Ondoy) struck Metro Manila. The heavy rain caused the Marikina River to overflow, destroying areas also affected by Ketsana, triggering a landslide in the Commonwealth area and collapsing the northbound Marcos Highway.
Caparangasan is an island barangay located in Gandara, Samar province of the Philippines.

The indigenous religious beliefs of the Tagalog people were well documented by Spanish missionaries, mostly in the form of epistolary accounts (relaciones) and entries in various dictionaries compiled by missionary friars.

Balesin Island is a tropical island and barangay off the eastern coast of Luzon in the Philippines. It is located in Lamon Bay and is administered as part of the municipality of Polillo of Quezon province.
References
- 1 2 English, Fr. Leo James (2004). Tagalog-English Dictionary. Manila: Congregation of the Most Holy Redeemer. ISBN 971-08-4357-5.
- ↑ "Philippines : Weather". Lonely Planet (travel guidebook). Archived from the original on 2017-09-10. Retrieved 2013-06-28.