A nickname is a substitute for the proper name of a person, place or thing. It is commonly used to express affection, amusement, a character trait or defamation of character. It is distinct from a pseudonym, stage name or title, although the concepts can overlap. Nicknames are typically informal.

An ethnic stereotype or racial stereotype involves part of a system of beliefs about typical characteristics of members of a given ethnic group, their status, societal and cultural norms. A national stereotype does the same for a given nationality. The stereotyping may be used for humor in jokes, and/or may be associated with racism.

An ethnic joke is a remark aiming at humor relating to an ethnic, racial or cultural group, often referring to an ethnic stereotype of the group in question for its punchline.

British humour carries a strong element of satire aimed at the absurdity of everyday life. Common themes include sarcasm, tongue-in-cheek, banter, insults, self-deprecation, taboo subjects, puns, innuendo, wit, and the British class system. These are often accompanied by a deadpan delivery which is present throughout the British sense of humour. It may be used to bury emotions in a way that seems unkind in the eyes of other cultures. Jokes are told about everything and almost no subject is off-limits, though a lack of subtlety when discussing controversial issues is sometimes considered insensitive. Many British comedy series have become successful internationally, serving as a representation of British culture to overseas audiences.
Russian jokes are short fictional stories or dialogs with a punch line, which commonly appear in Russian humor. Russian joke culture includes a series of categories with fixed settings and characters. Russian jokes treat topics found everywhere in the world, including sex, politics, spousal relations, or mothers-in-law. This article discusses Russian joke subjects that are particular to Russian or Soviet culture.
Blason populaire is an umbrella genre in the field of folkloristics used to designate any item of any genre which makes use of stereotypes, usually, but not always, negative stereotypes, of a particular group. "These stereotypes are manifested in a wide array of folkloric genres, including proverbs, other traditional sayings, nicknames, jokes, songs, rhymes, and football chants. All share a common function in that they are invoked to highlight positive aspects of the in-group by explicit auto-stereotyping or, alternatively, to identify the negative characteristics of out-groups. The explicit positive stereotyping of an in-group may often implicitly suggest negative characteristics of a rival out-group." In blasons populaires nations are homogeneous and have national characteristics.
"England Your England" is an essay written by the English author George Orwell during The Blitz of 1941 as bombers of Nazi Germany flew overhead. It was his attempt to define English culture and the English people for the rest of the world as he feared that it might soon be wiped out by the Nazis. In the essay he also wrote that England would not change into a fascist state and could not unless she was thoroughly broken.
Comedic device refers to a kind of device used to make a statement more humorous. In layman's terms, it is what makes things funny.

The Bellman joke is a type of simple joke cycle popular among Swedish schoolchildren, always including a person named Bellman as the main character.
Chinaman is a term referring to a Chinese man or person, a Mainland Chinese national or, in some cases, a person native to geographical East Asia or of perceived East Asian race. While the term has no negative connotations in older dictionaries and the usage of such compound terms as Englishman, Scotsman, Frenchman, Dutchman, Irishman, and Welshman are sometimes cited as unobjectionable parallels, the term is noted as having pejorative overtones by modern dictionaries. Its derogatory connotations evolved from its use in pejorative contexts regarding Chinese people and other Asians as well as its grammatical incorrectness which resembles stereotypical characterizations of Chinese accents in English-speaking associated with discrimination. The usage of the term Chinaman is strongly discouraged by Asian American organizations.
Colin Lynes is a British former professional boxer who competed from 1998 to 2017. He held the IBO super lightweight title from 2004 to 2005. At regional level, he held the British super lightweight title in 2007; the EBU European super lightweight title from 2007 to 2008; and the British welterweight title from 2011 to 2012.
In folklore, a simpleton is a person whose foolish actions are the subject of often-repeated stories. Simpletons are also known as noodles or fools. Folklore often holds, with no basis in fact, that certain towns or countries are thought to be home to large numbers of simpletons. The ancient Greeks told tales of stupid populations in Abdera and other cities; in Germany, men of Schilda are conspicuous in these stories; in Spain hundreds of jokes exist about the supposed foolishness of the people from Lepe; and in England, the village of Gotham in Nottinghamshire is reputed to be populated by simpletons. In Sri Lanka whole districts in the central, southern, and western provinces are credited with being the abode of foolish people.
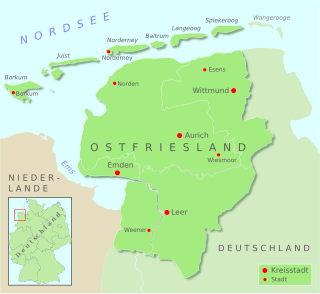
In German humour, East Frisian jokes belong to the group of riddle jokes about certain nationalities, in this case the East Frisians of northern Germany.

The fool is a stock character in creative works and folklore. There are several distinct, although overlapping, categories of fool: simpleton fool, wise fool, and serendipitous fool.

Countryballs, also known as Polandball, is a geopolitical satirical art style, genre, and internet meme, predominantly used in online comics strips in which countries or political entities are personified as balls with eyes without pupils, decorated with their national flags. Comics feature the characters in various scenarios, generally poking fun at national stereotypes, international relations, and historical events, with them moving about by walking or jumping. Other common features in Countryball strips include non-English countries speaking in broken English—with vocabularies of their national languages included—political incorrectness, and black comedy. Strips are generally created using Microsoft Paint or more advanced tools, often made to intentionally look crudely drawn.
A conditional joke is a joke meant for a qualified audience only. If a joke requires from the audience a certain knowledge or a belief, then Ted Cohen calls such jokes hermetic. Possessing prior knowledge and understanding of the topic, which in turn enables them to understand the joke. Such ability is also called the prerequisite condition for laughter. The conditional joke is one of two main categories of jokes, according to Ted Cohen; the main one being a universal joke, which does not require familiarity with the hermetic language of a conditional joke.
Stereotypes of British people are found in several cultures. Some stereotypes relate to many specific ethnic groups of Britain while others are directed at British nationals in general.

Jet was a weekly British comics periodical published by Fleetway Publications from 1 May to 25 September 1971. A boys' adventure comic, the title only lasted for 22 editions before being merged with another Fleetway title, the long-established Buster.

A town of fools is the base of a number of joke cycles found in various cultures. Jokes of these cycles poke fun at the stupidity of the inhabitants of a real or fictional populated place. In English folklore the best known butt of jokes of this type are the Wise Men of Gotham. A number of works of satire are set in a town of fools.








