Related Research Articles

Systems engineering is an interdisciplinary field of engineering and engineering management that focuses on how to design, integrate, and manage complex systems over their life cycles. At its core, systems engineering utilizes systems thinking principles to organize this body of knowledge. The individual outcome of such efforts, an engineered system, can be defined as a combination of components that work in synergy to collectively perform a useful function.

The Department of Defense Architecture Framework (DoDAF) is an architecture framework for the United States Department of Defense (DoD) that provides visualization infrastructure for specific stakeholders concerns through viewpoints organized by various views. These views are artifacts for visualizing, understanding, and assimilating the broad scope and complexities of an architecture description through tabular, structural, behavioral, ontological, pictorial, temporal, graphical, probabilistic, or alternative conceptual means. The current release is DoDAF 2.02.
The Joint Capabilities Integration and Development System (JCIDS), is the formal United States Department of Defense (DoD) process which defines acquisition requirements and evaluation criteria for future defense programs. JCIDS was created to replace the previous service-specific requirements generation system that allowed redundancies in capabilities and failed to meet the combined needs of all US military services. In order to correct these problems, JCIDS is intended to guide the development of requirements for future acquisition systems to reflect the needs of all four services by focusing the requirements generation process on needed capabilities as requested or defined by one of the US combatant commanders. In an ideal implementation of the JCIDS process, regional and functional combatant commanders give early and continuous feedback into the acquisition and sustainment processes to ensure their current and evolving requirements are known and met.
Value measuring methodology (VMM) is a tool that helps financial planners balance both tangible and intangible values when making investment decisions, and monitor benefits.
The Transformational Satellite Communications System (TSAT) program was a United States Department of Defense (DOD) program sponsored by the U.S. Air Force for a secure, high-capacity global communications network serving the Department of Defense, NASA and the United States Intelligence Community (IC). It was intended as an enabler of net-centric warfare that would facilitate defense and intelligence professionals making rapid decisions based on integrated, comprehensive information. In 2003, the estimated project costs for the period up to 2015 were estimated to US$ 12 billion. In October 2008, the DoD announced that it was postponing making a decision on choosing a contractor to build the system until 2010. In April 2009 Secretary of Defence Robert M. Gates asked that the project be canceled in its entirety.
Capability management is a high-level integrative management function, with particular application in the context of defense.
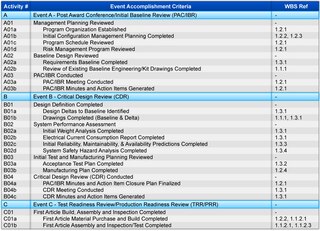
In the United States Department of Defense, the Integrated Master Plan (IMP) and the Integrated Master Schedule (IMS) are important program management tools that provide significant assistance in the planning and scheduling of work efforts in large and complex materiel acquisitions. The IMP is an event-driven plan that documents the significant accomplishments necessary to complete the work and ties each accomplishment to a key program event. The IMP is expanded to a time-based IMS to produce a networked and multi-layered schedule showing all detailed tasks required to accomplish the work effort contained in the IMP. The IMS flows directly from the IMP and supplements it with additional levels of detail——both then form the foundations to implement an Earned Value Management System.
A glossary of terms relating to project management and consulting.

Military acquisition or defense acquisition is the "bureaucratic management and procurement process", dealing with a nation's investments in the technologies, programs, and product support necessary to achieve its national security strategy and support its armed forces. Its objective is to acquire products that satisfy specified needs and provide measurable improvement to mission capability at a fair and reasonable price.
In the United States military integrated acquisition lifecycle the Technical section has multiple acquisition "Technical Reviews". Technical reviews and audits assist the acquisition and the number and types are tailored to the acquisition. Overall guidance flows from the Defense Acquisition Guidebook chapter 4, with local details further defined by the review organizations. Typical topics examined include adequacy of program/contract metrics, proper staffing, risks, budget, and schedule.

A sixth-generation fighter is a conceptualized class of jet fighter aircraft design more advanced than the fifth-generation jet fighters that are currently in service and development. Several countries have announced the development of a sixth-generation aircraft program, including the United States, Japan, Russia, the United Kingdom, Sweden, Italy, France, Germany, Spain, China, and India. The first sixth-generation fighters are expected to enter service in the 2030s.
The manufacturing readiness level (MRL) is a measure developed by the United States Department of Defense (DOD) to assess the maturity of manufacturing readiness, similar to how technology readiness levels (TRL) are used for technology readiness. They can be used in general industry assessments, or for more specific application in assessing capabilities of possible suppliers. The Government Accountability Office has described it as best practice for improving acquisition outcomes. The United States Department of Defense adopted the usage of MRLs in 2005, but the GAO continued to note inconsistent application across DOD components. In 2011, consideration of manufacturing readiness and related processes of potential contractors and subcontractors was made mandatory as part of the source selection process in major acquisition programs.

The Ground Combat Vehicle (GCV) was the United States Army's replacement program for armored fighting vehicles in Armored and Stryker brigade combat teams. The GCV was organized under the Follow On Incremental Capabilities Package of the BCT Modernization program. The first variant of the vehicle was to be prototyped in 2015 and fielded by 2017. It replaced the canceled Future Combat Systems, manned ground vehicles program. The GCV program was cancelled in February 2014. Its replacement was the Optionally Manned Fighting Vehicle.

The Marine Personnel Carrier (MPC) is a wheeled armored personnel carrier under development for acquisition by the United States Marine Corps. The program was canceled in 2013 but resurrected in 2014 as part of phase one of the Amphibious Combat Vehicle.
Test and evaluation master plan (TEMP) is a critical aspect of project management involving complex systems that must satisfy specification requirements. The TEMP is used to support programmatic events called milestone decisions that separate the individual phases of a project. For military systems, the level of funding determines the Acquisition Category and the organization responsible for the milestone decision.

The Amphibious Combat Vehicle (ACV) is a program initiated by Marine Corps Systems Command to procure an amphibious assault vehicle for the United States Marine Corps to supplement and ultimately replace the aging Assault Amphibious Vehicle (AAV). The program replaces the Expeditionary Fighting Vehicle (EFV) program canceled in 2011. Originally a plan to develop a high-water-speed vehicle, the program has expanded into a multi-phased approach to procure and develop several types of amphibious-capable vehicles to address near and long-term requirements.

The AN/TPS-80 Ground/Air Task Oriented Radar (G/ATOR) is the United States Marine Corps next generation Air Surveillance/Air Defense and Air Traffic Control (ATC) Radar. The mobile active electronically scanned array radar system is currently being developed by Northrop Grumman and was expected to reach initial operating capability in August 2016.
Key Performance Parameters (KPPs) specify what the critical performance goals are in a United States Department of Defense (DoD) acquisition under the JCIDS process.
Cyber Quest is an annual U.S. Army event held at Fort Gordon in which participants assess new technologies against documented Cyberspace, Electronic Warfare (EW), and Signal operational requirements. Cyber Quest is sponsored by the Cyber Battle Laboratory (CBL) of the Cyber Center of Excellence (CCOE)

The United States Army Acquisition Corps (AAC) is the officer / NCO corps of the United States Army Acquisition Workforce (AAW), a branch which includes civilians, officers, and NCOs. The Acquisition Corps is composed of army officers who serve in acquisition, a specialized form of product development, fielding, and support and Noncommissioned Officers who specialize in Contracting, Level I Program Management and Purchasing. These officers begin their careers in the other branches of the army for eight years, after which they may elect the Acquisition branch as their career as assistant program managers (APMs), program managers (PMs), and program executive officers (PEOs). The Noncommissioned Officers (NCOs) are reclassified in the Army Acquisition NCO Corps after serving 7-10 years in their respective enlisted career management fields, and serve primarily in the Army Acquisition Career Management Field - 51 and (MOS) 51C. 4% percentage of the Army Acquisition Officers serve among the 40,000 members of the army acquisition workforce, 6% in MOS 51C - Acquisition, Logistics and Technology Contracting Noncommissioned Officer, and the remainder 90% percentage consist largely of Department of the Army civilians.
References
- ↑ U.S. Office of Management and Budget. Circular No. A–11, Preparation, Submission, And Execution Of The Budget. Washington, DC: Executive Office of the President, 2008.
- ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-03-04. Retrieved 2010-05-26.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ Ullman, David G. Making Robust Decisions: Decision Management for Technical, Business, & Service Teams. Victoria, B.C.: Trafford Publishing, 2006. The Mechanical Design Process, 4th edition. New York: McGraw Hill, 2009.
- ↑ Ullman D. G.; R. Ast (September 2011). "Analysis of Alternatives (AoA) Based Decisions" (PDF). MORS, Phalanx, Vol 44, No 3. p. 24. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-01-04. Retrieved 2013-04-07.
- ↑ "Teaching Note, Analysis of Alternatives" (PDF). Defense Acquisition University. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 January 2017. Retrieved 15 December 2016.
- ↑ DOD Instruction 5000.02, USD(AT&L) December 8, 2008 "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2010-10-10. Retrieved 2010-09-10.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ "Defense Acquisition Guide, 3.3 Analysis of Alternatives". Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 15 December 2016.
- ↑ "Analysis of Alternatives (AoA) Handbook, A Practical Guide to Analyses of Alternatives" (PDF). Office of Aerospace Studies, Air Force Materiel Command (AFMC) OAS/A9. Retrieved 15 December 2016.
- ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2010-10-10. Retrieved 2010-09-10.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)